DDB2 Antibody - #DF2439
| Product: | DDB2 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF2439 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to DDB2 |
| Application: | WB IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 45 kDa; 48kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q92466 |
| RRID: | AB_2839645 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF2439, RRID:AB_2839645.
Fold/Unfold
damage-specific DNA binding protein 2; Damage-specific DNA-binding protein 2; DDB p48 subunit; Ddb2; DDB2_HUMAN; DDBb; DNA damage-binding protein 2; UV-damaged DNA-binding protein 2; UV-DDB 2; Xeroderma pigmentosum group E protei;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human DDB2, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Ubiquitously expressed; with highest levels in corneal endothelium and lowest levels in brain. Isoform D1 is highly expressed in brain and heart. Isoform D2, isoform D3 and isoform D4 are weakly expressed.
- Q92466 DDB2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAPKKRPETQKTSEIVLRPRNKRSRSPLELEPEAKKLCAKGSGPSRRCDSDCLWVGLAGPQILPPCRSIVRTLHQHKLGRASWPSVQQGLQQSFLHTLDSYRILQKAAPFDRRATSLAWHPTHPSTVAVGSKGGDIMLWNFGIKDKPTFIKGIGAGGSITGLKFNPLNTNQFYASSMEGTTRLQDFKGNILRVFASSDTINIWFCSLDVSASSRMVVTGDNVGNVILLNMDGKELWNLRMHKKKVTHVALNPCCDWFLATASVDQTVKIWDLRQVRGKASFLYSLPHRHPVNAACFSPDGARLLTTDQKSEIRVYSASQWDCPLGLIPHPHRHFQHLTPIKAAWHPRYNLIVVGRYPDPNFKSCTPYELRTIDVFDGNSGKMMCQLYDPESSGISSLNEFNPMGDTLASAMGYHILIWSQEEARTRK
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Required for DNA repair. Binds to DDB1 to form the UV-damaged DNA-binding protein complex (the UV-DDB complex). The UV-DDB complex may recognize UV-induced DNA damage and recruit proteins of the nucleotide excision repair pathway (the NER pathway) to initiate DNA repair. The UV-DDB complex preferentially binds to cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPD), 6-4 photoproducts (6-4 PP), apurinic sites and short mismatches. Also appears to function as the substrate recognition module for the DCX (DDB1-CUL4-X-box) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex DDB1-CUL4-ROC1 (also known as CUL4-DDB-ROC1 and CUL4-DDB-RBX1). The DDB1-CUL4-ROC1 complex may ubiquitinate histone H2A, histone H3 and histone H4 at sites of UV-induced DNA damage. The ubiquitination of histones may facilitate their removal from the nucleosome and promote subsequent DNA repair. The DDB1-CUL4-ROC1 complex also ubiquitinates XPC, which may enhance DNA-binding by XPC and promote NER. Isoform D1 and isoform D2 inhibit UV-damaged DNA repair.
Phosphorylation by ABL1 negatively regulate UV-DDB activity.
Ubiquitinated by CUL4A in response to UV irradiation. Ubiquitination appears to both impair DNA-binding and promotes ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis. Degradation of DDB2 at sites of DNA damage may be a prerequisite for their recognition by XPC and subsequent repair. CUL4A-mediated degradation appears to be promoted by ABL1.
Ubiquitinated, leading to proteasomal degradation, and deubiquitinated by USP24.
Nucleus.
Note: Accumulates at sites of DNA damage following UV irradiation.
Ubiquitously expressed; with highest levels in corneal endothelium and lowest levels in brain. Isoform D1 is highly expressed in brain and heart. Isoform D2, isoform D3 and isoform D4 are weakly expressed.
The DWD box is required for interaction with DDB1.
Interblade loops of the WD repeat region mediate most of the interaction with DNA. A hairpin between blades 5 and 6 inserts into DNA minor groove and mediates recognition of lesions and separation of the damaged and undamaged strands.
Belongs to the WD repeat DDB2/WDR76 family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > p53 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Genetic Information Processing > Replication and repair > Nucleotide excision repair.
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Transcriptional misregulation in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Colorectal cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Pancreatic cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Endometrial cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Glioma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Thyroid cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Basal cell carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Melanoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Chronic myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Non-small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
References
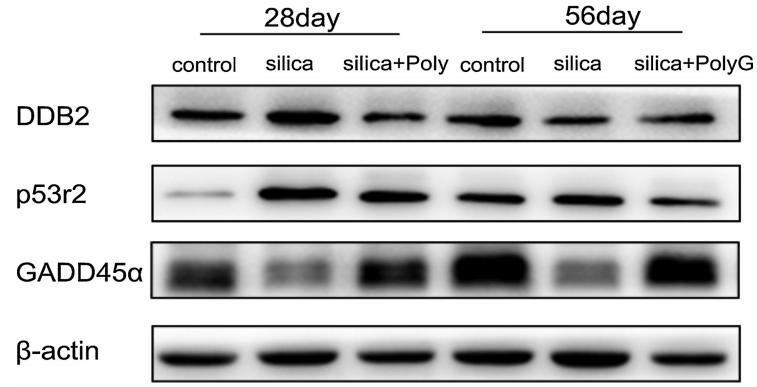
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: lung
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.