CACNA1C Antibody - #DF2267
| Product: | CACNA1C Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF2267 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to CACNA1C |
| Application: | WB |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 249 kDa; 249kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q13936 |
| RRID: | AB_2839496 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF2267, RRID:AB_2839496.
Fold/Unfold
alpha-1 polypeptide; cardiac muscle; isoform 1; L type; CAC1C_HUMAN; CACH 2; CACH2; CACN 2; CACN2; CACNA1C; CACNL1A1; Calcium channel; Calcium channel cardic dihydropyridine sensitive alpha 1 subunit; Calcium channel L type alpha 1 polypeptide isoform 1 cardiac muscle; Calcium channel voltage dependent L type alpha 1C subunit; CaV1.2; CCHL1A1; DHPR alpha 1; DHPR alpha 1 subunit; LQT8; TS; Voltage dependent L type calcium channel alpha 1C subunit; Voltage dependent L type calcium channel subunit alpha 1C; Voltage gated calcium channel alpha subunit Cav1.2; Voltage gated calcium channel subunit alpha Cav1.2; Voltage gated L type calcium channel Cav1.2 alpha 1 subunit, splice variant 10*; Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1C; Voltage-gated calcium channel subunit alpha Cav1.2;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human CACNA1C, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Detected throughout the brain, including hippocampus, cerebellum and amygdala, throughout the heart and vascular system, including ductus arteriosus, in urinary bladder, and in retina and sclera in the eye (PubMed:15454078). Expressed in brain, heart, jejunum, ovary, pancreatic beta-cells and vascular smooth muscle. Overall expression is reduced in atherosclerotic vascular smooth muscle.
- Q13936 CAC1C_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MVNENTRMYIPEENHQGSNYGSPRPAHANMNANAAAGLAPEHIPTPGAALSWQAAIDAARQAKLMGSAGNATISTVSSTQRKRQQYGKPKKQGSTTATRPPRALLCLTLKNPIRRACISIVEWKPFEIIILLTIFANCVALAIYIPFPEDDSNATNSNLERVEYLFLIIFTVEAFLKVIAYGLLFHPNAYLRNGWNLLDFIIVVVGLFSAILEQATKADGANALGGKGAGFDVKALRAFRVLRPLRLVSGVPSLQVVLNSIIKAMVPLLHIALLVLFVIIIYAIIGLELFMGKMHKTCYNQEGIADVPAEDDPSPCALETGHGRQCQNGTVCKPGWDGPKHGITNFDNFAFAMLTVFQCITMEGWTDVLYWVNDAVGRDWPWIYFVTLIIIGSFFVLNLVLGVLSGEFSKEREKAKARGDFQKLREKQQLEEDLKGYLDWITQAEDIDPENEDEGMDEEKPRNMSMPTSETESVNTENVAGGDIEGENCGARLAHRISKSKFSRYWRRWNRFCRRKCRAAVKSNVFYWLVIFLVFLNTLTIASEHYNQPNWLTEVQDTANKALLALFTAEMLLKMYSLGLQAYFVSLFNRFDCFVVCGGILETILVETKIMSPLGISVLRCVRLLRIFKITRYWNSLSNLVASLLNSVRSIASLLLLLFLFIIIFSLLGMQLFGGKFNFDEMQTRRSTFDNFPQSLLTVFQILTGEDWNSVMYDGIMAYGGPSFPGMLVCIYFIILFICGNYILLNVFLAIAVDNLADAESLTSAQKEEEEEKERKKLARTASPEKKQELVEKPAVGESKEEKIELKSITADGESPPATKINMDDLQPNENEDKSPYPNPETTGEEDEEEPEMPVGPRPRPLSELHLKEKAVPMPEASAFFIFSSNNRFRLQCHRIVNDTIFTNLILFFILLSSISLAAEDPVQHTSFRNHILFYFDIVFTTIFTIEIALKILGNADYVFTSIFTLEIILKMTAYGAFLHKGSFCRNYFNILDLLVVSVSLISFGIQSSAINVVKILRVLRVLRPLRAINRAKGLKHVVQCVFVAIRTIGNIVIVTTLLQFMFACIGVQLFKGKLYTCSDSSKQTEAECKGNYITYKDGEVDHPIIQPRSWENSKFDFDNVLAAMMALFTVSTFEGWPELLYRSIDSHTEDKGPIYNYRVEISIFFIIYIIIIAFFMMNIFVGFVIVTFQEQGEQEYKNCELDKNQRQCVEYALKARPLRRYIPKNQHQYKVWYVVNSTYFEYLMFVLILLNTICLAMQHYGQSCLFKIAMNILNMLFTGLFTVEMILKLIAFKPKGYFSDPWNVFDFLIVIGSIIDVILSETNHYFCDAWNTFDALIVVGSIVDIAITEVNPAEHTQCSPSMNAEENSRISITFFRLFRVMRLVKLLSRGEGIRTLLWTFIKSFQALPYVALLIVMLFFIYAVIGMQVFGKIALNDTTEINRNNNFQTFPQAVLLLFRCATGEAWQDIMLACMPGKKCAPESEPSNSTEGETPCGSSFAVFYFISFYMLCAFLIINLFVAVIMDNFDYLTRDWSILGPHHLDEFKRIWAEYDPEAKGRIKHLDVVTLLRRIQPPLGFGKLCPHRVACKRLVSMNMPLNSDGTVMFNATLFALVRTALRIKTEGNLEQANEELRAIIKKIWKRTSMKLLDQVVPPAGDDEVTVGKFYATFLIQEYFRKFKKRKEQGLVGKPSQRNALSLQAGLRTLHDIGPEIRRAISGDLTAEEELDKAMKEAVSAASEDDIFRRAGGLFGNHVSYYQSDGRSAFPQTFTTQRPLHINKAGSSQGDTESPSHEKLVDSTFTPSSYSSTGSNANINNANNTALGRLPRPAGYPSTVSTVEGHGPPLSPAIRVQEVAWKLSSNRERHVPMCEDLELRRDSGSAGTQAHCLLLRKANPSRCHSRESQAAMAGQEETSQDETYEVKMNHDTEACSEPSLLSTEMLSYQDDENRQLTLPEEDKRDIRQSPKRGFLRSASLGRRASFHLECLKRQKDRGGDISQKTVLPLHLVHHQALAVAGLSPLLQRSHSPASFPRPFATPPATPGSRGWPPQPVPTLRLEGVESSEKLNSSFPSIHCGSWAETTPGGGGSSAARRVRPVSLMVPSQAGAPGRQFHGSASSLVEAVLISEGLGQFAQDPKFIEVTTQELADACDMTIEEMESAADNILSGGAPQSPNGALLPFVNCRDAGQDRAGGEEDAGCVRARGRPSEEELQDSRVYVSSL
