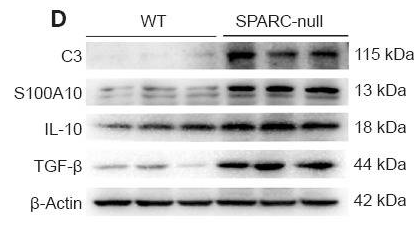
C3 Antibody - #DF13224
| Product: | C3 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF13224 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to C3 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 187kDa; 187kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P01024 |
| RRID: | AB_2846243 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF13224, RRID:AB_2846243.
Fold/Unfold
acylation-stimulating protein cleavage product; AHUS5; ARMD9; ASP; C3 and PZP-like alpha-2-macroglobulin domain-containing protein 1; C3; c3 complement; C3a anaphylatoxin; C3a; C3b; CO3_HUMAN; Complement C3; Complement C3c alpha' chain fragment 2; Complement C3c; Complement component 3; Complement component C3; Complement component C3a; Complement component C3b; Complement factor 3; CPAMD1; Prepro C3;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human C3, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Plasma. The acylation stimulating protein (ASP) is expressed in adipocytes and released into the plasma during both the fasting and postprandial periods.
- P01024 CO3_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MGPTSGPSLLLLLLTHLPLALGSPMYSIITPNILRLESEETMVLEAHDAQGDVPVTVTVHDFPGKKLVLSSEKTVLTPATNHMGNVTFTIPANREFKSEKGRNKFVTVQATFGTQVVEKVVLVSLQSGYLFIQTDKTIYTPGSTVLYRIFTVNHKLLPVGRTVMVNIENPEGIPVKQDSLSSQNQLGVLPLSWDIPELVNMGQWKIRAYYENSPQQVFSTEFEVKEYVLPSFEVIVEPTEKFYYIYNEKGLEVTITARFLYGKKVEGTAFVIFGIQDGEQRISLPESLKRIPIEDGSGEVVLSRKVLLDGVQNPRAEDLVGKSLYVSATVILHSGSDMVQAERSGIPIVTSPYQIHFTKTPKYFKPGMPFDLMVFVTNPDGSPAYRVPVAVQGEDTVQSLTQGDGVAKLSINTHPSQKPLSITVRTKKQELSEAEQATRTMQALPYSTVGNSNNYLHLSVLRTELRPGETLNVNFLLRMDRAHEAKIRYYTYLIMNKGRLLKAGRQVREPGQDLVVLPLSITTDFIPSFRLVAYYTLIGASGQREVVADSVWVDVKDSCVGSLVVKSGQSEDRQPVPGQQMTLKIEGDHGARVVLVAVDKGVFVLNKKNKLTQSKIWDVVEKADIGCTPGSGKDYAGVFSDAGLTFTSSSGQQTAQRAELQCPQPAARRRRSVQLTEKRMDKVGKYPKELRKCCEDGMRENPMRFSCQRRTRFISLGEACKKVFLDCCNYITELRRQHARASHLGLARSNLDEDIIAEENIVSRSEFPESWLWNVEDLKEPPKNGISTKLMNIFLKDSITTWEILAVSMSDKKGICVADPFEVTVMQDFFIDLRLPYSVVRNEQVEIRAVLYNYRQNQELKVRVELLHNPAFCSLATTKRRHQQTVTIPPKSSLSVPYVIVPLKTGLQEVEVKAAVYHHFISDGVRKSLKVVPEGIRMNKTVAVRTLDPERLGREGVQKEDIPPADLSDQVPDTESETRILLQGTPVAQMTEDAVDAERLKHLIVTPSGCGEQNMIGMTPTVIAVHYLDETEQWEKFGLEKRQGALELIKKGYTQQLAFRQPSSAFAAFVKRAPSTWLTAYVVKVFSLAVNLIAIDSQVLCGAVKWLILEKQKPDGVFQEDAPVIHQEMIGGLRNNNEKDMALTAFVLISLQEAKDICEEQVNSLPGSITKAGDFLEANYMNLQRSYTVAIAGYALAQMGRLKGPLLNKFLTTAKDKNRWEDPGKQLYNVEATSYALLALLQLKDFDFVPPVVRWLNEQRYYGGGYGSTQATFMVFQALAQYQKDAPDHQELNLDVSLQLPSRSSKITHRIHWESASLLRSEETKENEGFTVTAEGKGQGTLSVVTMYHAKAKDQLTCNKFDLKVTIKPAPETEKRPQDAKNTMILEICTRYRGDQDATMSILDISMMTGFAPDTDDLKQLANGVDRYISKYELDKAFSDRNTLIIYLDKVSHSEDDCLAFKVHQYFNVELIQPGAVKVYAYYNLEESCTRFYHPEKEDGKLNKLCRDELCRCAEENCFIQKSDDKVTLEERLDKACEPGVDYVYKTRLVKVQLSNDFDEYIMAIEQTIKSGSDEVQVGQQRTFISPIKCREALKLEEKKHYLMWGLSSDFWGEKPNLSYIIGKDTWVEHWPEEDECQDEENQKQCQDLGAFTESMVVFGCPN
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
C3 plays a central role in the activation of the complement system. Its processing by C3 convertase is the central reaction in both classical and alternative complement pathways. After activation C3b can bind covalently, via its reactive thioester, to cell surface carbohydrates or immune aggregates.
Derived from proteolytic degradation of complement C3, C3a anaphylatoxin is a mediator of local inflammatory process. In chronic inflammation, acts as a chemoattractant for neutrophils (By similarity). It induces the contraction of smooth muscle, increases vascular permeability and causes histamine release from mast cells and basophilic leukocytes.
Acts as a chemoattractant for neutrophils in chronic inflammation.
adipogenic hormone that stimulates triglyceride (TG) synthesis and glucose transport in adipocytes, regulating fat storage and playing a role in postprandial TG clearance. Appears to stimulate TG synthesis via activation of the PLC, MAPK and AKT signaling pathways. Ligand for C5AR2. Promotes the phosphorylation, ARRB2-mediated internalization and recycling of C5AR2.
C3b is rapidly split in two positions by factor I and a cofactor to form iC3b (inactivated C3b) and C3f which is released. Then iC3b is slowly cleaved (possibly by factor I) to form C3c (beta chain + alpha' chain fragment 1 + alpha' chain fragment 2), C3dg and C3f. Other proteases produce other fragments such as C3d or C3g. C3a is further processed by carboxypeptidases to release the C-terminal arginine residue generating the acylation stimulating protein (ASP). Levels of ASP are increased in adipocytes in the postprandial period and by insulin and dietary chylomicrons.
(Microbial infection) C3 is cleaved by Staphylococcus aureus aureolysin; this cleavage renders C3a and C3b inactive. C3b is rapidly degraded by host factors CFH and CFI preventing its deposition on the bacterial surface while C3a is further inactivated by aureolysin.
Phosphorylated by FAM20C in the extracellular medium.
Secreted.
Plasma. The acylation stimulating protein (ASP) is expressed in adipocytes and released into the plasma during both the fasting and postprandial periods.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Phagosome. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pertussis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Legionellosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Leishmaniasis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Staphylococcus aureus infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Tuberculosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Herpes simplex infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
· Human Diseases > Immune diseases > Systemic lupus erythematosus.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Complement and coagulation cascades. (View pathway)
References
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: IF/ICC Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: spinal cord
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: spinal cord
Application: IF/ICC Species: Rat Sample: spinal cord
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.