Phospho-c-Jun (Tyr170) Antibody - #AF3094
| Product: | Phospho-c-Jun (Tyr170) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF3094 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-c-Jun (Tyr170) |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 37~45kDa; 36kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P05412 |
| RRID: | AB_2834531 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF3094, RRID:AB_2834531.
Fold/Unfold
Activator protein 1; AP 1; AP1; cJun; Enhancer Binding Protein AP1; Jun Activation Domain Binding Protein; JUN; Jun oncogene; JUN protein; Jun proto oncogene; JUN_HUMAN; JUNC; Oncogene JUN; p39; Proto oncogene c jun; Proto oncogene cJun; Proto-oncogene c-jun; Transcription Factor AP 1; Transcription factor AP-1; Transcription Factor AP1; V jun avian sarcoma virus 17 oncogene homolog; V jun sarcoma virus 17 oncogene homolog (avian); V jun sarcoma virus 17 oncogene homolog; V-jun avian sarcoma virus 17 oncogene homolog; vJun Avian Sarcoma Virus 17 Oncogene Homolog;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human c-Jun around the phosphorylation site of Tyr170.
- P05412 JUN_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MTAKMETTFYDDALNASFLPSESGPYGYSNPKILKQSMTLNLADPVGSLKPHLRAKNSDLLTSPDVGLLKLASPELERLIIQSSNGHITTTPTPTQFLCPKNVTDEQEGFAEGFVRALAELHSQNTLPSVTSAAQPVNGAGMVAPAVASVAGGSGSGGFSASLHSEPPVYANLSNFNPGALSSGGGAPSYGAAGLAFPAQPQQQQQPPHHLPQQMPVQHPRLQALKEEPQTVPEMPGETPPLSPIDMESQERIKAERKRMRNRIAASKCRKRKLERIARLEEKVKTLKAQNSELASTANMLREQVAQLKQKVMNHVNSGCQLMLTQQLQTF
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Transcription factor that recognizes and binds to the enhancer heptamer motif 5'-TGA[CG]TCA-3'. Promotes activity of NR5A1 when phosphorylated by HIPK3 leading to increased steroidogenic gene expression upon cAMP signaling pathway stimulation. Involved in activated KRAS-mediated transcriptional activation of USP28 in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells. Binds to the USP28 promoter in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells.
Ubiquitinated by the SCF(FBXW7), leading to its degradation. Ubiquitination takes place following phosphorylation, that promotes interaction with FBXW7.
Phosphorylated by CaMK4 and PRKDC; phosphorylation enhances the transcriptional activity. Phosphorylated by HIPK3. Phosphorylated by DYRK2 at Ser-243; this primes the protein for subsequent phosphorylation by GSK3B at Thr-239. Phosphorylated at Thr-239, Ser-243 and Ser-249 by GSK3B; phosphorylation reduces its ability to bind DNA. Phosphorylated by PAK2 at Thr-2, Thr-8, Thr-89, Thr-93 and Thr-286 thereby promoting JUN-mediated cell proliferation and transformation. Phosphorylated by PLK3 following hypoxia or UV irradiation, leading to increase DNA-binding activity.
Acetylated at Lys-271 by EP300.
Nucleus.
Expressed in the developing and adult prostate and prostate cancer cells.
Belongs to the bZIP family. Jun subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Focal adhesion. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Tight junction. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > ErbB signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Wnt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TNF signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Endocrine resistance.
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Cocaine addiction.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Amphetamine addiction.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Salmonella infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pertussis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Leishmaniasis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Herpes simplex infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Colorectal cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Renal cell carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Choline metabolism in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Immune diseases > Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
· Human Diseases > Immune diseases > Rheumatoid arthritis.
· Organismal Systems > Development > Osteoclast differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > NOD-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > IL-17 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th17 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > T cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > B cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Neurotrophin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Estrogen signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Oxytocin signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Relaxin signaling pathway.
References
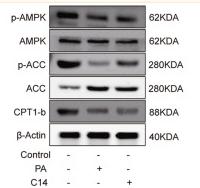
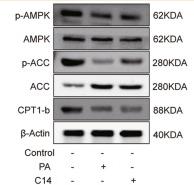
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: H9c2 cells
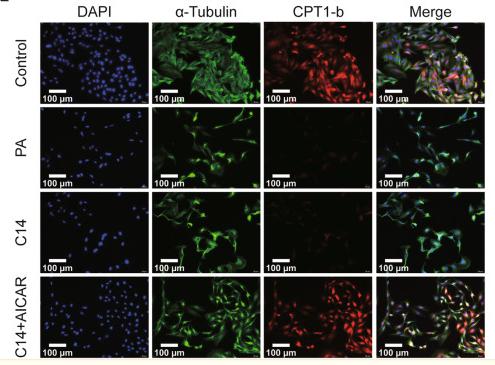
Application: IF/ICC Species: Rat Sample: H9c2 cells
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: H9c2 cells
Application: IF/ICC Species: Rat Sample: H9c2 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.