p70 S6 Kinase Antibody - #AF6226
| Product: | p70 S6 Kinase Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF6226 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to p70 S6 Kinase |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 70kDa; 59kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P23443 |
| RRID: | AB_2835100 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6226, RRID:AB_2835100.
Fold/Unfold
70 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1; KS6B1_HUMAN; p70 alpha; P70 beta 1; p70 ribosomal S6 kinase alpha; p70 ribosomal S6 kinase beta 1; p70 S6 kinase alpha; P70 S6 Kinase; p70 S6 kinase, alpha 1; p70 S6 kinase, alpha 2; p70 S6K; p70 S6K-alpha; p70 S6KA; p70(S6K) alpha; p70(S6K)-alpha; p70-alpha; p70-S6K 1; p70-S6K; P70S6K; P70S6K1; p70S6Kb; PS6K; Ribosomal protein S6 kinase 70kDa polypeptide 1; Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta 1; Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1; Ribosomal protein S6 kinase I; RPS6KB1; S6K; S6K-beta-1; S6K1; Serine/threonine kinase 14 alpha; Serine/threonine-protein kinase 14A; STK14A;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human p70 S6 Kinase, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- P23443 KS6B1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MRRRRRRDGFYPAPDFRDREAEDMAGVFDIDLDQPEDAGSEDELEEGGQLNESMDHGGVGPYELGMEHCEKFEISETSVNRGPEKIRPECFELLRVLGKGGYGKVFQVRKVTGANTGKIFAMKVLKKAMIVRNAKDTAHTKAERNILEEVKHPFIVDLIYAFQTGGKLYLILEYLSGGELFMQLEREGIFMEDTACFYLAEISMALGHLHQKGIIYRDLKPENIMLNHQGHVKLTDFGLCKESIHDGTVTHTFCGTIEYMAPEILMRSGHNRAVDWWSLGALMYDMLTGAPPFTGENRKKTIDKILKCKLNLPPYLTQEARDLLKKLLKRNAASRLGAGPGDAGEVQAHPFFRHINWEELLARKVEPPFKPLLQSEEDVSQFDSKFTRQTPVDSPDDSTLSESANQVFLGFTYVAPSVLESVKEKFSFEPKIRSPRRFIGSPRTPVSPVKFSPGDFWGRGASASTANPQTPVEYPMETSGIEQMDVTMSGEASAPLPIRQPNSGPYKKQAFPMISKRPEHLRMNL
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Serine/threonine-protein kinase that acts downstream of mTOR signaling in response to growth factors and nutrients to promote cell proliferation, cell growth and cell cycle progression. Regulates protein synthesis through phosphorylation of EIF4B, RPS6 and EEF2K, and contributes to cell survival by repressing the pro-apoptotic function of BAD. Under conditions of nutrient depletion, the inactive form associates with the EIF3 translation initiation complex. Upon mitogenic stimulation, phosphorylation by the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) leads to dissociation from the EIF3 complex and activation. The active form then phosphorylates and activates several substrates in the pre-initiation complex, including the EIF2B complex and the cap-binding complex component EIF4B. Also controls translation initiation by phosphorylating a negative regulator of EIF4A, PDCD4, targeting it for ubiquitination and subsequent proteolysis. Promotes initiation of the pioneer round of protein synthesis by phosphorylating POLDIP3/SKAR. In response to IGF1, activates translation elongation by phosphorylating EEF2 kinase (EEF2K), which leads to its inhibition and thus activation of EEF2. Also plays a role in feedback regulation of mTORC2 by mTORC1 by phosphorylating RICTOR, resulting in the inhibition of mTORC2 and AKT1 signaling. Mediates cell survival by phosphorylating the pro-apoptotic protein BAD and suppressing its pro-apoptotic function. Phosphorylates mitochondrial URI1 leading to dissociation of a URI1-PPP1CC complex. The free mitochondrial PPP1CC can then dephosphorylate RPS6KB1 at Thr-412, which is proposed to be a negative feedback mechanism for the RPS6KB1 anti-apoptotic function. Mediates TNF-alpha-induced insulin resistance by phosphorylating IRS1 at multiple serine residues, resulting in accelerated degradation of IRS1. In cells lacking functional TSC1-2 complex, constitutively phosphorylates and inhibits GSK3B. May be involved in cytoskeletal rearrangement through binding to neurabin. Phosphorylates and activates the pyrimidine biosynthesis enzyme CAD, downstream of MTOR. Following activation by mTORC1, phosphorylates EPRS and thereby plays a key role in fatty acid uptake by adipocytes and also most probably in interferon-gamma-induced translation inhibition.
Phosphorylation at Thr-412 is regulated by mTORC1. The phosphorylation at this site is maintained by an agonist-dependent autophosphorylation mechanism (By similarity). Activated by phosphorylation at Thr-252 by PDPK1. Dephosphorylation by PPP1CC at Thr-412 in mitochondrion.
