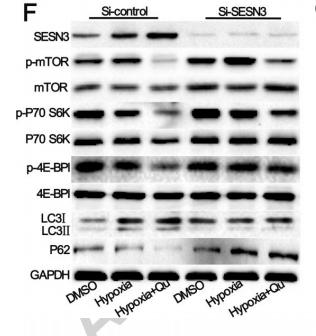
Phospho-mTOR (Thr2446) Antibody - #AF3310
| Product: | Phospho-mTOR (Thr2446) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF3310 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-mTOR (Thr2446) |
| Application: | WB |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 220kDa; 289kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P42345 |
| RRID: | AB_2834729 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF3310, RRID:AB_2834729.
Fold/Unfold
dJ576K7.1 (FK506 binding protein 12 rapamycin associated protein 1); FK506 binding protein 12 rapamycin associated protein 1; FK506 binding protein 12 rapamycin associated protein 2; FK506 binding protein 12 rapamycin complex associated protein 1; FK506-binding protein 12-rapamycin complex-associated protein 1; FKBP rapamycin associated protein; FKBP12 rapamycin complex associated protein; FKBP12-rapamycin complex-associated protein 1; FKBP12-rapamycin complex-associated protein; FLJ44809; FRAP; FRAP1; FRAP2; Mammalian target of rapamycin; Mechanistic target of rapamycin; mTOR; MTOR_HUMAN; OTTHUMP00000001983; RAFT1; Rapamycin and FKBP12 target 1; Rapamycin associated protein FRAP2; Rapamycin target protein 1; Rapamycin target protein; RAPT1; Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human mTOR around the phosphorylation site of Thr2446.
- P42345 MTOR_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MLGTGPAAATTAATTSSNVSVLQQFASGLKSRNEETRAKAAKELQHYVTMELREMSQEESTRFYDQLNHHIFELVSSSDANERKGGILAIASLIGVEGGNATRIGRFANYLRNLLPSNDPVVMEMASKAIGRLAMAGDTFTAEYVEFEVKRALEWLGADRNEGRRHAAVLVLRELAISVPTFFFQQVQPFFDNIFVAVWDPKQAIREGAVAALRACLILTTQREPKEMQKPQWYRHTFEEAEKGFDETLAKEKGMNRDDRIHGALLILNELVRISSMEGERLREEMEEITQQQLVHDKYCKDLMGFGTKPRHITPFTSFQAVQPQQSNALVGLLGYSSHQGLMGFGTSPSPAKSTLVESRCCRDLMEEKFDQVCQWVLKCRNSKNSLIQMTILNLLPRLAAFRPSAFTDTQYLQDTMNHVLSCVKKEKERTAAFQALGLLSVAVRSEFKVYLPRVLDIIRAALPPKDFAHKRQKAMQVDATVFTCISMLARAMGPGIQQDIKELLEPMLAVGLSPALTAVLYDLSRQIPQLKKDIQDGLLKMLSLVLMHKPLRHPGMPKGLAHQLASPGLTTLPEASDVGSITLALRTLGSFEFEGHSLTQFVRHCADHFLNSEHKEIRMEAARTCSRLLTPSIHLISGHAHVVSQTAVQVVADVLSKLLVVGITDPDPDIRYCVLASLDERFDAHLAQAENLQALFVALNDQVFEIRELAICTVGRLSSMNPAFVMPFLRKMLIQILTELEHSGIGRIKEQSARMLGHLVSNAPRLIRPYMEPILKALILKLKDPDPDPNPGVINNVLATIGELAQVSGLEMRKWVDELFIIIMDMLQDSSLLAKRQVALWTLGQLVASTGYVVEPYRKYPTLLEVLLNFLKTEQNQGTRREAIRVLGLLGALDPYKHKVNIGMIDQSRDASAVSLSESKSSQDSSDYSTSEMLVNMGNLPLDEFYPAVSMVALMRIFRDQSLSHHHTMVVQAITFIFKSLGLKCVQFLPQVMPTFLNVIRVCDGAIREFLFQQLGMLVSFVKSHIRPYMDEIVTLMREFWVMNTSIQSTIILLIEQIVVALGGEFKLYLPQLIPHMLRVFMHDNSPGRIVSIKLLAAIQLFGANLDDYLHLLLPPIVKLFDAPEAPLPSRKAALETVDRLTESLDFTDYASRIIHPIVRTLDQSPELRSTAMDTLSSLVFQLGKKYQIFIPMVNKVLVRHRINHQRYDVLICRIVKGYTLADEEEDPLIYQHRMLRSGQGDALASGPVETGPMKKLHVSTINLQKAWGAARRVSKDDWLEWLRRLSLELLKDSSSPSLRSCWALAQAYNPMARDLFNAAFVSCWSELNEDQQDELIRSIELALTSQDIAEVTQTLLNLAEFMEHSDKGPLPLRDDNGIVLLGERAAKCRAYAKALHYKELEFQKGPTPAILESLISINNKLQQPEAAAGVLEYAMKHFGELEIQATWYEKLHEWEDALVAYDKKMDTNKDDPELMLGRMRCLEALGEWGQLHQQCCEKWTLVNDETQAKMARMAAAAAWGLGQWDSMEEYTCMIPRDTHDGAFYRAVLALHQDLFSLAQQCIDKARDLLDAELTAMAGESYSRAYGAMVSCHMLSELEEVIQYKLVPERREIIRQIWWERLQGCQRIVEDWQKILMVRSLVVSPHEDMRTWLKYASLCGKSGRLALAHKTLVLLLGVDPSRQLDHPLPTVHPQVTYAYMKNMWKSARKIDAFQHMQHFVQTMQQQAQHAIATEDQQHKQELHKLMARCFLKLGEWQLNLQGINESTIPKVLQYYSAATEHDRSWYKAWHAWAVMNFEAVLHYKHQNQARDEKKKLRHASGANITNATTAATTAATATTTASTEGSNSESEAESTENSPTPSPLQKKVTEDLSKTLLMYTVPAVQGFFRSISLSRGNNLQDTLRVLTLWFDYGHWPDVNEALVEGVKAIQIDTWLQVIPQLIARIDTPRPLVGRLIHQLLTDIGRYHPQALIYPLTVASKSTTTARHNAANKILKNMCEHSNTLVQQAMMVSEELIRVAILWHEMWHEGLEEASRLYFGERNVKGMFEVLEPLHAMMERGPQTLKETSFNQAYGRDLMEAQEWCRKYMKSGNVKDLTQAWDLYYHVFRRISKQLPQLTSLELQYVSPKLLMCRDLELAVPGTYDPNQPIIRIQSIAPSLQVITSKQRPRKLTLMGSNGHEFVFLLKGHEDLRQDERVMQLFGLVNTLLANDPTSLRKNLSIQRYAVIPLSTNSGLIGWVPHCDTLHALIRDYREKKKILLNIEHRIMLRMAPDYDHLTLMQKVEVFEHAVNNTAGDDLAKLLWLKSPSSEVWFDRRTNYTRSLAVMSMVGYILGLGDRHPSNLMLDRLSGKILHIDFGDCFEVAMTREKFPEKIPFRLTRMLTNAMEVTGLDGNYRITCHTVMEVLREHKDSVMAVLEAFVYDPLLNWRLMDTNTKGNKRSRTRTDSYSAGQSVEILDGVELGEPAHKKTGTTVPESIHSFIGDGLVKPEALNKKAIQIINRVRDKLTGRDFSHDDTLDVPTQVELLIKQATSHENLCQCYIGWCPFW
