ADIPOQ Antibody - #DF7000
| Product: | ADIPOQ Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF7000 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to ADIPOQ |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 28kDa; 26kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q15848 |
| RRID: | AB_2838956 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF7000, RRID:AB_2838956.
Fold/Unfold
30 kDa adipocyte complement related protein; 30 kDa adipocyte complement-related protein; ACDC; ACRP30; ADIPO_HUMAN; Adipocyte; Adipocyte C1q and collagen domain containing protein; Adipocyte complement related 30 kDa protein; Adipocyte complement related protein of 30 kDa; Adipocyte complement-related 30 kDa protein; adipocyte-specific secretory protein; Adiponectin; Adiponectin precursor; adiponectin, C1Q and collagen domain containing; Adipoq; Adipose most abundant gene transcript 1; Adipose most abundant gene transcript 1 protein; Adipose specific collagen like factor; ADIPQTL1; ADPN; APM 1; apM-1; APM1; C1q and collagen domain-containing protein; GBP28; Gelatin binding protein; Gelatin binding protein 28; Gelatin-binding protein;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human ADIPOQ, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
- Q15848 ADIPO_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MLLLGAVLLLLALPGHDQETTTQGPGVLLPLPKGACTGWMAGIPGHPGHNGAPGRDGRDGTPGEKGEKGDPGLIGPKGDIGETGVPGAEGPRGFPGIQGRKGEPGEGAYVYRSAFSVGLETYVTIPNMPIRFTKIFYNQQNHYDGSTGKFHCNIPGLYYFAYHITVYMKDVKVSLFKKDKAMLFTYDQYQENNVDQASGSVLLHLEVGDQVWLQVYGEGERNGLYADNDNDSTFTGFLLYHDTN
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Important adipokine involved in the control of fat metabolism and insulin sensitivity, with direct anti-diabetic, anti-atherogenic and anti-inflammatory activities. Stimulates AMPK phosphorylation and activation in the liver and the skeletal muscle, enhancing glucose utilization and fatty-acid combustion. Antagonizes TNF-alpha by negatively regulating its expression in various tissues such as liver and macrophages, and also by counteracting its effects. Inhibits endothelial NF-kappa-B signaling through a cAMP-dependent pathway. May play a role in cell growth, angiogenesis and tissue remodeling by binding and sequestering various growth factors with distinct binding affinities, depending on the type of complex, LMW, MMW or HMW.
HMW complexes are more extensively glycosylated than smaller oligomers. Hydroxylation and glycosylation of the lysine residues within the collagen-like domain of adiponectin seem to be critically involved in regulating the formation and/or secretion of HMW complexes and consequently contribute to the insulin-sensitizing activity of adiponectin in hepatocytes.
O-glycosylated. Not N-glycosylated. O-linked glycans on hydroxylysines consist of Glc-Gal disaccharides bound to the oxygen atom of post-translationally added hydroxyl groups. Sialylated to varying degrees depending on tissue. Thr-22 appears to be the major site of sialylation. Higher sialylation found in SGBS adipocytes than in HEK fibroblasts. Sialylation is not required neither for heterodimerization nor for secretion. Not sialylated on the glycosylated hydroxylysines. Desialylated forms are rapidly cleared from the circulation.
Succination of Cys-36 by the Krebs cycle intermediate fumarate, which leads to S-(2-succinyl)cysteine residues, inhibits polymerization and secretion of adiponectin. Adiponectin is a major target for succination in both adipocytes and adipose tissue of diabetic mammals. It was proposed that succination of proteins is a biomarker of mitochondrial stress and accumulation of Krebs cycle intermediates in adipose tissue in diabetes and that succination of adiponectin may contribute to the decrease in plasma adiponectin in diabetes.
Secreted.
Synthesized exclusively by adipocytes and secreted into plasma.
The C1q domain is commonly called the globular domain.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > AMPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Type II diabetes mellitus.
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > PPAR signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Adipocytokine signaling pathway.
References
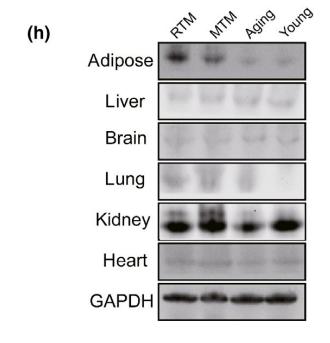
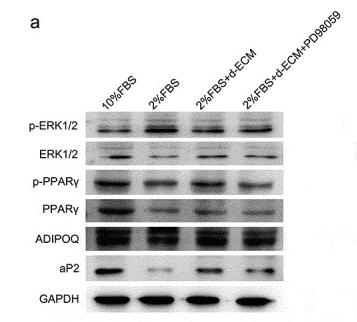
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: lung
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: ADSCs
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.