APC Antibody - #AF0547
| Product: | APC Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF0547 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to APC |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse |
| Mol.Wt.: | 310kDa; 312kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P25054 |
| RRID: | AB_2834125 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF0547, RRID:AB_2834125.
Fold/Unfold
Adenomatous Polyposis Coli; Adenomatous polyposis coli protein; Apc; APC_HUMAN; CC1; Deleted in polyposis 2.5; DP2; DP2.5; DP3; FAP; FPC; GS; Protein APC;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human APC , corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Expressed in a variety of tissues: brain, small intestine, colon, thymus, skeletal muscle, heart, prostate, lung, spleen, ovary, testis kidney, placenta, blood and liver (PubMed:21643010, PubMed:27217144). Isoform 1A: Very strongly expressed in brain but has relatively low expression levels in other tissues (PubMed:19527921, PubMed:21643010, PubMed:27217144). Isoform 1B: Predominant form in all tissues except for brain, including gastric mucosa and blood (PubMed:19527921, PubMed:21643010, PubMed:27217144).
- P25054 APC_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAAASYDQLLKQVEALKMENSNLRQELEDNSNHLTKLETEASNMKEVLKQLQGSIEDEAMASSGQIDLLERLKELNLDSSNFPGVKLRSKMSLRSYGSREGSVSSRSGECSPVPMGSFPRRGFVNGSRESTGYLEELEKERSLLLADLDKEEKEKDWYYAQLQNLTKRIDSLPLTENFSLQTDMTRRQLEYEARQIRVAMEEQLGTCQDMEKRAQRRIARIQQIEKDILRIRQLLQSQATEAERSSQNKHETGSHDAERQNEGQGVGEINMATSGNGQGSTTRMDHETASVLSSSSTHSAPRRLTSHLGTKVEMVYSLLSMLGTHDKDDMSRTLLAMSSSQDSCISMRQSGCLPLLIQLLHGNDKDSVLLGNSRGSKEARARASAALHNIIHSQPDDKRGRREIRVLHLLEQIRAYCETCWEWQEAHEPGMDQDKNPMPAPVEHQICPAVCVLMKLSFDEEHRHAMNELGGLQAIAELLQVDCEMYGLTNDHYSITLRRYAGMALTNLTFGDVANKATLCSMKGCMRALVAQLKSESEDLQQVIASVLRNLSWRADVNSKKTLREVGSVKALMECALEVKKESTLKSVLSALWNLSAHCTENKADICAVDGALAFLVGTLTYRSQTNTLAIIESGGGILRNVSSLIATNEDHRQILRENNCLQTLLQHLKSHSLTIVSNACGTLWNLSARNPKDQEALWDMGAVSMLKNLIHSKHKMIAMGSAAALRNLMANRPAKYKDANIMSPGSSLPSLHVRKQKALEAELDAQHLSETFDNIDNLSPKASHRSKQRHKQSLYGDYVFDTNRHDDNRSDNFNTGNMTVLSPYLNTTVLPSSSSSRGSLDSSRSEKDRSLERERGIGLGNYHPATENPGTSSKRGLQISTTAAQIAKVMEEVSAIHTSQEDRSSGSTTELHCVTDERNALRRSSAAHTHSNTYNFTKSENSNRTCSMPYAKLEYKRSSNDSLNSVSSSDGYGKRGQMKPSIESYSEDDESKFCSYGQYPADLAHKIHSANHMDDNDGELDTPINYSLKYSDEQLNSGRQSPSQNERWARPKHIIEDEIKQSEQRQSRNQSTTYPVYTESTDDKHLKFQPHFGQQECVSPYRSRGANGSETNRVGSNHGINQNVSQSLCQEDDYEDDKPTNYSERYSEEEQHEEEERPTNYSIKYNEEKRHVDQPIDYSLKYATDIPSSQKQSFSFSKSSSGQSSKTEHMSSSSENTSTPSSNAKRQNQLHPSSAQSRSGQPQKAATCKVSSINQETIQTYCVEDTPICFSRCSSLSSLSSAEDEIGCNQTTQEADSANTLQIAEIKEKIGTRSAEDPVSEVPAVSQHPRTKSSRLQGSSLSSESARHKAVEFSSGAKSPSKSGAQTPKSPPEHYVQETPLMFSRCTSVSSLDSFESRSIASSVQSEPCSGMVSGIISPSDLPDSPGQTMPPSRSKTPPPPPQTAQTKREVPKNKAPTAEKRESGPKQAAVNAAVQRVQVLPDADTLLHFATESTPDGFSCSSSLSALSLDEPFIQKDVELRIMPPVQENDNGNETESEQPKESNENQEKEAEKTIDSEKDLLDDSDDDDIEILEECIISAMPTKSSRKAKKPAQTASKLPPPVARKPSQLPVYKLLPSQNRLQPQKHVSFTPGDDMPRVYCVEGTPINFSTATSLSDLTIESPPNELAAGEGVRGGAQSGEFEKRDTIPTEGRSTDEAQGGKTSSVTIPELDDNKAEEGDILAECINSAMPKGKSHKPFRVKKIMDQVQQASASSSAPNKNQLDGKKKKPTSPVKPIPQNTEYRTRVRKNADSKNNLNAERVFSDNKDSKKQNLKNNSKVFNDKLPNNEDRVRGSFAFDSPHHYTPIEGTPYCFSRNDSLSSLDFDDDDVDLSREKAELRKAKENKESEAKVTSHTELTSNQQSANKTQAIAKQPINRGQPKPILQKQSTFPQSSKDIPDRGAATDEKLQNFAIENTPVCFSHNSSLSSLSDIDQENNNKENEPIKETEPPDSQGEPSKPQASGYAPKSFHVEDTPVCFSRNSSLSSLSIDSEDDLLQECISSAMPKKKKPSRLKGDNEKHSPRNMGGILGEDLTLDLKDIQRPDSEHGLSPDSENFDWKAIQEGANSIVSSLHQAAAAACLSRQASSDSDSILSLKSGISLGSPFHLTPDQEEKPFTSNKGPRILKPGEKSTLETKKIESESKGIKGGKKVYKSLITGKVRSNSEISGQMKQPLQANMPSISRGRTMIHIPGVRNSSSSTSPVSKKGPPLKTPASKSPSEGQTATTSPRGAKPSVKSELSPVARQTSQIGGSSKAPSRSGSRDSTPSRPAQQPLSRPIQSPGRNSISPGRNGISPPNKLSQLPRTSSPSTASTKSSGSGKMSYTSPGRQMSQQNLTKQTGLSKNASSIPRSESASKGLNQMNNGNGANKKVELSRMSSTKSSGSESDRSERPVLVRQSTFIKEAPSPTLRRKLEESASFESLSPSSRPASPTRSQAQTPVLSPSLPDMSLSTHSSVQAGGWRKLPPNLSPTIEYNDGRPAKRHDIARSHSESPSRLPINRSGTWKREHSKHSSSLPRVSTWRRTGSSSSILSASSESSEKAKSEDEKHVNSISGTKQSKENQVSAKGTWRKIKENEFSPTNSTSQTVSSGATNGAESKTLIYQMAPAVSKTEDVWVRIEDCPINNPRSGRSPTGNTPPVIDSVSEKANPNIKDSKDNQAKQNVGNGSVPMRTVGLENRLNSFIQVDAPDQKGTEIKPGQNNPVPVSETNESSIVERTPFSSSSSSKHSSPSGTVAARVTPFNYNPSPRKSSADSTSARPSQIPTPVNNNTKKRDSKTDSTESSGTQSPKRHSGSYLVTSV
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Tumor suppressor. Promotes rapid degradation of CTNNB1 and participates in Wnt signaling as a negative regulator. APC activity is correlated with its phosphorylation state. Activates the GEF activity of SPATA13 and ARHGEF4. Plays a role in hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-induced cell migration. Required for MMP9 up-regulation via the JNK signaling pathway in colorectal tumor cells. Acts as a mediator of ERBB2-dependent stabilization of microtubules at the cell cortex. It is required for the localization of MACF1 to the cell membrane and this localization of MACF1 is critical for its function in microtubule stabilization.
Phosphorylated by GSK3B.
Ubiquitinated, leading to its degradation by the proteasome. Ubiquitination is facilitated by Axin. Deubiquitinated by ZRANB1/TRABID.
Cell junction>Adherens junction. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton. Cell projection>Lamellipodium. Cell projection>Ruffle membrane. Cytoplasm. Cell membrane.
Note: Associated with the microtubule network at the growing distal tip of microtubules (PubMed:19632184). Accumulates in the lamellipodium and ruffle membrane in response to hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) treatment (PubMed:19151759). The MEMO1-RHOA-DIAPH1 signaling pathway controls localization of the phosphorylated form to the cell membrane (PubMed:20937854).
Expressed in a variety of tissues: brain, small intestine, colon, thymus, skeletal muscle, heart, prostate, lung, spleen, ovary, testis kidney, placenta, blood and liver. Isoform 1A: Very strongly expressed in brain but has relatively low expression levels in other tissues. Isoform 1B: Predominant form in all tissues except for brain, including gastric mucosa and blood.
The microtubule tip localization signal (MtLS) motif; mediates interaction with MAPRE1 and targeting to the growing microtubule plus ends.
Belongs to the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell motility > Regulation of actin cytoskeleton. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Wnt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > MicroRNAs in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Colorectal cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Endometrial cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Basal cell carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
References
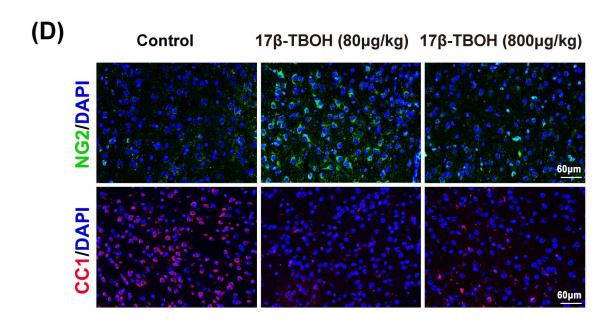
Application: IF/ICC Species: mice Sample: medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC)
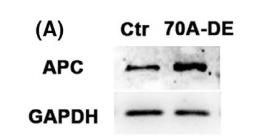
Application: WB Species: mice Sample: Oocytes
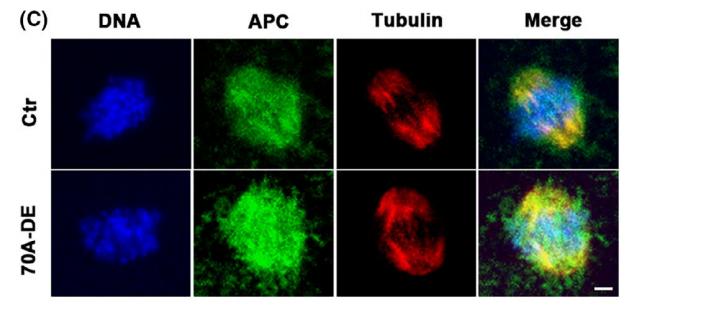
Application: IF/ICC Species: mice Sample: Oocytes
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.