p27 Kip1 Antibody - #DF6090
| Product: | p27 Kip1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6090 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to p27 Kip1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Bovine, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 27kDa; 22kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P46527 |
| RRID: | AB_2838058 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6090, RRID:AB_2838058.
Fold/Unfold
AA408329; AI843786; Cdki1b; CDKN 1B; CDKN 4; CDKN1B; CDKN4; CDN1B_HUMAN; Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1B; Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor p27; Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (p27, Kip1); Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B; Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27; Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 Kip1; KIP 1; KIP1; MEN1B; MEN4; OTTHUMP00000195098; OTTHUMP00000195099; p27; p27 Kip1; P27-like cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor; p27Kip1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human p27 Kip1, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Expressed in all tissues tested. Highest levels in skeletal muscle, lowest in liver and kidney.
- P46527 CDN1B_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSNVRVSNGSPSLERMDARQAEHPKPSACRNLFGPVDHEELTRDLEKHCRDMEEASQRKWNFDFQNHKPLEGKYEWQEVEKGSLPEFYYRPPRPPKGACKVPAQESQDVSGSRPAAPLIGAPANSEDTHLVDPKTDPSDSQTGLAEQCAGIRKRPATDDSSTQNKRANRTEENVSDGSPNAGSVEQTPKKPGLRRRQT
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Important regulator of cell cycle progression. Inhibits the kinase activity of CDK2 bound to cyclin A, but has little inhibitory activity on CDK2 bound to SPDYA. Involved in G1 arrest. Potent inhibitor of cyclin E- and cyclin A-CDK2 complexes. Forms a complex with cyclin type D-CDK4 complexes and is involved in the assembly, stability, and modulation of CCND1-CDK4 complex activation. Acts either as an inhibitor or an activator of cyclin type D-CDK4 complexes depending on its phosphorylation state and/or stoichometry.
Phosphorylated; phosphorylation occurs on serine, threonine and tyrosine residues. Phosphorylation on Ser-10 is the major site of phosphorylation in resting cells, takes place at the G(0)-G(1) phase and leads to protein stability. Phosphorylation on other sites is greatly enhanced by mitogens, growth factors, cMYC and in certain cancer cell lines. The phosphorylated form found in the cytoplasm is inactivate. Phosphorylation on Thr-198 is required for interaction with 14-3-3 proteins. Phosphorylation on Thr-187, by CDK1 and CDK2 leads to protein ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Tyrosine phosphorylation promotes this process. Phosphorylation by PKB/AKT1 can be suppressed by LY294002, an inhibitor of the catalytic subunit of PI3K. Phosphorylation on Tyr-88 and Tyr-89 has no effect on binding CDK2, but is required for binding CDK4. Dephosphorylated on tyrosine residues by G-CSF.
Ubiquitinated; in the cytoplasm by the KPC complex (composed of RNF123/KPC1 and UBAC1/KPC2) and, in the nucleus, by SCF(SKP2). The latter requires prior phosphorylation on Thr-187. Ubiquitinated; by a TRIM21-containing SCF(SKP2)-like complex; leads to its degradation.
Subject to degradation in the lysosome. Interaction with SNX6 promotes lysosomal degradation (By similarity).
Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Endosome.
Note: Nuclear and cytoplasmic in quiescent cells. AKT- or RSK-mediated phosphorylation on Thr-198, binds 14-3-3, translocates to the cytoplasm and promotes cell cycle progression. Mitogen-activated UHMK1 phosphorylation on Ser-10 also results in translocation to the cytoplasm and cell cycle progression. Phosphorylation on Ser-10 facilitates nuclear export. Translocates to the nucleus on phosphorylation of Tyr-88 and Tyr-89. Colocalizes at the endosome with SNX6; this leads to lysosomal degradation (By similarity).
Expressed in all tissues tested. Highest levels in skeletal muscle, lowest in liver and kidney.
A peptide sequence containing only AA 28-79 retains substantial Kip1 cyclin A/CDK2 inhibitory activity.
Belongs to the CDI family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > ErbB signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > HIF-1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > FoxO signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Endocrine resistance.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Measles.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Transcriptional misregulation in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > MicroRNAs in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Chronic myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
References
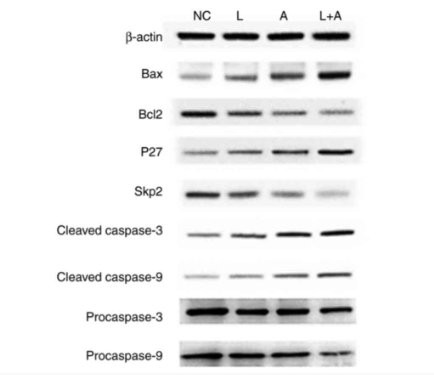
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: K562 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.