p21 Cip1 Antibody - #DF6423
| Product: | p21 Cip1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6423 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to p21 Cip1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Horse, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 21kDa; 18kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P38936 |
| RRID: | AB_2838386 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6423, RRID:AB_2838386.
Fold/Unfold
CAP20; CDK-interacting protein 1; CDKI; CDKN1; Cdkn1a; CDN1A_HUMAN; CIP1; Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1A; Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1; Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (P21); Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (p21, Cip1); DNA Synthesis Inhibitor; MDA-6; MDA6; Melanoma differentiation-associated protein 6; Melanoma differentiation-associated protein; p21; P21 protein; p21CIP1; p21Cip1/Waf1; p21WAF; PIC1; SDI1; SLC12A9; WAF1; Wild type p53 activated fragment 1 (WAF1); Wild type p53 activated fragment 1; Wildtype p53-activated fragment 1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human p21 Cip1, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- P38936 CDN1A_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSEPAGDVRQNPCGSKACRRLFGPVDSEQLSRDCDALMAGCIQEARERWNFDFVTETPLEGDFAWERVRGLGLPKLYLPTGPRRGRDELGGGRRPGTSPALLQGTAEEDHVDLSLSCTLVPRSGEQAEGSPGGPGDSQGRKRRQTSMTDFYHSKRRLIFSKRKP
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
May be involved in p53/TP53 mediated inhibition of cellular proliferation in response to DNA damage. Binds to and inhibits cyclin-dependent kinase activity, preventing phosphorylation of critical cyclin-dependent kinase substrates and blocking cell cycle progression. Functions in the nuclear localization and assembly of cyclin D-CDK4 complex and promotes its kinase activity towards RB1. At higher stoichiometric ratios, inhibits the kinase activity of the cyclin D-CDK4 complex. Inhibits DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase delta by competing with POLD3 for PCNA binding. Plays an important role in controlling cell cycle progression and DNA damage-induced G2 arrest.
Phosphorylation of Thr-145 by Akt or of Ser-146 by PKC impairs binding to PCNA. Phosphorylation at Ser-114 by GSK3-beta enhances ubiquitination by the DCX(DTL) complex. Phosphorylation of Thr-145 by PIM2 enhances CDKN1A stability and inhibits cell proliferation. Phosphorylation of Thr-145 by PIM1 results in the relocation of CDKN1A to the cytoplasm and enhanced CDKN1A protein stability. UV radiation-induced phosphorylation at Thr-80 by LKB1 and at Ser-146 by NUAK1 leads to its degradation.
Ubiquitinated by MKRN1; leading to polyubiquitination and 26S proteasome-dependent degradation. Ubiquitinated by the DCX(DTL) complex, also named CRL4(CDT2) complex, leading to its degradation during S phase or following UV irradiation. Ubiquitination by the DCX(DTL) complex is essential to control replication licensing and is PCNA-dependent: interacts with PCNA via its PIP-box, while the presence of the containing the 'K+4' motif in the PIP box, recruit the DCX(DTL) complex, leading to its degradation. Ubiquitination at Ser-2 leads to degradation by the proteasome pathway. Ubiquitinated by RNF114; leading to proteasomal degradation.
Acetylation leads to protein stability. Acetylated in vitro on Lys-141, Lys-154, Lys-161 and Lys-163. Deacetylation by HDAC1 is prevented by competitive binding of C10orf90/FATS to HDAC1 (By similarity).
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Expressed in all adult tissues, with 5-fold lower levels observed in the brain.
The PIP-box K+4 motif mediates both the interaction with PCNA and the recruitment of the DCX(DTL) complex: while the PIP-box interacts with PCNA, the presence of the K+4 submotif, recruits the DCX(DTL) complex, leading to its ubiquitination.
The C-terminal is required for nuclear localization of the cyclin D-CDK4 complex.
Belongs to the CDI family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > p53 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cellular senescence. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > ErbB signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > HIF-1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > FoxO signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Jak-STAT signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Endocrine resistance.
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Platinum drug resistance.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis C.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Transcriptional misregulation in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > MicroRNAs in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Colorectal cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Renal cell carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Pancreatic cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Endometrial cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Glioma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Thyroid cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Basal cell carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Melanoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Bladder cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Chronic myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Non-small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Oxytocin signaling pathway.
References
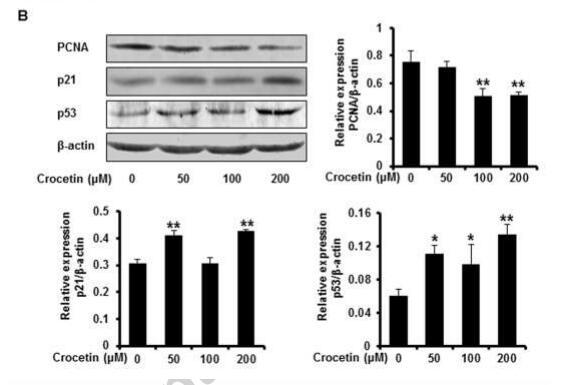
Application: WB Species: human Sample: NP cell
Application: WB Species: human Sample:
Application: IF/ICC Species: Mouse Sample:
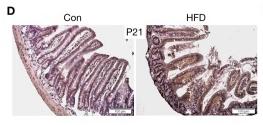
Application: IHC Species: Mice Sample: apoptotic cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.