Phospho-AKT2 (Ser474) Antibody - #AF3264
| Product: | Phospho-AKT2 (Ser474) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF3264 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-AKT2 (Ser474) |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 60kDa; 56kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P31751 |
| RRID: | AB_2834690 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF3264, RRID:AB_2834690.
Fold/Unfold
Akt2; AKT2_HUMAN; HIHGHH; murine thymoma viral (v-akt) homolog-2; PKB; PKB beta; PKBB; PKBBETA; PRKBB; Protein kinase Akt 2; Protein kinase Akt-2; Protein kinase B beta; rac protein kinase beta; RAC-BETA; RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase; RAC-PK-beta; v akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 2;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Akt2 around the phosphorylation site of Ser474.
- P31751 AKT2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MNEVSVIKEGWLHKRGEYIKTWRPRYFLLKSDGSFIGYKERPEAPDQTLPPLNNFSVAECQLMKTERPRPNTFVIRCLQWTTVIERTFHVDSPDEREEWMRAIQMVANSLKQRAPGEDPMDYKCGSPSDSSTTEEMEVAVSKARAKVTMNDFDYLKLLGKGTFGKVILVREKATGRYYAMKILRKEVIIAKDEVAHTVTESRVLQNTRHPFLTALKYAFQTHDRLCFVMEYANGGELFFHLSRERVFTEERARFYGAEIVSALEYLHSRDVVYRDIKLENLMLDKDGHIKITDFGLCKEGISDGATMKTFCGTPEYLAPEVLEDNDYGRAVDWWGLGVVMYEMMCGRLPFYNQDHERLFELILMEEIRFPRTLSPEAKSLLAGLLKKDPKQRLGGGPSDAKEVMEHRFFLSINWQDVVQKKLLPPFKPQVTSEVDTRYFDDEFTAQSITITPPDRYDSLGLLELDQRTHFPQFSYSASIRE
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
AKT2 is one of 3 closely related serine/threonine-protein kinases (AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3) called the AKT kinase, and which regulate many processes including metabolism, proliferation, cell survival, growth and angiogenesis. This is mediated through serine and/or threonine phosphorylation of a range of downstream substrates. Over 100 substrate candidates have been reported so far, but for most of them, no isoform specificity has been reported. AKT is responsible of the regulation of glucose uptake by mediating insulin-induced translocation of the SLC2A4/GLUT4 glucose transporter to the cell surface. Phosphorylation of PTPN1 at 'Ser-50' negatively modulates its phosphatase activity preventing dephosphorylation of the insulin receptor and the attenuation of insulin signaling. Phosphorylation of TBC1D4 triggers the binding of this effector to inhibitory 14-3-3 proteins, which is required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport. AKT regulates also the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen by phosphorylating GSK3A at 'Ser-21' and GSK3B at 'Ser-9', resulting in inhibition of its kinase activity. Phosphorylation of GSK3 isoforms by AKT is also thought to be one mechanism by which cell proliferation is driven. AKT regulates also cell survival via the phosphorylation of MAP3K5 (apoptosis signal-related kinase). Phosphorylation of 'Ser-83' decreases MAP3K5 kinase activity stimulated by oxidative stress and thereby prevents apoptosis. AKT mediates insulin-stimulated protein synthesis by phosphorylating TSC2 at 'Ser-939' and 'Thr-1462', thereby activating mTORC1 signaling and leading to both phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and in activation of RPS6KB1. AKT is involved in the phosphorylation of members of the FOXO factors (Forkhead family of transcription factors), leading to binding of 14-3-3 proteins and cytoplasmic localization. In particular, FOXO1 is phosphorylated at 'Thr-24', 'Ser-256' and 'Ser-319'. FOXO3 and FOXO4 are phosphorylated on equivalent sites. AKT has an important role in the regulation of NF-kappa-B-dependent gene transcription and positively regulates the activity of CREB1 (cyclic AMP (cAMP)-response element binding protein). The phosphorylation of CREB1 induces the binding of accessory proteins that are necessary for the transcription of pro-survival genes such as BCL2 and MCL1. AKT phosphorylates 'Ser-454' on ATP citrate lyase (ACLY), thereby potentially regulating ACLY activity and fatty acid synthesis. Activates the 3B isoform of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE3B) via phosphorylation of 'Ser-273', resulting in reduced cyclic AMP levels and inhibition of lipolysis. Phosphorylates PIKFYVE on 'Ser-318', which results in increased PI(3)P-5 activity. The Rho GTPase-activating protein DLC1 is another substrate and its phosphorylation is implicated in the regulation cell proliferation and cell growth. AKT plays a role as key modulator of the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway controlling the tempo of the process of newborn neurons integration during adult neurogenesis, including correct neuron positioning, dendritic development and synapse formation. Signals downstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI(3)K) to mediate the effects of various growth factors such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I). AKT mediates the antiapoptotic effects of IGF-I. Essential for the SPATA13-mediated regulation of cell migration and adhesion assembly and disassembly. May be involved in the regulation of the placental development.
