Phospho-TGFBR1 (Ser165) Antibody - #AF8080
| Product: | Phospho-TGFBR1 (Ser165) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF8080 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-TGFBR1 (Ser165) |
| Application: | WB |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 56 kDa.; 56kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P36897 |
| RRID: | AB_2840143 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF8080, RRID:AB_2840143.
Fold/Unfold
AAT 5; AAT5; Activin A receptor type II like kinase 53kDa; Activin A receptor type II like kinase, 53kD; Activin A receptor type II like protein kinase of 53kD; activin A receptor type II-like kinase, 53kDa; activin A receptor type II-like protein kinase of 53kD; Activin receptor like kinase 5; Activin receptor-like kinase 5; ACVRLK 4; ACVRLK4; ALK 5; ALK-5; ALK5; LDS1A; LDS2A; MSSE; Serine/threonine protein kinase receptor R4; Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R4; SKR 4; SKR4; TbetaR I; TbetaR-I; TGF beta receptor type 1; TGF beta receptor type I; TGF beta type I receptor; TGF-beta receptor type I; TGF-beta receptor type-1; TGF-beta type I receptor; TGFBR 1; TGFBR1; TGFBR1 protein; TGFR 1; TGFR-1; TGFR1; TGFR1_HUMAN; Transforming growth factor beta receptor 1; Transforming growth factor beta receptor I (activin A receptor type II like kinase, 53kD); Transforming growth factor beta receptor I; transforming growth factor, beta receptor 1; transforming growth factor, beta receptor I (activin A receptor type II-like kinase, 53kD); Transforming growth factor-beta receptor type I;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human TGF β Receptor I around the phosphorylation site of Ser165.
Found in all tissues examined, most abundant in placenta and least abundant in brain and heart. Expressed in a variety of cancer cell lines (PubMed:25893292).
- P36897 TGFR1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MEAAVAAPRPRLLLLVLAAAAAAAAALLPGATALQCFCHLCTKDNFTCVTDGLCFVSVTETTDKVIHNSMCIAEIDLIPRDRPFVCAPSSKTGSVTTTYCCNQDHCNKIELPTTVKSSPGLGPVELAAVIAGPVCFVCISLMLMVYICHNRTVIHHRVPNEEDPSLDRPFISEGTTLKDLIYDMTTSGSGSGLPLLVQRTIARTIVLQESIGKGRFGEVWRGKWRGEEVAVKIFSSREERSWFREAEIYQTVMLRHENILGFIAADNKDNGTWTQLWLVSDYHEHGSLFDYLNRYTVTVEGMIKLALSTASGLAHLHMEIVGTQGKPAIAHRDLKSKNILVKKNGTCCIADLGLAVRHDSATDTIDIAPNHRVGTKRYMAPEVLDDSINMKHFESFKRADIYAMGLVFWEIARRCSIGGIHEDYQLPYYDLVPSDPSVEEMRKVVCEQKLRPNIPNRWQSCEALRVMAKIMRECWYANGAARLTALRIKKTLSQLSQQEGIKM
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Transmembrane serine/threonine kinase forming with the TGF-beta type II serine/threonine kinase receptor, TGFBR2, the non-promiscuous receptor for the TGF-beta cytokines TGFB1, TGFB2 and TGFB3. Transduces the TGFB1, TGFB2 and TGFB3 signal from the cell surface to the cytoplasm and is thus regulating a plethora of physiological and pathological processes including cell cycle arrest in epithelial and hematopoietic cells, control of mesenchymal cell proliferation and differentiation, wound healing, extracellular matrix production, immunosuppression and carcinogenesis. The formation of the receptor complex composed of 2 TGFBR1 and 2 TGFBR2 molecules symmetrically bound to the cytokine dimer results in the phosphorylation and the activation of TGFBR1 by the constitutively active TGFBR2. Activated TGFBR1 phosphorylates SMAD2 which dissociates from the receptor and interacts with SMAD4. The SMAD2-SMAD4 complex is subsequently translocated to the nucleus where it modulates the transcription of the TGF-beta-regulated genes. This constitutes the canonical SMAD-dependent TGF-beta signaling cascade. Also involved in non-canonical, SMAD-independent TGF-beta signaling pathways. For instance, TGFBR1 induces TRAF6 autoubiquitination which in turn results in MAP3K7 ubiquitination and activation to trigger apoptosis. Also regulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition through a SMAD-independent signaling pathway through PARD6A phosphorylation and activation.