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Pore-forming, alpha-1C subunit of the voltage-gated calcium channel that gives rise to L-type calcium currents. Mediates influx of calcium ions into the cytoplasm, and thereby triggers calcium release from the sarcoplasm (By similarity). Plays an important role in excitation-contraction coupling in the heart. Required for normal heart development and normal regulation of heart rhythm. Required for normal contraction of smooth muscle cells in blood vessels and in the intestine. Essential for normal blood pressure regulation via its role in the contraction of arterial smooth muscle cells. Long-lasting (L-type) calcium channels belong to the 'high-voltage activated' (HVA) group (Probable).
(Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Influenzavirus. May play a critical role in allowing virus entry when sialylated and expressed on lung tissues.
Phosphorylation by PKA activates the channel. Elevated levels of blood glucose lead to increased phosphorylation by PKA.
Cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell membrane>Sarcolemma>Multi-pass membrane protein. Perikaryon. Cell junction>Synapse>Postsynaptic density membrane. Cell projection>Dendrite. Cell membrane>Sarcolemma>T-tubule.
Note: Colocalizes with ryanodine receptors in distinct clusters at the junctional membrane, where the sarcolemma and the sarcoplasmic reticulum are in close contact. The interaction between RRAD and CACNB2 promotes the expression of CACNA1C at the cell membrane.
Detected throughout the brain, including hippocampus, cerebellum and amygdala, throughout the heart and vascular system, including ductus arteriosus, in urinary bladder, and in retina and sclera in the eye. Expressed in brain, heart, jejunum, ovary, pancreatic beta-cells and vascular smooth muscle. Overall expression is reduced in atherosclerotic vascular smooth muscle.
Each of the four internal repeats contains five hydrophobic transmembrane segments (S1, S2, S3, S5, S6) and one positively charged transmembrane segment (S4). S4 segments probably represent the voltage-sensor and are characterized by a series of positively charged amino acids at every third position.
Binding of intracellular calcium through the EF-hand motif inhibits the opening of the channel.
Belongs to the calcium channel alpha-1 subunit (TC 1.A.1.11) family. CACNA1C subfamily.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Calcium signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Type II diabetes mellitus.
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Alzheimer's disease.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Amphetamine addiction.
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM).
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC).
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM).
· Organismal Systems > Circulatory system > Cardiac muscle contraction. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Circulatory system > Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Circulatory system > Vascular smooth muscle contraction. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Environmental adaptation > Circadian entrainment.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Long-term potentiation.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Glutamatergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Cholinergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Serotonergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > GABAergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Dopaminergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Sensory system > Taste transduction.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Insulin secretion. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Oxytocin signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Renin secretion.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Aldosterone synthesis and secretion.
References
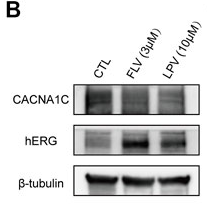
Application: WB Species: Human Sample:
Application: WB Species: rat Sample:
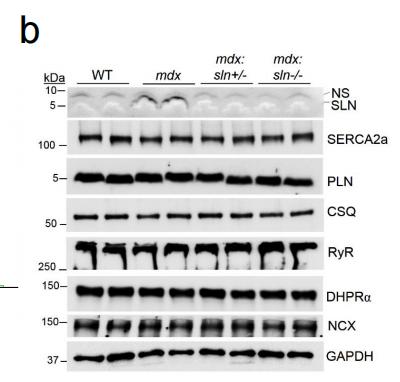
Application: WB Species: mice Sample: Heart
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.