One of the few specific substrates of AKT2 identified recently is PITX2. Phosphorylation of PITX2 impairs its association with the CCND1 mRNA-stabilizing complex thus shortening the half-life of CCND1. AKT2 seems also to be the principal isoform responsible of the regulation of glucose uptake. Phosphorylates C2CD5 on 'Ser-197' during insulin-stimulated adipocytes. AKT2 is also specifically involved in skeletal muscle differentiation, one of its substrates in this process being ANKRD2. Down-regulation by RNA interference reduces the expression of the phosphorylated form of BAD, resulting in the induction of caspase-dependent apoptosis. Phosphorylates CLK2 on 'Thr-343'.
Phosphorylation on Thr-309 and Ser-474 is required for full activity.
Ubiquitinated; undergoes both 'Lys-48'- and 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination. TRAF6-induced 'Lys-63'-linked AKT2 ubiquitination. When fully phosphorylated and translocated into the nucleus, undergoes 'Lys-48'-polyubiquitination catalyzed by TTC3, leading to its degradation by the proteasome.
O-GlcNAcylation at Thr-306 and Thr-313 inhibits activating phosphorylation at Thr-309 via disrupting the interaction between AKT and PDK1.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cell membrane>Peripheral membrane protein. Early endosome.
Note: Localizes within both nucleus and cytoplasm of proliferative primary myoblasts and mostly within the nucleus of differentiated primary myoblasts. By virtue of the N-terminal PH domain, is recruited to sites of the plasma membrane containing increased PI(3,4,5)P3 or PI(3,4)P2, cell membrane targeting is also facilitared by interaction with CLIP3. Colocalizes with WDFY2 in early endosomes (By similarity).
Expressed in all cell types so far analyzed.
Binding of the PH domain to phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PI(3,4,5)P3) following phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase alpha (PIK3CA) activity results in its targeting to the plasma membrane.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. RAC subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Autophagy - animal. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cellular senescence. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Focal adhesion. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > ErbB signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Ras signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Rap1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > HIF-1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > FoxO signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Sphingolipid signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Phospholipase D signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > mTOR signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > AMPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Apelin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Jak-STAT signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TNF signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance.
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Endocrine resistance.
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Platinum drug resistance.
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Insulin resistance.
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Toxoplasmosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Tuberculosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis C.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Measles.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Colorectal cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Renal cell carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Pancreatic cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Endometrial cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Glioma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Melanoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Chronic myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Acute myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Non-small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Central carbon metabolism in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Choline metabolism in cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Chemokine signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Circulatory system > Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Development > Osteoclast differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Platelet activation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > T cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > B cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Neurotrophin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Cholinergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Dopaminergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Insulin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Estrogen signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Prolactin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Thyroid hormone signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Adipocytokine signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Glucagon signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Relaxin signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Carbohydrate digestion and absorption.
References
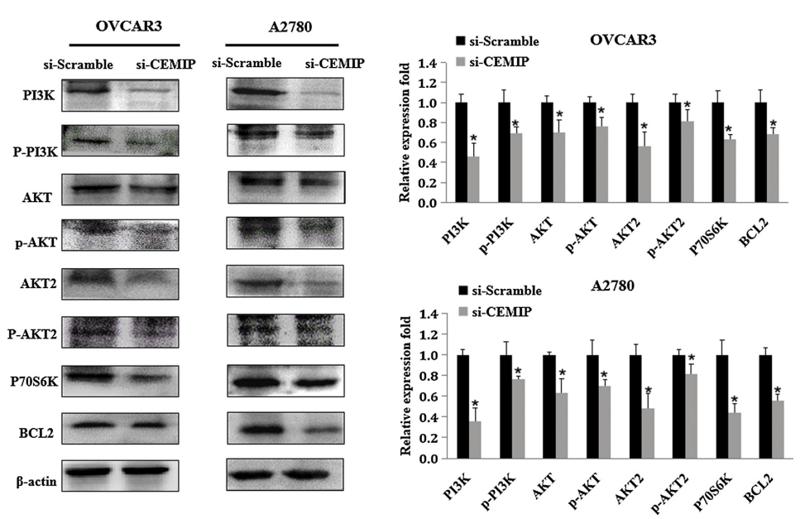
Application: WB Species: human Sample: ovarian cancer cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.