Phospho-TIE2 (Tyr992) Antibody - #AF2424
| Product: | Phospho-TIE2 (Tyr992) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF2424 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-TIE2 (Tyr992) |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 160kDa; 126kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q02763 |
| RRID: | AB_2845437 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF2424, RRID:AB_2845437.
Fold/Unfold
Angiopoietin 1 receptor; Angiopoietin-1 receptor; CD202b; CD202b antigen; Endothelial tyrosine kinase; Endothelium specific receptor tyrosine kinase 2; hTIE 2; hTIE2; Hyk; p140 TEK; Soluble TIE2 variant 1; Soluble TIE2 variant 2; Tek; tek tyrosine kinase; TEK tyrosine kinase endothelial; tek tyrosine kinase, endothelial; TIE 2; TIE2; TIE2_HUMAN; Tunica interna endothelial cell kinase; Tyrosine kinase with Ig and EGF homology domains 2; Tyrosine kinase with Ig and EGF homology domains-2; Tyrosine protein kinase receptor TEK; Tyrosine protein kinase receptor TIE 2; Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TEK; Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TIE-2; Venous malformations multiple cutaneous and mucosal; VMCM 1; VMCM; VMCM1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human TIE2 around the phosphorylation site of Tyr992.
Detected in umbilical vein endothelial cells. Proteolytic processing gives rise to a soluble extracellular domain that is detected in blood plasma (at protein level). Predominantly expressed in endothelial cells and their progenitors, the angioblasts. Has been directly found in placenta and lung, with a lower level in umbilical vein endothelial cells, brain and kidney.
- Q02763 TIE2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MDSLASLVLCGVSLLLSGTVEGAMDLILINSLPLVSDAETSLTCIASGWRPHEPITIGRDFEALMNQHQDPLEVTQDVTREWAKKVVWKREKASKINGAYFCEGRVRGEAIRIRTMKMRQQASFLPATLTMTVDKGDNVNISFKKVLIKEEDAVIYKNGSFIHSVPRHEVPDILEVHLPHAQPQDAGVYSARYIGGNLFTSAFTRLIVRRCEAQKWGPECNHLCTACMNNGVCHEDTGECICPPGFMGRTCEKACELHTFGRTCKERCSGQEGCKSYVFCLPDPYGCSCATGWKGLQCNEACHPGFYGPDCKLRCSCNNGEMCDRFQGCLCSPGWQGLQCEREGIQRMTPKIVDLPDHIEVNSGKFNPICKASGWPLPTNEEMTLVKPDGTVLHPKDFNHTDHFSVAIFTIHRILPPDSGVWVCSVNTVAGMVEKPFNISVKVLPKPLNAPNVIDTGHNFAVINISSEPYFGDGPIKSKKLLYKPVNHYEAWQHIQVTNEIVTLNYLEPRTEYELCVQLVRRGEGGEGHPGPVRRFTTASIGLPPPRGLNLLPKSQTTLNLTWQPIFPSSEDDFYVEVERRSVQKSDQQNIKVPGNLTSVLLNNLHPREQYVVRARVNTKAQGEWSEDLTAWTLSDILPPQPENIKISNITHSSAVISWTILDGYSISSITIRYKVQGKNEDQHVDVKIKNATITQYQLKGLEPETAYQVDIFAENNIGSSNPAFSHELVTLPESQAPADLGGGKMLLIAILGSAGMTCLTVLLAFLIILQLKRANVQRRMAQAFQNVREEPAVQFNSGTLALNRKVKNNPDPTIYPVLDWNDIKFQDVIGEGNFGQVLKARIKKDGLRMDAAIKRMKEYASKDDHRDFAGELEVLCKLGHHPNIINLLGACEHRGYLYLAIEYAPHGNLLDFLRKSRVLETDPAFAIANSTASTLSSQQLLHFAADVARGMDYLSQKQFIHRDLAARNILVGENYVAKIADFGLSRGQEVYVKKTMGRLPVRWMAIESLNYSVYTTNSDVWSYGVLLWEIVSLGGTPYCGMTCAELYEKLPQGYRLEKPLNCDDEVYDLMRQCWREKPYERPSFAQILVSLNRMLEERKTYVNTTLYEKFTYAGIDCSAEEAA
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for ANGPT1, ANGPT2 and ANGPT4 and regulates angiogenesis, endothelial cell survival, proliferation, migration, adhesion and cell spreading, reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, but also maintenance of vascular quiescence. Has anti-inflammatory effects by preventing the leakage of proinflammatory plasma proteins and leukocytes from blood vessels. Required for normal angiogenesis and heart development during embryogenesis. Required for post-natal hematopoiesis. After birth, activates or inhibits angiogenesis, depending on the context. Inhibits angiogenesis and promotes vascular stability in quiescent vessels, where endothelial cells have tight contacts. In quiescent vessels, ANGPT1 oligomers recruit TEK to cell-cell contacts, forming complexes with TEK molecules from adjoining cells, and this leads to preferential activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and the AKT1 signaling cascades. In migrating endothelial cells that lack cell-cell adhesions, ANGT1 recruits TEK to contacts with the extracellular matrix, leading to the formation of focal adhesion complexes, activation of PTK2/FAK and of the downstream kinases MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1, and ultimately to the stimulation of sprouting angiogenesis. ANGPT1 signaling triggers receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation at specific tyrosine residues that then serve as binding sites for scaffold proteins and effectors. Signaling is modulated by ANGPT2 that has lower affinity for TEK, can promote TEK autophosphorylation in the absence of ANGPT1, but inhibits ANGPT1-mediated signaling by competing for the same binding site. Signaling is also modulated by formation of heterodimers with TIE1, and by proteolytic processing that gives rise to a soluble TEK extracellular domain. The soluble extracellular domain modulates signaling by functioning as decoy receptor for angiopoietins. TEK phosphorylates DOK2, GRB7, GRB14, PIK3R1; SHC1 and TIE1.
