IKB alpha Antibody - #AF6239
| Product: | IKB alpha Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF6239 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to IKB alpha |
| Application: | WB IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 35kDa; 36kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P25963 |
| RRID: | AB_2835104 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6239, RRID:AB_2835104.
Fold/Unfold
I kappa B alpha; I-kappa-B-alpha; IkappaBalpha; IkB-alpha; IKBA; IKBA_HUMAN; IKBalpha; MAD 3; MAD3; Major histocompatibility complex enhancer-binding protein MAD3; NF kappa B inhibitor alpha; NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha; NFKBI; NFKBIA; Nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B cells; Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells inhibitor alpha;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human IKB alpha, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
- P25963 IKBA_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MFQAAERPQEWAMEGPRDGLKKERLLDDRHDSGLDSMKDEEYEQMVKELQEIRLEPQEVPRGSEPWKQQLTEDGDSFLHLAIIHEEKALTMEVIRQVKGDLAFLNFQNNLQQTPLHLAVITNQPEIAEALLGAGCDPELRDFRGNTPLHLACEQGCLASVGVLTQSCTTPHLHSILKATNYNGHTCLHLASIHGYLGIVELLVSLGADVNAQEPCNGRTALHLAVDLQNPDLVSLLLKCGADVNRVTYQGYSPYQLTWGRPSTRIQQQLGQLTLENLQMLPESEDEESYDTESEFTEFTEDELPYDDCVFGGQRLTL
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Inhibits the activity of dimeric NF-kappa-B/REL complexes by trapping REL dimers in the cytoplasm through masking of their nuclear localization signals. On cellular stimulation by immune and proinflammatory responses, becomes phosphorylated promoting ubiquitination and degradation, enabling the dimeric RELA to translocate to the nucleus and activate transcription.
Phosphorylated; disables inhibition of NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity. Phosphorylation at positions 32 and 36 is prerequisite to recognition by UBE2D3 leading to polyubiquitination and subsequent degradation.
Sumoylated; sumoylation requires the presence of the nuclear import signal. Sumoylation blocks ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation of the protein thereby increasing the protein stability.
Monoubiquitinated at Lys-21 and/or Lys-22 by UBE2D3. Ubiquitin chain elongation is then performed by CDC34 in cooperation with the SCF(FBXW11) E3 ligase complex, building ubiquitin chains from the UBE2D3-primed NFKBIA-linked ubiquitin. The resulting polyubiquitination leads to protein degradation. Also ubiquitinated by SCF(BTRC) following stimulus-dependent phosphorylation at Ser-32 and Ser-36.
Deubiquitinated by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus Nsp2 protein, which thereby interferes with NFKBIA degradation and impairs subsequent NF-kappa-B activation.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: Shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm by a nuclear localization signal (NLS) and a CRM1-dependent nuclear export.
Belongs to the NF-kappa-B inhibitor family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > NF-kappa B signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TNF signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Insulin resistance.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Shigellosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Legionellosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Leishmaniasis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Toxoplasmosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis C.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Measles.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Herpes simplex infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Chronic myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Chemokine signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Development > Osteoclast differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > NOD-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > IL-17 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th17 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > T cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > B cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Neurotrophin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Adipocytokine signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Relaxin signaling pathway.
References
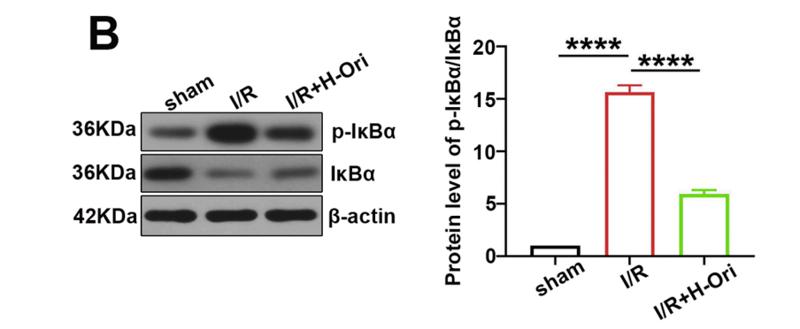
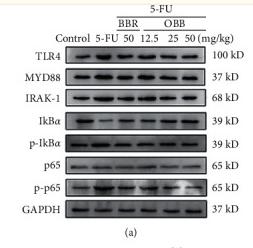
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: lung tissue
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: brain
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.