Cell junction>Synapse>Synaptosome. Mitochondrion outer membrane. Mitochondrion.
Note: Colocalizes with URI1 at mitochondrion.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
Cytoplasm.
Widely expressed.
The autoinhibitory domain is believed to block phosphorylation within the AGC-kinase C-terminal domain and the activation loop.
The TOS (TOR signaling) motif is essential for activation by mTORC1.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. S6 kinase subfamily.
Research Fields
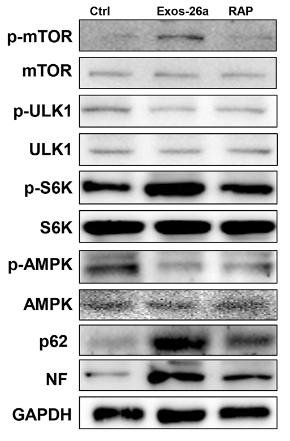
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Autophagy - animal. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > ErbB signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > HIF-1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > mTOR signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > AMPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TGF-beta signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Apelin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance.
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Endocrine resistance.
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Insulin resistance.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Colorectal cancer. (View pathway)
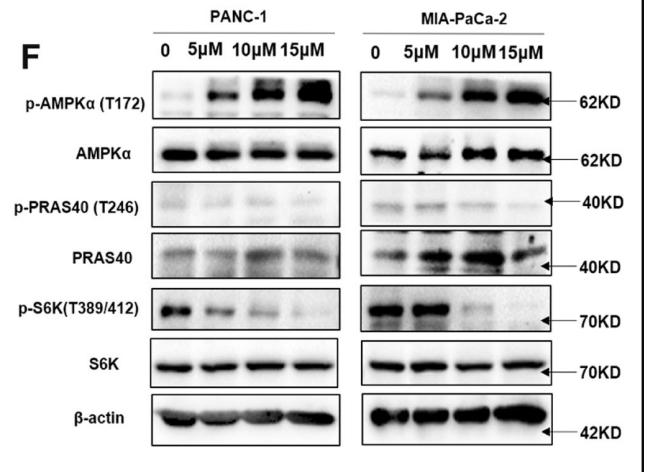
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Pancreatic cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Acute myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Choline metabolism in cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Insulin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
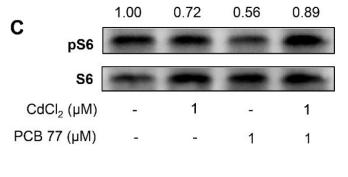
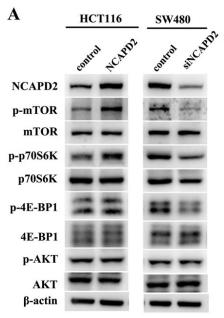
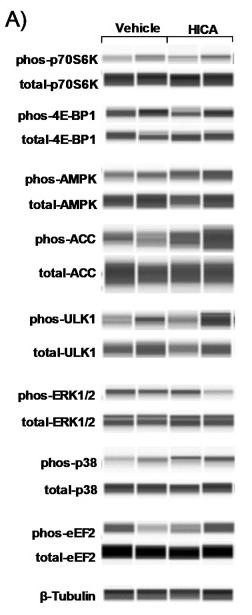
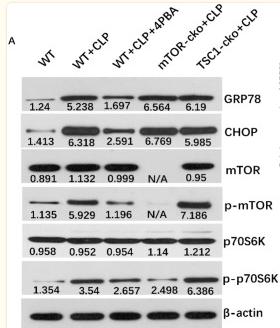
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HEL cells
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: CRC cells
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: pancreatic cancer tissue
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: PC16 cells
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: osteoblasts
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: hippocampus
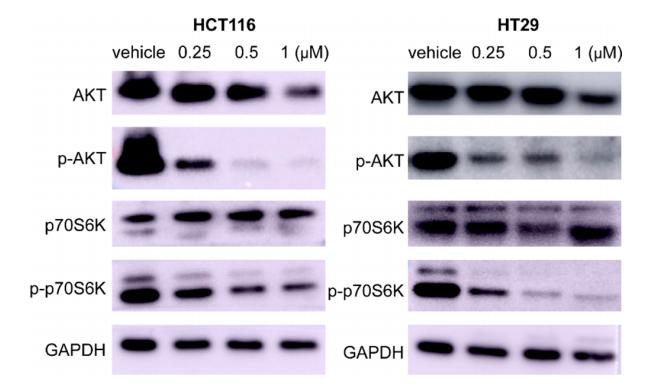
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HCT116 and HT-29 cells
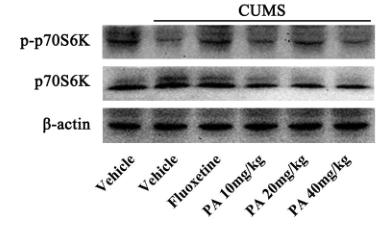
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: lung tissues
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: Hep-G2 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.