Cyclin E1 Antibody - #AF0144
| Product: | Cyclin E1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF0144 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Cyclin E1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Mol.Wt.: | 49kDa; 47kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P24864 |
| RRID: | AB_2833326 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF0144, RRID:AB_2833326.
Fold/Unfold
CCNE; Ccne1; CCNE1_HUMAN; cyclin E variant ex5del; cyclin E variant ex7del; Cyclin E1; Cyclin Es; Cyclin Et; CyclinE; G1/S specific cyclin E; G1/S-specific cyclin-E1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Cyclin E1, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Highly expressed in testis and placenta. Low levels in bronchial epithelial cells.
- P24864 CCNE1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MPRERRERDAKERDTMKEDGGAEFSARSRKRKANVTVFLQDPDEEMAKIDRTARDQCGSQPWDNNAVCADPCSLIPTPDKEDDDRVYPNSTCKPRIIAPSRGSPLPVLSWANREEVWKIMLNKEKTYLRDQHFLEQHPLLQPKMRAILLDWLMEVCEVYKLHRETFYLAQDFFDRYMATQENVVKTLLQLIGISSLFIAAKLEEIYPPKLHQFAYVTDGACSGDEILTMELMIMKALKWRLSPLTIVSWLNVYMQVAYLNDLHEVLLPQYPQQIFIQIAELLDLCVLDVDCLEFPYGILAASALYHFSSSELMQKVSGYQWCDIENCVKWMVPFAMVIRETGSSKLKHFRGVADEDAHNIQTHRDSLDLLDKARAKKAMLSEQNRASPLPSGLLTPPQSGKKQSSGPEMA
Research Backgrounds
Essential for the control of the cell cycle at the G1/S (start) transition.
Phosphorylation of both Thr-395 by GSK3 and Ser-399 by CDK2 creates a high affinity degron recognized by FBXW7, and accelerates degradation via the ubiquitin proteasome pathway. Phosphorylation at Thr-77 creates a low affinity degron also recognized by FBXW7.
Ubiquitinated by UHRF2; appears to occur independently of phosphorylation.
Nucleus.
Highly expressed in testis and placenta. Low levels in bronchial epithelial cells.
Belongs to the cyclin family. Cyclin E subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Oocyte meiosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > p53 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cellular senescence. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Measles.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > MicroRNAs in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
References
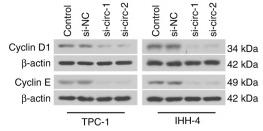
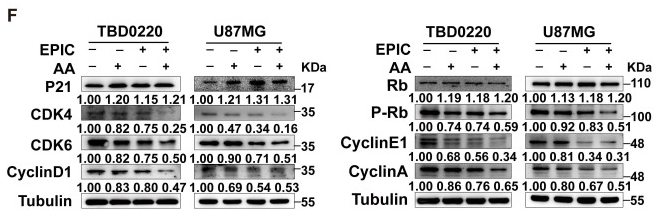
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: TBD0220 and U87MG cells
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HCT116 and SW480 cells
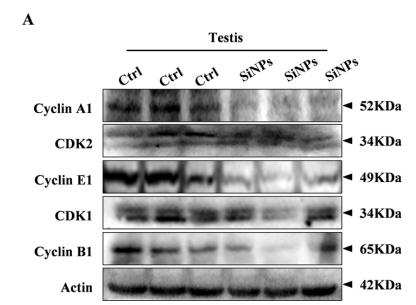
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: testis
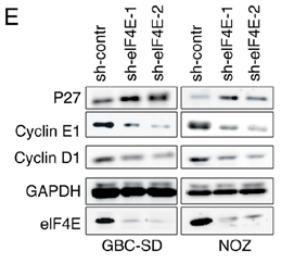
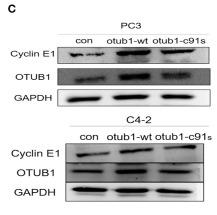
Application: WB Species: human Sample: GBC and NOZ cells
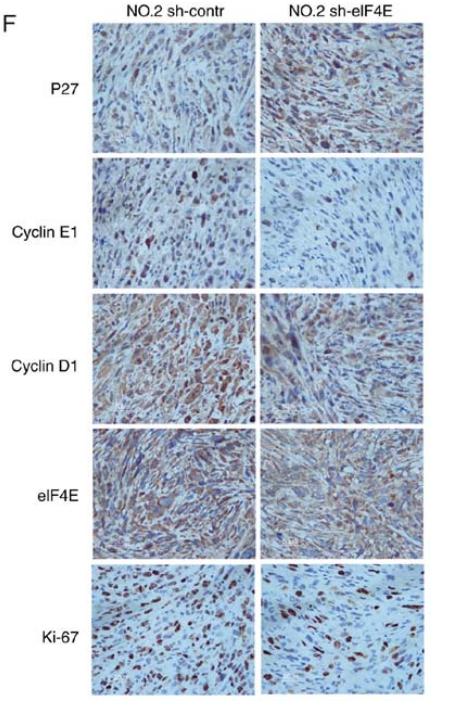
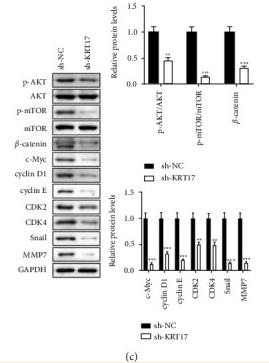
Application: IHC Species: human Sample: GBC tumor
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.