GLUT1 Antibody - #AF5462
| Product: | GLUT1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF5462 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to GLUT1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 45-60kDa; 54kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P11166 |
| RRID: | AB_2837946 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5462, RRID:AB_2837946.
Fold/Unfold
Choreoathetosis/spasticity episodic (paroxysmal choreoathetosis/spasticity); CSE; DYT17; DYT18; DYT9; EIG12; erythrocyte/brain; Erythrocyte/hepatoma glucose transporter; facilitated glucose transporter member 1; Glucose transporter 1; Glucose transporter type 1; Glucose transporter type 1, erythrocyte/brain; GLUT; GLUT-1; GLUT1; GLUT1DS; GLUTB; GT1; GTG1; Gtg3; GTR1_HUMAN; HepG2 glucose transporter; HTLVR; Human T cell leukemia virus (I and II) receptor; MGC141895; MGC141896; PED; RATGTG1; Receptor for HTLV 1 and HTLV 2; SLC2A1; Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 1; Solute carrier family 2; Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human GLUT1, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Detected in erythrocytes (at protein level). Expressed at variable levels in many human tissues.
- P11166 GTR1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MEPSSKKLTGRLMLAVGGAVLGSLQFGYNTGVINAPQKVIEEFYNQTWVHRYGESILPTTLTTLWSLSVAIFSVGGMIGSFSVGLFVNRFGRRNSMLMMNLLAFVSAVLMGFSKLGKSFEMLILGRFIIGVYCGLTTGFVPMYVGEVSPTALRGALGTLHQLGIVVGILIAQVFGLDSIMGNKDLWPLLLSIIFIPALLQCIVLPFCPESPRFLLINRNEENRAKSVLKKLRGTADVTHDLQEMKEESRQMMREKKVTILELFRSPAYRQPILIAVVLQLSQQLSGINAVFYYSTSIFEKAGVQQPVYATIGSGIVNTAFTVVSLFVVERAGRRTLHLIGLAGMAGCAILMTIALALLEQLPWMSYLSIVAIFGFVAFFEVGPGPIPWFIVAELFSQGPRPAAIAVAGFSNWTSNFIVGMCFQYVEQLCGPYVFIIFTVLLVLFFIFTYFKVPETKGRTFDEIASGFRQGGASQSDKTPEELFHPLGADSQV
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Facilitative glucose transporter, which is responsible for constitutive or basal glucose uptake. Has a very broad substrate specificity; can transport a wide range of aldoses including both pentoses and hexoses. Most important energy carrier of the brain: present at the blood-brain barrier and assures the energy-independent, facilitative transport of glucose into the brain.
Phosphorylation at Ser-226 by PKC promotes glucose uptake by increasing cell membrane localization.
Cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Melanosome.
Note: Localizes primarily at the cell surface (PubMed:18245775, PubMed:19449892, PubMed:23219802, PubMed:25982116, PubMed:24847886). Identified by mass spectrometry in melanosome fractions from stage I to stage IV (PubMed:17081065).
Detected in erythrocytes (at protein level). Expressed at variable levels in many human tissues.
Belongs to the major facilitator superfamily. Sugar transporter (TC 2.A.1.1) family. Glucose transporter subfamily.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > HIF-1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Insulin resistance.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Renal cell carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Central carbon metabolism in cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Insulin secretion. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Thyroid hormone signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Adipocytokine signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Glucagon signaling pathway.
References
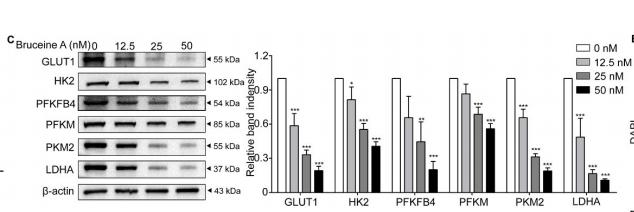
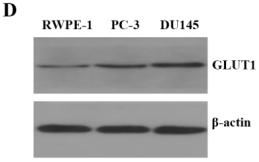
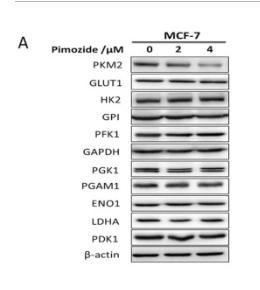
Application: WB Species: human Sample: MIA PaCa-2 cells
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: MCF-7 cells
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: Huh7 cells
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: IHC Species: Mouse Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.