E2F1 Antibody - #DF6797
| Product: | E2F1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6797 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to E2F1 |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Rabbit |
| Mol.Wt.: | 47,70kDa; 47kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q01094 |
| RRID: | AB_2838759 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6797, RRID:AB_2838759.
Fold/Unfold
Dmel\CG6376; Dmel_CG6376; drosE2F1; E(Sev-CycE)3A; E(var)3-93E; E2-promoter binding facto; E2F 1; E2F transcription factor 1; E2F-1; E2f-PA; E2f-PB; E2f-PC; E2F1; E2f1 E2F transcription factor 1; E2F1_HUMAN; Evar(3)164; KIAA4009; l(3)07172; l(3)j3B1; l(3)j3C2; l(3)rM729; mKIAA4009; OTTHUMP00000030661; PBR3; PRB binding protein E2F 1; PRB-binding protein E2F-1; RBAP 1; RBAP-1; RBAP1; RBBP-3; RBBP3; RBP 3; RBP3; Retinoblastoma-associated protein 1; Retinoblastoma-binding protein 3; Transcription factor E2F1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human E2F1, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
- Q01094 E2F1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MALAGAPAGGPCAPALEALLGAGALRLLDSSQIVIISAAQDASAPPAPTGPAAPAAGPCDPDLLLFATPQAPRPTPSAPRPALGRPPVKRRLDLETDHQYLAESSGPARGRGRHPGKGVKSPGEKSRYETSLNLTTKRFLELLSHSADGVVDLNWAAEVLKVQKRRIYDITNVLEGIQLIAKKSKNHIQWLGSHTTVGVGGRLEGLTQDLRQLQESEQQLDHLMNICTTQLRLLSEDTDSQRLAYVTCQDLRSIADPAEQMVMVIKAPPETQLQAVDSSENFQISLKSKQGPIDVFLCPEETVGGISPGKTPSQEVTSEEENRATDSATIVSPPPSSPPSSLTTDPSQSLLSLEQEPLLSRMGSLRAPVDEDRLSPLVAADSLLEHVREDFSGLLPEEFISLSPPHEALDYHFGLEEGEGIRDLFDCDFGDLTPLDF
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Transcription activator that binds DNA cooperatively with DP proteins through the E2 recognition site, 5'-TTTC[CG]CGC-3' found in the promoter region of a number of genes whose products are involved in cell cycle regulation or in DNA replication. The DRTF1/E2F complex functions in the control of cell-cycle progression from G1 to S phase. E2F1 binds preferentially RB1 in a cell-cycle dependent manner. It can mediate both cell proliferation and TP53/p53-dependent apoptosis. Blocks adipocyte differentiation by binding to specific promoters repressing CEBPA binding to its target gene promoters. Positively regulates transcription of RRP1B.
Phosphorylated by CDK2 and cyclin A-CDK2 in the S-phase. Phosphorylation at Ser-364 by CHEK2 stabilizes E2F1 upon DNA damage and regulates its effect on transcription and apoptosis.
Acetylation stimulates DNA-binding. Enhanced under stress conditions such as DNA damage and inhibited by retinoblastoma protein RB1. Regulated by KAP1/TRIM28 which recruits HDAC1 to E2F1 resulting in deacetylation. Acetylated by P/CAF/KAT2B.
Nucleus.
Belongs to the E2F/DP family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cellular senescence. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Endocrine resistance.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > MicroRNAs in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Pancreatic cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Glioma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Melanoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Bladder cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Chronic myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Non-small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
References
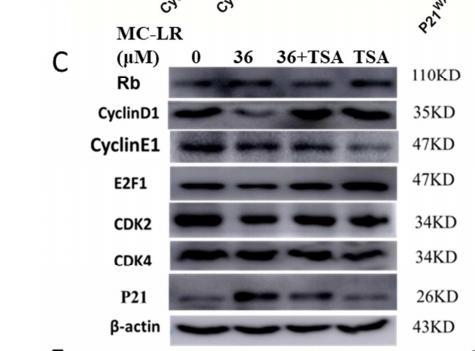
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: testicular tissue
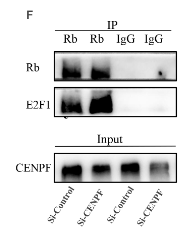
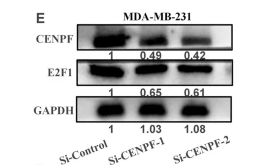
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: MDA-MB-231 cell
Application: WB Species: Human Sample:
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: MKN-28 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.