MEK4/MKK4 Antibody - #AF4734
| Product: | MEK4/MKK4 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF4734 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to MEK4/MKK4 |
| Application: | WB |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 44kDa; 44kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P45985 |
| RRID: | AB_2844733 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF4734, RRID:AB_2844733.
Fold/Unfold
c Jun N terminal kinase kinase 1; C-JUN N-terminal kinase kinase 1; Dual specificity mitogen activated protein kinase kinase 4; Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4; JNK Activated Kinase 1; JNK activating kinase 1; JNK-activating kinase 1; JNKK; JNKK1; MAP kinase kinase 4; Map2k4; MAPK ERK kinase 4; MAPK/ERK kinase 4; MAPKK 4; MAPKK4; MEK 4; MEK4; Mitogen activated protein kinase kinase 4; MKK 4; MKK4; MP2K4_HUMAN; PRKMK4; SAPK ERK kinase 1; SAPK/ERK kinase 1; SAPKK 1; SAPKK1; SEK1; SERK1; SKK1; Stress activated protein kinase kinase 1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human SEK1/MKK4, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Abundant expression is seen in the skeletal muscle. It is also widely expressed in other tissues.
- P45985 MP2K4_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAAPSPSGGGGSGGGSGSGTPGPVGSPAPGHPAVSSMQGKRKALKLNFANPPFKSTARFTLNPNPTGVQNPHIERLRTHSIESSGKLKISPEQHWDFTAEDLKDLGEIGRGAYGSVNKMVHKPSGQIMAVKRIRSTVDEKEQKQLLMDLDVVMRSSDCPYIVQFYGALFREGDCWICMELMSTSFDKFYKYVYSVLDDVIPEEILGKITLATVKALNHLKENLKIIHRDIKPSNILLDRSGNIKLCDFGISGQLVDSIAKTRDAGCRPYMAPERIDPSASRQGYDVRSDVWSLGITLYELATGRFPYPKWNSVFDQLTQVVKGDPPQLSNSEEREFSPSFINFVNLCLTKDESKRPKYKELLKHPFILMYEERAVEVACYVCKILDQMPATPSSPMYVD
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Dual specificity protein kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. Essential component of the stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (SAP/JNK) signaling pathway. With MAP2K7/MKK7, is the one of the only known kinase to directly activate the stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinases MAPK8/JNK1, MAPK9/JNK2 and MAPK10/JNK3. MAP2K4/MKK4 and MAP2K7/MKK7 both activate the JNKs by phosphorylation, but they differ in their preference for the phosphorylation site in the Thr-Pro-Tyr motif. MAP2K4 shows preference for phosphorylation of the Tyr residue and MAP2K7/MKK7 for the Thr residue. The phosphorylation of the Thr residue by MAP2K7/MKK7 seems to be the prerequisite for JNK activation at least in response to proinflammatory cytokines, while other stimuli activate both MAP2K4/MKK4 and MAP2K7/MKK7 which synergistically phosphorylate JNKs. MAP2K4 is required for maintaining peripheral lymphoid homeostasis. The MKK/JNK signaling pathway is also involved in mitochondrial death signaling pathway, including the release cytochrome c, leading to apoptosis. Whereas MAP2K7/MKK7 exclusively activates JNKs, MAP2K4/MKK4 additionally activates the p38 MAPKs MAPK11, MAPK12, MAPK13 and MAPK14.
Activated by phosphorylation on Ser-257 and Thr-261 by MAP kinase kinase kinases (MAP3Ks).
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Abundant expression is seen in the skeletal muscle. It is also widely expressed in other tissues.
The DVD domain (residues 364-387) contains a conserved docking site and is found in the mammalian MAP kinase kinases (MAP2Ks). The DVD sites bind to their specific upstream MAP kinase kinase kinases (MAP3Ks) and are essential for activation.
The D domain (residues 34-52) contains a conserved docking site and is required for the binding to MAPK substrates.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. STE Ser/Thr protein kinase family. MAP kinase kinase subfamily.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > ErbB signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TNF signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Relaxin signaling pathway.
References
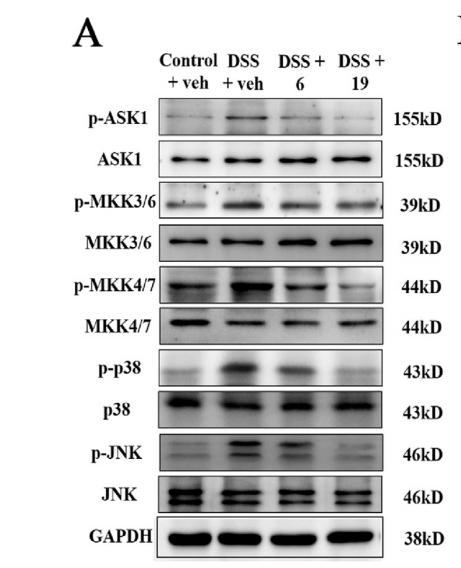
Application: WB Species: mice Sample: colon tissues
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.