Proteolytic processing leads to the shedding of the extracellular domain (soluble TIE-2 alias sTIE-2).
Autophosphorylated on tyrosine residues in response to ligand binding. Autophosphorylation occurs in trans, i.e. one subunit of the dimeric receptor phosphorylates tyrosine residues on the other subunit. Autophosphorylation occurs in a sequential manner, where Tyr-992 in the kinase activation loop is phosphorylated first, followed by autophosphorylation at Tyr-1108 and at additional tyrosine residues. ANGPT1-induced phosphorylation is impaired during hypoxia, due to increased expression of ANGPT2. Phosphorylation is important for interaction with GRB14, PIK3R1 and PTPN11. Phosphorylation at Tyr-1102 is important for interaction with SHC1, GRB2 and GRB7. Phosphorylation at Tyr-1108 is important for interaction with DOK2 and for coupling to downstream signal transduction pathways in endothelial cells. Dephosphorylated by PTPRB.
Ubiquitinated. The phosphorylated receptor is ubiquitinated and internalized, leading to its degradation.
Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell junction. Cell junction>Focal adhesion. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton. Secreted.
Note: Recruited to cell-cell contacts in quiescent endothelial cells (PubMed:18425120, PubMed:18425119). Colocalizes with the actin cytoskeleton and at actin stress fibers during cell spreading. Recruited to the lower surface of migrating cells, especially the rear end of the cell. Proteolytic processing gives rise to a soluble extracellular domain that is secreted (PubMed:11806244).
Detected in umbilical vein endothelial cells. Proteolytic processing gives rise to a soluble extracellular domain that is detected in blood plasma (at protein level). Predominantly expressed in endothelial cells and their progenitors, the angioblasts. Has been directly found in placenta and lung, with a lower level in umbilical vein endothelial cells, brain and kidney.
The soluble extracellular domain is functionally active in angiopoietin binding and can modulate the activity of the membrane-bound form by competing for angiopoietins.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. Tie subfamily.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Ras signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Rap1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > HIF-1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Immune diseases > Rheumatoid arthritis.
References
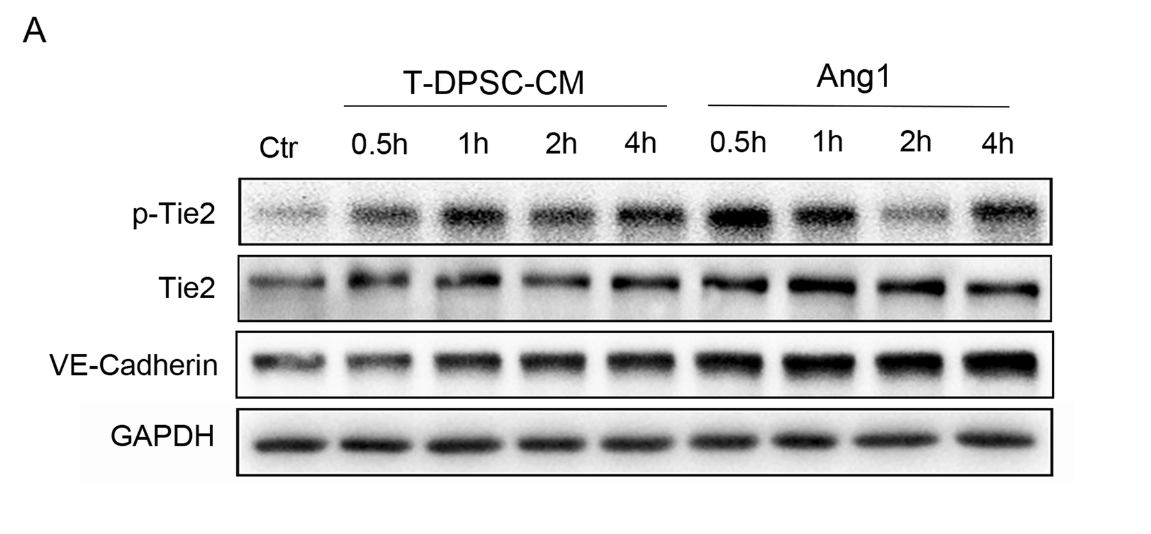
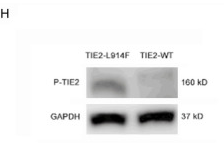
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HUVECs
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HUVECs
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.