Cyclin A1 Antibody - #AF5313
| Product: | Cyclin A1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF5313 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Cyclin A1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 52 kDa; 52kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P78396 |
| RRID: | AB_2837798 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5313, RRID:AB_2837798.
Fold/Unfold
CCN A1; CCNA 1; Ccna1; CCNA1_HUMAN; Cyclin-A1; CyclinA1; G2/mitotic specific cyclin A1; MGC132235; MGC159139;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Cyclin A1, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Very high levels in testis and very low levels in brain. Also found in myeloid leukemia cell lines.
- P78396 CCNA1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
METGFPAIMYPGSFIGGWGEEYLSWEGPGLPDFVFQQQPVESEAMHCSNPKSGVVLATVARGPDACQILTRAPLGQDPPQRTVLGLLTANGQYRRTCGQGITRIRCYSGSENAFPPAGKKALPDCGVQEPPKQGFDIYMDELEQGDRDSCSVREGMAFEDVYEVDTGTLKSDLHFLLDFNTVSPMLVDSSLLSQSEDISSLGTDVINVTEYAEEIYQYLREAEIRHRPKAHYMKKQPDITEGMRTILVDWLVEVGEEYKLRAETLYLAVNFLDRFLSCMSVLRGKLQLVGTAAMLLASKYEEIYPPEVDEFVYITDDTYTKRQLLKMEHLLLKVLAFDLTVPTTNQFLLQYLRRQGVCVRTENLAKYVAELSLLEADPFLKYLPSLIAAAAFCLANYTVNKHFWPETLAAFTGYSLSEIVPCLSELHKAYLDIPHRPQQAIREKYKASKYLCVSLMEPPAVLLLQ
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
May be involved in the control of the cell cycle at the G1/S (start) and G2/M (mitosis) transitions. May primarily function in the control of the germline meiotic cell cycle and additionally in the control of mitotic cell cycle in some somatic cells.
Polyubiquitinated via 'Lys-11'-linked ubiquitin by the anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C), leading to its degradation by the proteasome. Deubiquitinated and stabilized by USP37 enables entry into S phase.
Nucleus.
Very high levels in testis and very low levels in brain. Also found in myeloid leukemia cell lines.
Belongs to the cyclin family. Cyclin AB subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cellular senescence. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > AMPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Transcriptional misregulation in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Acute myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation.
References
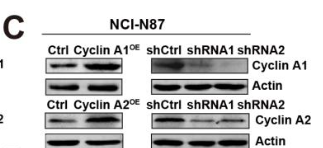
Application: WB Species: Human Sample:
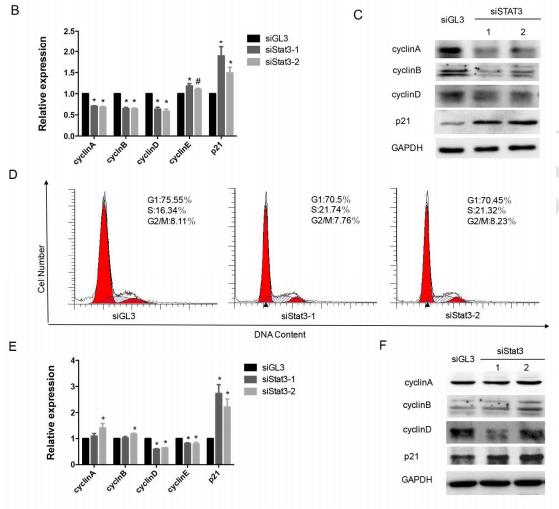
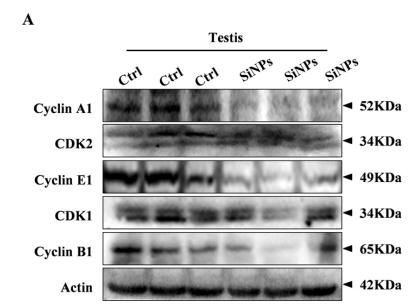
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: testis
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.