Phospho-IKK gamma (Ser85) Antibody - #AF3496
| Product: | Phospho-IKK gamma (Ser85) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF3496 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-IKK gamma (Ser85) |
| Application: | WB IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Prediction: | Pig, Horse, Rabbit |
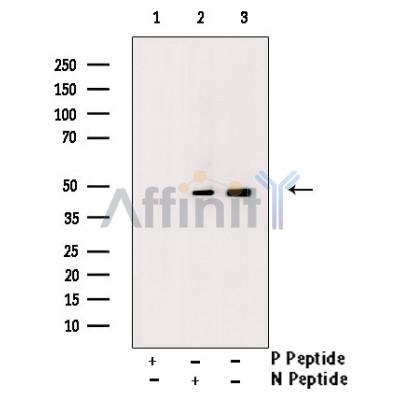
| Mol.Wt.: | 48kDa; 48kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q9Y6K9 |
| RRID: | AB_2834791 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF3496, RRID:AB_2834791.
Fold/Unfold
IkB kinase associated protein 1; IkB kinase subunit gamma; Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase subunit gamma; AMCBX1; FIP 3; FIP-3; FIP3; Fip3p; I kappa B kinase gamma; I-kappa-B kinase subunit gamma; IkB kinase gamma subunit; IkB kinase subunit gamma; IkB kinase-associated protein 1; Ikbkg; IKK-gamma; IKKAP1; IKKG; IMD33; Incontinentia pigmenti; Inhibitor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells, kinase gamma; Inhibitor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells, kinase of, gamma; Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit gamma; IP; IP1; IP2; IPD2; NEMO; NEMO_HUMAN; NF kappa B essential modifier; NF kappa B essential modulator; NF-kappa-B essential modifier; NF-kappa-B essential modulator; ZC2HC9;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human IKK gamma around the phosphorylation site of Ser85.
- Q9Y6K9 NEMO_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MNRHLWKSQLCEMVQPSGGPAADQDVLGEESPLGKPAMLHLPSEQGAPETLQRCLEENQELRDAIRQSNQILRERCEELLHFQASQREEKEFLMCKFQEARKLVERLGLEKLDLKRQKEQALREVEHLKRCQQQMAEDKASVKAQVTSLLGELQESQSRLEAATKECQALEGRARAASEQARQLESEREALQQQHSVQVDQLRMQGQSVEAALRMERQAASEEKRKLAQLQVAYHQLFQEYDNHIKSSVVGSERKRGMQLEDLKQQLQQAEEALVAKQEVIDKLKEEAEQHKIVMETVPVLKAQADIYKADFQAERQAREKLAEKKELLQEQLEQLQREYSKLKASCQESARIEDMRKRHVEVSQAPLPPAPAYLSSPLALPSQRRSPPEEPPDFCCPKCQYQAPDMDTLQIHVMECIE
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Regulatory subunit of the IKK core complex which phosphorylates inhibitors of NF-kappa-B thus leading to the dissociation of the inhibitor/NF-kappa-B complex and ultimately the degradation of the inhibitor. Its binding to scaffolding polyubiquitin seems to play a role in IKK activation by multiple signaling receptor pathways. However, the specific type of polyubiquitin recognized upon cell stimulation (either 'Lys-63'-linked or linear polyubiquitin) and its functional importance is reported conflictingly. Also considered to be a mediator for TAX activation of NF-kappa-B. Could be implicated in NF-kappa-B-mediated protection from cytokine toxicity. Essential for viral activation of IRF3. Involved in TLR3- and IFIH1-mediated antiviral innate response; this function requires 'Lys-27'-linked polyubiquitination.
Phosphorylation at Ser-68 attenuates aminoterminal homodimerization.
Polyubiquitinated on Lys-285 through 'Lys-63'; the ubiquitination is mediated by NOD2 and RIPK2 and probably plays a role in signaling by facilitating interactions with ubiquitin domain-containing proteins and activates the NF-kappa-B pathway. Polyubiquitinated on Lys-399 through 'Lys-63'; the ubiquitination is mediated by BCL10, MALT1 and TRAF6 and probably plays a role in signaling by facilitating interactions with ubiquitin domain-containing proteins and activates the NF-kappa-B pathway. Monoubiquitinated on Lys-277 and Lys-309; promotes nuclear export. Polyubiquitinated through 'Lys-27' by TRIM23; involved in antiviral innate and inflammatory responses. Linear polyubiquitinated on Lys-111, Lys-143, Lys-226, Lys-246, Lys-264, Lys-277, Lys-285, Lys-292, Lys-302, Lys-309 and Lys-326; the head-to-tail polyubiquitination is mediated by the LUBAC complex and plays a key role in NF-kappa-B activation. Deubiquitinated by USP10 in a TANK-dependent and -independent manner, leading to the negative regulation of NF-kappa-B signaling upon DNA damage.
Sumoylated on Lys-277 and Lys-309 with SUMO1; the modification results in phosphorylation of Ser-85 by ATM leading to a replacement of the sumoylation by mono-ubiquitination on these residues.
Neddylated by TRIM40, resulting in stabilization of NFKBIA and down-regulation of NF-kappa-B activity.
(Microbial infection) Cleaved by hepatitis A virus (HAV) protease 3C allowing the virus to disrupt the host innate immune signaling.
(Microbial infection) Polyubiquitinated on Lys-309 and Lys-321 via 'Lys-27'-linked ubiquitin by Shigella flexneri E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ipah9.8, leading to its degradation by the proteasome.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: Sumoylated NEMO accumulates in the nucleus in response to genotoxic stress.
Heart, brain, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney and pancreas.
The leucine-zipper domain and the CCHC NOA-type zinc-finger are essential for polyubiquitin binding and for the activation of IRF3.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Ras signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > NF-kappa B signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TNF signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Antifolate resistance.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Shigellosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Toxoplasmosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis C.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Herpes simplex infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Pancreatic cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Chronic myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Acute myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Immune diseases > Primary immunodeficiency.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Chemokine signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Development > Osteoclast differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > NOD-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > IL-17 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th17 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > T cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > B cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Adipocytokine signaling pathway.
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.