MLKL Antibody - #DF7412
| Product: | MLKL Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF7412 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to MLKL |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Mol.Wt.: | 54kDa; 54kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q8NB16 |
| RRID: | AB_2839350 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF7412, RRID:AB_2839350.
Fold/Unfold
9130019I15Rik; FLJ34389; hMLKL; Mixed lineage kinase domain like; Mixed lineage kinase domain like protein; Mixed lineage kinase domain like pseudokinase; Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein; Mlkl; MLKL_HUMAN;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human MLKL, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- Q8NB16 MLKL_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MENLKHIITLGQVIHKRCEEMKYCKKQCRRLGHRVLGLIKPLEMLQDQGKRSVPSEKLTTAMNRFKAALEEANGEIEKFSNRSNICRFLTASQDKILFKDVNRKLSDVWKELSLLLQVEQRMPVSPISQGASWAQEDQQDADEDRRAFQMLRRDNEKIEASLRRLEINMKEIKETLRQYLPPKCMQEIPQEQIKEIKKEQLSGSPWILLRENEVSTLYKGEYHRAPVAIKVFKKLQAGSIAIVRQTFNKEIKTMKKFESPNILRIFGICIDETVTPPQFSIVMEYCELGTLRELLDREKDLTLGKRMVLVLGAARGLYRLHHSEAPELHGKIRSSNFLVTQGYQVKLAGFELRKTQTSMSLGTTREKTDRVKSTAYLSPQELEDVFYQYDVKSEIYSFGIVLWEIATGDIPFQGCNSEKIRKLVAVKRQQEPLGEDCPSELREIIDECRAHDPSVRPSVDEILKKLSTFSK
Research Backgrounds
Pseudokinase that plays a key role in TNF-induced necroptosis, a programmed cell death process. Activated following phosphorylation by RIPK3, leading to homotrimerization, localization to the plasma membrane and execution of programmed necrosis characterized by calcium influx and plasma membrane damage. Does not have protein kinase activity. Binds to highly phosphorylated inositol phosphates such as inositolhexakisphosphate (InsP6) which is essential for its necroptotic function.
Phosphorylation by RIPK3 induces a conformational switch that is required for necroptosis. It also induces homotrimerization and localization to the plasma membrane.
Cytoplasm. Cell membrane.
Note: Localizes to the cytoplasm and translocates to the plasma membrane on necroptosis induction.
The protein kinase domain is catalytically inactive but contains an unusual pseudoactive site with an interaction between Lys-230 and Gln-356 residues. Upon phosphorylation by RIPK3, undergoes an active conformation (By similarity).
The coiled coil region 2 is responsible for homotrimerization.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Necroptosis. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TNF signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
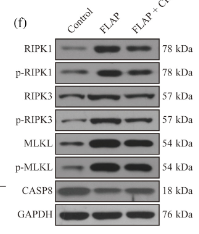
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: BLCA cells
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: cardiomyocytes
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.