Phosphorylated at basal levels in the absence of ligand. Activated upon phosphorylation by TGFBR2, mainly in the GS domain. Phosphorylation in the GS domain abrogates FKBP1A-binding.
N-Glycosylated.
Ubiquitinated; undergoes ubiquitination catalyzed by several E3 ubiquitin ligases including SMURF1, SMURF2 and NEDD4L2. Results in the proteasomal and/or lysosomal degradation of the receptor thereby negatively regulating its activity. Deubiquitinated by USP15, leading to stabilization of the protein and enhanced TGF-beta signal. Its ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation is negatively regulated by SDCBP.
Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell junction>Tight junction. Cell surface. Membrane raft.
Found in all tissues examined, most abundant in placenta and least abundant in brain and heart. Expressed in a variety of cancer cell lines.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. TKL Ser/Thr protein kinase family. TGFB receptor subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Endocytosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cellular senescence. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Adherens junction. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > FoxO signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TGF-beta signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Apelin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Colorectal cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Pancreatic cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Chronic myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Development > Osteoclast differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th17 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Relaxin signaling pathway.
References
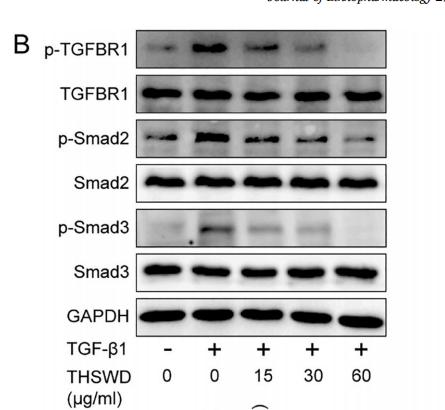
Application: WB Species: human Sample: HK-2 cells
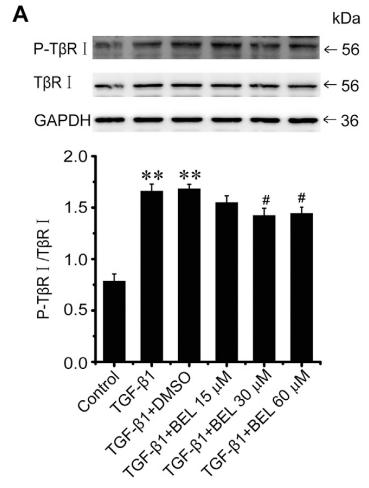
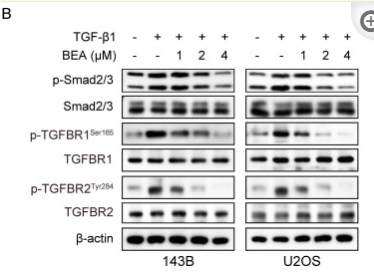
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: OS cells
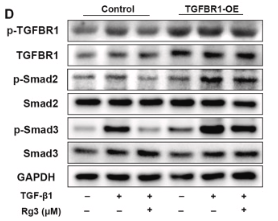
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: CFs
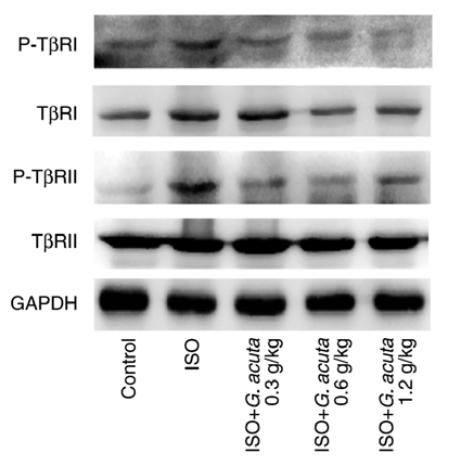
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: heart
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample:
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: CFs
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: heart and primary cardiac fibroblasts
Application: WB Species: mice Sample: cardiac fibroblasts
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.