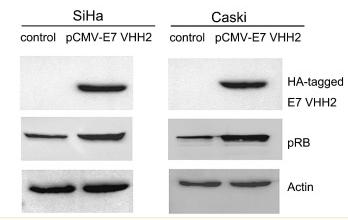
Phospho-Retinoblastoma (Thr826) Antibody - #AF0030
| Product: | Phospho-Retinoblastoma (Thr826) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF0030 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-Retinoblastoma (Thr826) |
| Application: | WB IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 110kDa; 106kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P06400 |
| RRID: | AB_2833290 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF0030, RRID:AB_2833290.
Fold/Unfold
Exon 17 tumor GOS561 substitution mutation causes premature stop; GOS563 exon 17 substitution mutation causes premature stop; OSRC; Osteosarcoma; p105-Rb; P105RB; PP105; pp110; PPP1R130; pRb; Prepro retinoblastoma associated protein; Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 130; Rb; RB transcriptional corepressor 1; RB_HUMAN; RB1; RB1 gene; Retinoblastoma 1; Retinoblastoma suspectibility protein; Retinoblastoma-associated protein;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Retinoblastoma around the phosphorylation site of Thr826.
Expressed in the retina. Expressed in foreskin keratinocytes (at protein level) (PubMed:20940255).
- P06400 RB_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MPPKTPRKTAATAAAAAAEPPAPPPPPPPEEDPEQDSGPEDLPLVRLEFEETEEPDFTALCQKLKIPDHVRERAWLTWEKVSSVDGVLGGYIQKKKELWGICIFIAAVDLDEMSFTFTELQKNIEISVHKFFNLLKEIDTSTKVDNAMSRLLKKYDVLFALFSKLERTCELIYLTQPSSSISTEINSALVLKVSWITFLLAKGEVLQMEDDLVISFQLMLCVLDYFIKLSPPMLLKEPYKTAVIPINGSPRTPRRGQNRSARIAKQLENDTRIIEVLCKEHECNIDEVKNVYFKNFIPFMNSLGLVTSNGLPEVENLSKRYEEIYLKNKDLDARLFLDHDKTLQTDSIDSFETQRTPRKSNLDEEVNVIPPHTPVRTVMNTIQQLMMILNSASDQPSENLISYFNNCTVNPKESILKRVKDIGYIFKEKFAKAVGQGCVEIGSQRYKLGVRLYYRVMESMLKSEEERLSIQNFSKLLNDNIFHMSLLACALEVVMATYSRSTSQNLDSGTDLSFPWILNVLNLKAFDFYKVIESFIKAEGNLTREMIKHLERCEHRIMESLAWLSDSPLFDLIKQSKDREGPTDHLESACPLNLPLQNNHTAADMYLSPVRSPKKKGSTTRVNSTANAETQATSAFQTQKPLKSTSLSLFYKKVYRLAYLRLNTLCERLLSEHPELEHIIWTLFQHTLQNEYELMRDRHLDQIMMCSMYGICKVKNIDLKFKIIVTAYKDLPHAVQETFKRVLIKEEEYDSIIVFYNSVFMQRLKTNILQYASTRPPTLSPIPHIPRSPYKFPSSPLRIPGGNIYISPLKSPYKISEGLPTPTKMTPRSRILVSIGESFGTSEKFQKINQMVCNSDRVLKRSAEGSNPPKPLKKLRFDIEGSDEADGSKHLPGESKFQQKLAEMTSTRTRMQKQKMNDSMDTSNKEEK
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Key regulator of entry into cell division that acts as a tumor suppressor. Promotes G0-G1 transition when phosphorylated by CDK3/cyclin-C. Acts as a transcription repressor of E2F1 target genes. The underphosphorylated, active form of RB1 interacts with E2F1 and represses its transcription activity, leading to cell cycle arrest. Directly involved in heterochromatin formation by maintaining overall chromatin structure and, in particular, that of constitutive heterochromatin by stabilizing histone methylation. Recruits and targets histone methyltransferases SUV39H1, KMT5B and KMT5C, leading to epigenetic transcriptional repression. Controls histone H4 'Lys-20' trimethylation. Inhibits the intrinsic kinase activity of TAF1. Mediates transcriptional repression by SMARCA4/BRG1 by recruiting a histone deacetylase (HDAC) complex to the c-FOS promoter. In resting neurons, transcription of the c-FOS promoter is inhibited by BRG1-dependent recruitment of a phospho-RB1-HDAC1 repressor complex. Upon calcium influx, RB1 is dephosphorylated by calcineurin, which leads to release of the repressor complex (By similarity).
(Microbial infection) In case of viral infections, interactions with SV40 large T antigen, HPV E7 protein or adenovirus E1A protein induce the disassembly of RB1-E2F1 complex thereby disrupting RB1's activity.
Phosphorylated by CDK6 and CDK4, and subsequently by CDK2 at Ser-567 in G1, thereby releasing E2F1 which is then able to activate cell growth. Dephosphorylated at the late M phase. SV40 large T antigen, HPV E7 and adenovirus E1A bind to the underphosphorylated, active form of pRb. Phosphorylation at Thr-821 and Thr-826 promotes interaction between the C-terminal domain C and the Pocket domain, and thereby inhibits interactions with heterodimeric E2F/DP transcription factor complexes. Dephosphorylated at Ser-795 by calcineruin upon calcium stimulation. CDK3/cyclin-C-mediated phosphorylation at Ser-807 and Ser-811 is required for G0-G1 transition. Phosphorylated by CDK1 and CDK2 upon TGFB1-mediated apoptosis (By similarity).
N-terminus is methylated by METTL11A/NTM1 (By similarity). Monomethylation at Lys-810 by SMYD2 enhances phosphorylation at Ser-807 and Ser-811, and promotes cell cycle progression. Monomethylation at Lys-860 by SMYD2 promotes interaction with L3MBTL1.
Acetylated during keratinocyte differentiation. Acetylation at Lys-873 and Lys-874 regulates subcellular localization. Can be deacetylated by SIRT1.
Nucleus.
Note: During keratinocyte differentiation, acetylation by KAT2B/PCAF is required for nuclear localization.
Expressed in the retina. Expressed in foreskin keratinocytes (at protein level).
The Pocket domain binds to the threonine-phosphorylated domain C, thereby preventing interaction with heterodimeric E2F/DP transcription factor complexes.
Belongs to the retinoblastoma protein (RB) family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cellular senescence. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Endocrine resistance.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Pancreatic cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Glioma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Melanoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Bladder cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Chronic myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Non-small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
References
Application: WB Species: human Sample:
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: CC and HPV positive cervical epithelia tissues
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.