Phospho-TLR4 (Ser800) Antibody - #AF7455
| Product: | Phospho-TLR4 (Ser800) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF7455 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-TLR4 (Ser800) |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 100~130kDa; 96kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | O00206 |
| RRID: | AB_2845460 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF7455, RRID:AB_2845460.
Fold/Unfold
ARMD10; CD284; CD284 antigen; Homolog of Drosophila toll; hToll; TLR 4; TLR4; TLR4_HUMAN; TOLL; Toll like receptor 4; Toll-like receptor 4;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human TLR4 around the phosphorylation site of Ser800.
Highly expressed in placenta, spleen and peripheral blood leukocytes (PubMed:9435236, PubMed:9237759). Detected in monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells and several types of T-cells (PubMed:9237759, PubMed:27022195).
- O00206 TLR4_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MMSASRLAGTLIPAMAFLSCVRPESWEPCVEVVPNITYQCMELNFYKIPDNLPFSTKNLDLSFNPLRHLGSYSFFSFPELQVLDLSRCEIQTIEDGAYQSLSHLSTLILTGNPIQSLALGAFSGLSSLQKLVAVETNLASLENFPIGHLKTLKELNVAHNLIQSFKLPEYFSNLTNLEHLDLSSNKIQSIYCTDLRVLHQMPLLNLSLDLSLNPMNFIQPGAFKEIRLHKLTLRNNFDSLNVMKTCIQGLAGLEVHRLVLGEFRNEGNLEKFDKSALEGLCNLTIEEFRLAYLDYYLDDIIDLFNCLTNVSSFSLVSVTIERVKDFSYNFGWQHLELVNCKFGQFPTLKLKSLKRLTFTSNKGGNAFSEVDLPSLEFLDLSRNGLSFKGCCSQSDFGTTSLKYLDLSFNGVITMSSNFLGLEQLEHLDFQHSNLKQMSEFSVFLSLRNLIYLDISHTHTRVAFNGIFNGLSSLEVLKMAGNSFQENFLPDIFTELRNLTFLDLSQCQLEQLSPTAFNSLSSLQVLNMSHNNFFSLDTFPYKCLNSLQVLDYSLNHIMTSKKQELQHFPSSLAFLNLTQNDFACTCEHQSFLQWIKDQRQLLVEVERMECATPSDKQGMPVLSLNITCQMNKTIIGVSVLSVLVVSVVAVLVYKFYFHLMLLAGCIKYGRGENIYDAFVIYSSQDEDWVRNELVKNLEEGVPPFQLCLHYRDFIPGVAIAANIIHEGFHKSRKVIVVVSQHFIQSRWCIFEYEIAQTWQFLSSRAGIIFIVLQKVEKTLLRQQVELYRLLSRNTYLEWEDSVLGRHIFWRRLRKALLDGKSWNPEGTVGTGCNWQEATSI
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Cooperates with LY96 and CD14 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Acts via MYD88, TIRAP and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. Also involved in LPS-independent inflammatory responses triggered by free fatty acids, such as palmitate, and Ni(2+). Responses triggered by Ni(2+) require non-conserved histidines and are, therefore, species-specific. Both M.tuberculosis HSP70 (dnaK) and HSP65 (groEL-2) act via this protein to stimulate NF-kappa-B expression. In complex with TLR6, promotes sterile inflammation in monocytes/macrophages in response to oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) or amyloid-beta 42. In this context, the initial signal is provided by oxLDL- or amyloid-beta 42-binding to CD36. This event induces the formation of a heterodimer of TLR4 and TLR6, which is rapidly internalized and triggers inflammatory response, leading to the NF-kappa-B-dependent production of CXCL1, CXCL2 and CCL9 cytokines, via MYD88 signaling pathway, and CCL5 cytokine, via TICAM1 signaling pathway, as well as IL1B secretion. Binds electronegative LDL (LDL(-)) and mediates the cytokine release induced by LDL(-). Stimulation of monocytes in vitro with M.tuberculosis PstS1 induces p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 activation primarily via TLR2, but also partially via this receptor.
N-glycosylated. Glycosylation of Asn-526 and Asn-575 seems to be necessary for the expression of TLR4 on the cell surface and the LPS-response. Likewise, mutants lacking two or more of the other N-glycosylation sites were deficient in interaction with LPS.
Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by LYN after binding lipopolysaccharide.
Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein. Early endosome. Cell projection>Ruffle.
Note: Upon complex formation with CD36 and TLR6, internalized through dynamin-dependent endocytosis (PubMed:20037584). Colocalizes with RFTN1 at cell membrane and then together with RFTN1 moves to endosomes, upon lipopolysaccharide stimulation.
Highly expressed in placenta, spleen and peripheral blood leukocytes. Detected in monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells and several types of T-cells.
The TIR domain mediates interaction with NOX4.
The TIR domain mediates NAD(+) hydrolase (NADase) activity. Self-association of TIR domains is required for NADase activity.
Belongs to the Toll-like receptor family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Phagosome. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Necroptosis. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > NF-kappa B signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > HIF-1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Salmonella infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pertussis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Legionellosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Leishmaniasis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Malaria.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Toxoplasmosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Amoebiasis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Tuberculosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Measles.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Immune diseases > Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
· Human Diseases > Immune diseases > Rheumatoid arthritis.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > NOD-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
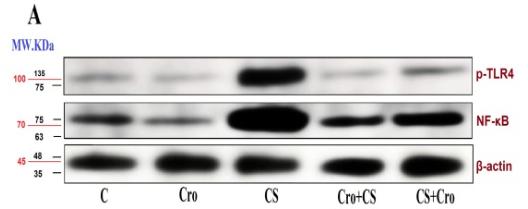
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.