ZAP70 Antibody - #AF6312
| Product: | ZAP70 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF6312 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to ZAP70 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 70kDa; 70kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P43403 |
| RRID: | AB_2835171 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6312, RRID:AB_2835171.
Fold/Unfold
70 kDa zeta associated protein; 70 kDa zeta-associated protein; EC 2.7.10.2; FLJ17670; FLJ17679; Selective T cell defect; SRK; STD; Syk related tyrosine kinase; Syk-related tyrosine kinase; Truncated ZAP kinase; Tyrosine protein kinase ZAP70; Tyrosine-protein kinase ZAP-70; TZK; ZAP 70; ZAP70; ZAP70_HUMAN; Zeta chain associated protein kinase 70kD; Zeta chain associated protein kinase 70kDa; Zeta chain associated protein kinase 70kDa isoform 1; Zeta chain associated protein kinase 70kDa isoform 2; Zeta chain TCR associated protein kinase 70kD; Zeta chain TCR associated protein kinase 70kDa;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human ZAP70, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Expressed in T- and natural killer cells. Also present in early thymocytes and pro/pre B-cells.
- P43403 ZAP70_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MPDPAAHLPFFYGSISRAEAEEHLKLAGMADGLFLLRQCLRSLGGYVLSLVHDVRFHHFPIERQLNGTYAIAGGKAHCGPAELCEFYSRDPDGLPCNLRKPCNRPSGLEPQPGVFDCLRDAMVRDYVRQTWKLEGEALEQAIISQAPQVEKLIATTAHERMPWYHSSLTREEAERKLYSGAQTDGKFLLRPRKEQGTYALSLIYGKTVYHYLISQDKAGKYCIPEGTKFDTLWQLVEYLKLKADGLIYCLKEACPNSSASNASGAAAPTLPAHPSTLTHPQRRIDTLNSDGYTPEPARITSPDKPRPMPMDTSVYESPYSDPEELKDKKLFLKRDNLLIADIELGCGNFGSVRQGVYRMRKKQIDVAIKVLKQGTEKADTEEMMREAQIMHQLDNPYIVRLIGVCQAEALMLVMEMAGGGPLHKFLVGKREEIPVSNVAELLHQVSMGMKYLEEKNFVHRDLAARNVLLVNRHYAKISDFGLSKALGADDSYYTARSAGKWPLKWYAPECINFRKFSSRSDVWSYGVTMWEALSYGQKPYKKMKGPEVMAFIEQGKRMECPPECPPELYALMSDCWIYKWEDRPDFLTVEQRMRACYYSLASKVEGPPGSTQKAEAACA
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Tyrosine kinase that plays an essential role in regulation of the adaptive immune response. Regulates motility, adhesion and cytokine expression of mature T-cells, as well as thymocyte development. Contributes also to the development and activation of primary B-lymphocytes. When antigen presenting cells (APC) activate T-cell receptor (TCR), a serie of phosphorylations lead to the recruitment of ZAP70 to the doubly phosphorylated TCR component CD247/CD3Z through ITAM motif at the plasma membrane. This recruitment serves to localization to the stimulated TCR and to relieve its autoinhibited conformation. Release of ZAP70 active conformation is further stabilized by phosphorylation mediated by LCK. Subsequently, ZAP70 phosphorylates at least 2 essential adapter proteins: LAT and LCP2. In turn, a large number of signaling molecules are recruited and ultimately lead to lymphokine production, T-cell proliferation and differentiation. Furthermore, ZAP70 controls cytoskeleton modifications, adhesion and mobility of T-lymphocytes, thus ensuring correct delivery of effectors to the APC. ZAP70 is also required for TCR-CD247/CD3Z internalization and degradation through interaction with the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL and adapter proteins SLA and SLA2. Thus, ZAP70 regulates both T-cell activation switch on and switch off by modulating TCR expression at the T-cell surface. During thymocyte development, ZAP70 promotes survival and cell-cycle progression of developing thymocytes before positive selection (when cells are still CD4/CD8 double negative). Additionally, ZAP70-dependent signaling pathway may also contribute to primary B-cells formation and activation through B-cell receptor (BCR).
Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues upon T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) stimulation. Phosphorylation of Tyr-315 and Tyr-319 are essential for ZAP70 positive function on T-lymphocyte activation whereas Tyr-292 has a negative regulatory role. Within the C-terminal kinase domain, Tyr-492 and Tyr-493 are phosphorylated after TCR induction, Tyr-492 playing a negative regulatory role and Tyr-493 a positive. Tyr-493 is dephosphorylated by PTN22.
Ubiquitinated in response to T cell activation. Deubiquitinated by OTUD7B.
Cytoplasm. Cell membrane>Peripheral membrane protein.
Note: In quiescent T-lymphocytes, it is cytoplasmic. Upon TCR activation, it is recruited at the plasma membrane by interacting with CD247/CD3Z. Colocalizes together with RHOH in the immunological synapse. RHOH is required for its proper localization to the cell membrane and cytoskeleton fractions in the thymocytes (By similarity).
Expressed in T- and natural killer cells. Also present in early thymocytes and pro/pre B-cells.
Composed of 2 N-terminal SH2 domains and a C-terminal kinase domain. The tandem SH2 domains bind to the doubly phosphorylated tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) of CD247/CD3Z and the non-canonical phosphorylated tyrosine-based activation motif (TAM) of RHOH (By similarity). The interdomain B located between the second SH2 and the kinase domain contains 3 tyrosines (Tyr-292, Tyr-315, Tyr-319) that are phosphorylated following TCR activation. These sites have been implicated in binding to other signaling molecules including CBL or VAV1. Thus, ZAP70 can also function as a scaffold by recruiting additional factors to the stimulated TCR complex.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. SYK/ZAP-70 subfamily.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Ras signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > NF-kappa B signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Immune diseases > Primary immunodeficiency.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th17 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > T cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
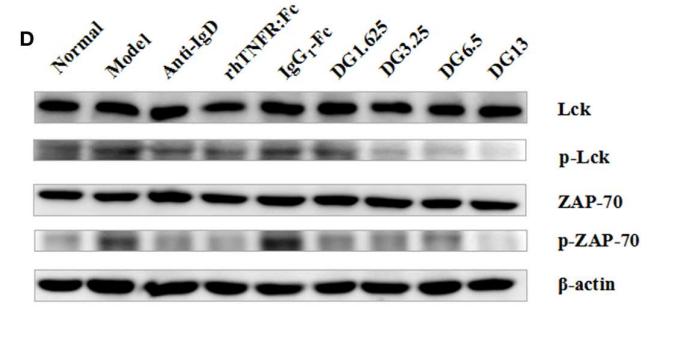
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: spleen
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.