CDK6 Antibody - #DF6448
| Product: | CDK6 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6448 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to CDK6 |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 36kDa; 37kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q00534 |
| RRID: | AB_2838411 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6448, RRID:AB_2838411.
Fold/Unfold
CDK 6; CDK6; CDK6_HUMAN; Cell division protein kinase 6; Crk 2; Crk2; Cyclin dependent kinase 6; Cyclin-dependent kinase 6; MCPH12; MGC59692; p40; PLSTIRE; Serine/threonine protein kinase PLSTIRE; Serine/threonine-protein kinase PLSTIRE; STQTL11;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human CDK6, corresponding to a region within N-terminal amino acids.
Expressed ubiquitously. Accumulates in squamous cell carcinomas, proliferating hematopoietic progenitor cells, beta-cells of pancreatic islets of Langerhans, and neuroblastomas. Reduced levels in differentiating cells.
- Q00534 CDK6_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MEKDGLCRADQQYECVAEIGEGAYGKVFKARDLKNGGRFVALKRVRVQTGEEGMPLSTIREVAVLRHLETFEHPNVVRLFDVCTVSRTDRETKLTLVFEHVDQDLTTYLDKVPEPGVPTETIKDMMFQLLRGLDFLHSHRVVHRDLKPQNILVTSSGQIKLADFGLARIYSFQMALTSVVVTLWYRAPEVLLQSSYATPVDLWSVGCIFAEMFRRKPLFRGSSDVDQLGKILDVIGLPGEEDWPRDVALPRQAFHSKSAQPIEKFVTDIDELGKDLLLKCLTFNPAKRISAYSALSHPYFQDLERCKENLDSHLPPSQNTSELNTA
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Serine/threonine-protein kinase involved in the control of the cell cycle and differentiation; promotes G1/S transition. Phosphorylates pRB/RB1 and NPM1. Interacts with D-type G1 cyclins during interphase at G1 to form a pRB/RB1 kinase and controls the entrance into the cell cycle. Involved in initiation and maintenance of cell cycle exit during cell differentiation; prevents cell proliferation and regulates negatively cell differentiation, but is required for the proliferation of specific cell types (e.g. erythroid and hematopoietic cells). Essential for cell proliferation within the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus and the subventricular zone of the lateral ventricles. Required during thymocyte development. Promotes the production of newborn neurons, probably by modulating G1 length. Promotes, at least in astrocytes, changes in patterns of gene expression, changes in the actin cytoskeleton including loss of stress fibers, and enhanced motility during cell differentiation. Prevents myeloid differentiation by interfering with RUNX1 and reducing its transcription transactivation activity, but promotes proliferation of normal myeloid progenitors. Delays senescence. Promotes the proliferation of beta-cells in pancreatic islets of Langerhans. May play a role in the centrosome organization during the cell cycle phases.
Thr-177 phosphorylation and Tyr-24 dephosphorylation promotes kinase activity.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cell projection>Ruffle. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Microtubule organizing center>Centrosome.
Note: Localized to the ruffling edge of spreading fibroblasts. Kinase activity only in nucleus. Localized to the cytosol of neurons and showed prominent staining around either side of the nucleus (By similarity). Present in the cytosol and in the nucleus in interphase cells and at the centrosome during mitosis from prophase to telophase (PubMed:23918663).
Expressed ubiquitously. Accumulates in squamous cell carcinomas, proliferating hematopoietic progenitor cells, beta-cells of pancreatic islets of Langerhans, and neuroblastomas. Reduced levels in differentiating cells.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. CDC2/CDKX subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > p53 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cellular senescence. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Measles.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > MicroRNAs in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Pancreatic cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Glioma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Melanoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Chronic myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Non-small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
References
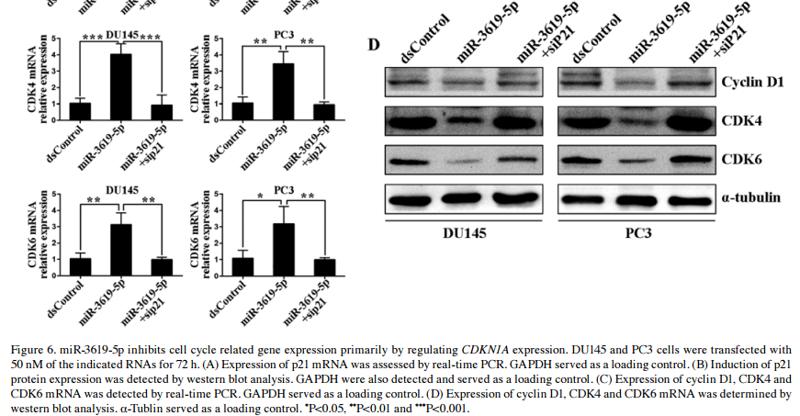
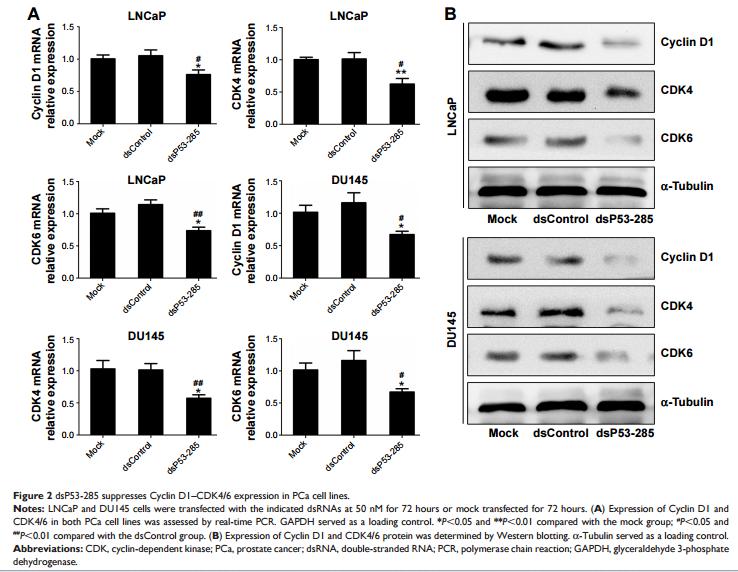
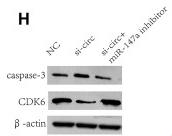
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample:
Application: WB Species: human Sample: HN4 and CAL27 cells
Application: WB Species: human Sample:
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HO8910 and A2780 cells
Application: WB Species: human Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.