VEGFC Antibody - #DF7011
| Product: | VEGFC Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF7011 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to VEGFC |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 46kDa; 47kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P49767 |
| RRID: | AB_2838967 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF7011, RRID:AB_2838967.
Fold/Unfold
Flt 4L; Flt4 ligand; FLT4 ligand DHM; Flt4-L; Flt4L; Vascular endothelial growth factor C; Vascular endothelial growth factor related protein; Vascular endothelial growth factor-related protein; VEGF C; VEGF-C; Vegfc; VEGFC_HUMAN; VRP;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human VEGFC, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Spleen, lymph node, thymus, appendix, bone marrow, heart, placenta, ovary, skeletal muscle, prostate, testis, colon and small intestine and fetal liver, lung and kidney, but not in peripheral blood lymphocyte.
- P49767 VEGFC_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MHLLGFFSVACSLLAAALLPGPREAPAAAAAFESGLDLSDAEPDAGEATAYASKDLEEQLRSVSSVDELMTVLYPEYWKMYKCQLRKGGWQHNREQANLNSRTEETIKFAAAHYNTEILKSIDNEWRKTQCMPREVCIDVGKEFGVATNTFFKPPCVSVYRCGGCCNSEGLQCMNTSTSYLSKTLFEITVPLSQGPKPVTISFANHTSCRCMSKLDVYRQVHSIIRRSLPATLPQCQAANKTCPTNYMWNNHICRCLAQEDFMFSSDAGDDSTDGFHDICGPNKELDEETCQCVCRAGLRPASCGPHKELDRNSCQCVCKNKLFPSQCGANREFDENTCQCVCKRTCPRNQPLNPGKCACECTESPQKCLLKGKKFHHQTCSCYRRPCTNRQKACEPGFSYSEEVCRCVPSYWKRPQMS
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Growth factor active in angiogenesis, and endothelial cell growth, stimulating their proliferation and migration and also has effects on the permeability of blood vessels. May function in angiogenesis of the venous and lymphatic vascular systems during embryogenesis, and also in the maintenance of differentiated lymphatic endothelium in adults. Binds and activates KDR/VEGFR2 and FLT4/VEGFR3 receptors.
Undergoes a complex proteolytic maturation which generates a variety of processed secreted forms with increased activity toward VEGFR-3, but only the fully processed form could activate VEGFR-2. VEGF-C first form an antiparallel homodimer linked by disulfide bonds. Before secretion, a cleavage occurs between Arg-227 and Ser-228 producing a heterotetramer. The next extracellular step of the processing removes the N-terminal propeptide. Finally the mature VEGF-C is composed mostly of two VEGF homology domains (VHDs) bound by non-covalent interactions.
Secreted.
Spleen, lymph node, thymus, appendix, bone marrow, heart, placenta, ovary, skeletal muscle, prostate, testis, colon and small intestine and fetal liver, lung and kidney, but not in peripheral blood lymphocyte.
Belongs to the PDGF/VEGF growth factor family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Focal adhesion. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Ras signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Rap1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TNF signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Relaxin signaling pathway.
References
Application: WB Species: human Sample: SW480 and HCT116 cells
Application: IF/ICC Species: Human Sample: γδ T+ Cells
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: lung cancer
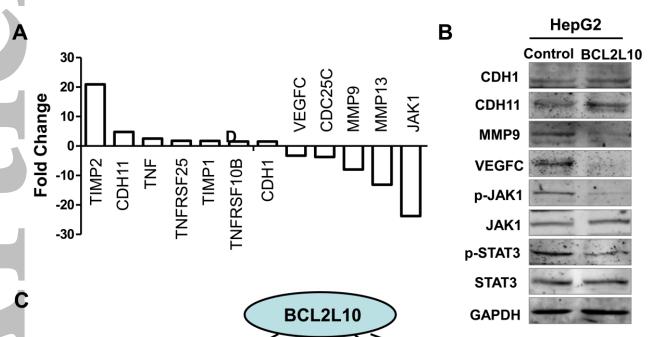
Application: WB Species: human Sample: HepG2
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.