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Serine/threonine protein kinase which is a central regulator of cellular metabolism, growth and survival in response to hormones, growth factors, nutrients, energy and stress signals. MTOR directly or indirectly regulates the phosphorylation of at least 800 proteins. Functions as part of 2 structurally and functionally distinct signaling complexes mTORC1 and mTORC2 (mTOR complex 1 and 2). Activated mTORC1 up-regulates protein synthesis by phosphorylating key regulators of mRNA translation and ribosome synthesis. This includes phosphorylation of EIF4EBP1 and release of its inhibition toward the elongation initiation factor 4E (eiF4E) (By similarity). Moreover, phosphorylates and activates RPS6KB1 and RPS6KB2 that promote protein synthesis by modulating the activity of their downstream targets including ribosomal protein S6, eukaryotic translation initiation factor EIF4B, and the inhibitor of translation initiation PDCD4. Stimulates the pyrimidine biosynthesis pathway, both by acute regulation through RPS6KB1-mediated phosphorylation of the biosynthetic enzyme CAD, and delayed regulation, through transcriptional enhancement of the pentose phosphate pathway which produces 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP), an allosteric activator of CAD at a later step in synthesis, this function is dependent on the mTORC1 complex. Regulates ribosome synthesis by activating RNA polymerase III-dependent transcription through phosphorylation and inhibition of MAF1 an RNA polymerase III-repressor. In parallel to protein synthesis, also regulates lipid synthesis through SREBF1/SREBP1 and LPIN1 (By similarity). To maintain energy homeostasis mTORC1 may also regulate mitochondrial biogenesis through regulation of PPARGC1A (By similarity). mTORC1 also negatively regulates autophagy through phosphorylation of ULK1 (By similarity). Under nutrient sufficiency, phosphorylates ULK1 at 'Ser-758', disrupting the interaction with AMPK and preventing activation of ULK1 (By similarity). Also prevents autophagy through phosphorylation of the autophagy inhibitor DAP. Also prevents autophagy by phosphorylating RUBCNL/Pacer under nutrient-rich conditions. mTORC1 exerts a feedback control on upstream growth factor signaling that includes phosphorylation and activation of GRB10 a INSR-dependent signaling suppressor. Among other potential targets mTORC1 may phosphorylate CLIP1 and regulate microtubules. As part of the mTORC2 complex MTOR may regulate other cellular processes including survival and organization of the cytoskeleton. Plays a critical role in the phosphorylation at 'Ser-473' of AKT1, a pro-survival effector of phosphoinositide 3-kinase, facilitating its activation by PDK1. mTORC2 may regulate the actin cytoskeleton, through phosphorylation of PRKCA, PXN and activation of the Rho-type guanine nucleotide exchange factors RHOA and RAC1A or RAC1B. mTORC2 also regulates the phosphorylation of SGK1 at 'Ser-422'. Regulates osteoclastogenesis by adjusting the expression of CEBPB isoforms (By similarity). Plays an important regulatory role in the circadian clock function; regulates period length and rhythm amplitude of the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) and liver clocks (By similarity). Phosphorylates SQSTM1, promoting interaction between SQSTM1 and KEAP1 and subsequent inactivation of the BCR(KEAP1) complex (By similarity).
Autophosphorylates when part of mTORC1 or mTORC2. Phosphorylation at Ser-1261, Ser-2159 and Thr-2164 promotes autophosphorylation. Phosphorylation in the kinase domain modulates the interactions of MTOR with RPTOR and PRAS40 and leads to increased intrinsic mTORC1 kinase activity. Phosphorylation at Thr-2173 in the ATP-binding region by AKT1 strongly reduces kinase activity.
Endoplasmic reticulum membrane>Peripheral membrane protein>Cytoplasmic side. Golgi apparatus membrane>Peripheral membrane protein>Cytoplasmic side. Mitochondrion outer membrane>Peripheral membrane protein>Cytoplasmic side. Lysosome. Cytoplasm. Nucleus>PML body. Microsome membrane. Lysosome membrane.
Note: Shuttles between cytoplasm and nucleus. Accumulates in the nucleus in response to hypoxia (By similarity). Targeting to lysosomes depends on amino acid availability and RRAGA and RRAGB (PubMed:18497260, PubMed:20381137). Lysosome targeting also depends on interaction with MEAK7. Translocates to the lysosome membrane in the presence of TM4SF5 (PubMed:30956113).
Expressed in numerous tissues, with highest levels in testis.
The kinase domain (PI3K/PI4K) is intrinsically active but has a highly restricted catalytic center.
The FAT domain forms three discontinuous subdomains of alpha-helical TPR repeats plus a single subdomain of HEAT repeats. The four domains pack sequentially to form a C-shaped a-solenoid that clamps onto the kinase domain (PubMed:23636326).
Belongs to the PI3/PI4-kinase family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Autophagy - other. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Autophagy - animal. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cellular senescence. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > ErbB signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > HIF-1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Phospholipase D signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > mTOR signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > AMPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Apelin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Jak-STAT signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance.
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Endocrine resistance.
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Type II diabetes mellitus.
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Insulin resistance.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > MicroRNAs in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Colorectal cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Pancreatic cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Glioma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Acute myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Central carbon metabolism in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Choline metabolism in cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th17 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Insulin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Thyroid hormone signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Adipocytokine signaling pathway.
References
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.