Wnt5a Antibody - #DF6856
| Product: | Wnt5a Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6856 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Wnt5a |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 42kDa; 42kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P41221 |
| RRID: | AB_2838815 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6856, RRID:AB_2838815.
Fold/Unfold
hWNT 5A; hWNT5A; Protein Wnt 5a; Protein Wnt-5a; Protein Wnt5a; Wingless type MMTV integration site family member 5A; Wnt 5a; WNT 5A protein; WNT 5A protein precursor; WNT5A; WNT5A protein precursor; WNT5A_HUMAN;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Wnt5a, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Expression is increased in differentiated thyroid carcinomas compared to normal thyroid tissue and anaplastic thyroid tumors where expression is low or undetectable. Expression is found in thyrocytes but not in stromal cells (at protein level) (PubMed:15735754). Detected in neonate heart and lung (PubMed:8288227).
- P41221 WNT5A_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MKKSIGILSPGVALGMAGSAMSSKFFLVALAIFFSFAQVVIEANSWWSLGMNNPVQMSEVYIIGAQPLCSQLAGLSQGQKKLCHLYQDHMQYIGEGAKTGIKECQYQFRHRRWNCSTVDNTSVFGRVMQIGSRETAFTYAVSAAGVVNAMSRACREGELSTCGCSRAARPKDLPRDWLWGGCGDNIDYGYRFAKEFVDARERERIHAKGSYESARILMNLHNNEAGRRTVYNLADVACKCHGVSGSCSLKTCWLQLADFRKVGDALKEKYDSAAAMRLNSRGKLVQVNSRFNSPTTQDLVYIDPSPDYCVRNESTGSLGTQGRLCNKTSEGMDGCELMCCGRGYDQFKTVQTERCHCKFHWCCYVKCKKCTEIVDQFVCK
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Ligand for members of the frizzled family of seven transmembrane receptors. Can activate or inhibit canonical Wnt signaling, depending on receptor context. In the presence of FZD4, activates beta-catenin signaling. In the presence of ROR2, inhibits the canonical Wnt pathway by promoting beta-catenin degradation through a GSK3-independent pathway which involves down-regulation of beta-catenin-induced reporter gene expression (By similarity). Suppression of the canonical pathway allows chondrogenesis to occur and inhibits tumor formation. Stimulates cell migration. Decreases proliferation, migration, invasiveness and clonogenicity of carcinoma cells and may act as a tumor suppressor. Mediates motility of melanoma cells. Required during embryogenesis for extension of the primary anterior-posterior axis and for outgrowth of limbs and the genital tubercle. Inhibits type II collagen expression in chondrocytes (By similarity).
Glycosylation is necessary for secretion but not for activity.
Palmitoleoylation is required for efficient binding to frizzled receptors. Depalmitoleoylation leads to Wnt signaling pathway inhibition.
Proteolytic processing by TIKI1 and TIKI2 promotes oxidation and formation of large disulfide-bond oligomers, leading to inactivation of WNT5A.
Secreted>Extracellular space>Extracellular matrix. Secreted.
Expression is increased in differentiated thyroid carcinomas compared to normal thyroid tissue and anaplastic thyroid tumors where expression is low or undetectable. Expression is found in thyrocytes but not in stromal cells (at protein level). Detected in neonate heart and lung.
Belongs to the Wnt family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > mTOR signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Wnt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Basal cell carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Development > Axon guidance. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Melanogenesis.
References
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: HT29 and HCT116 cells
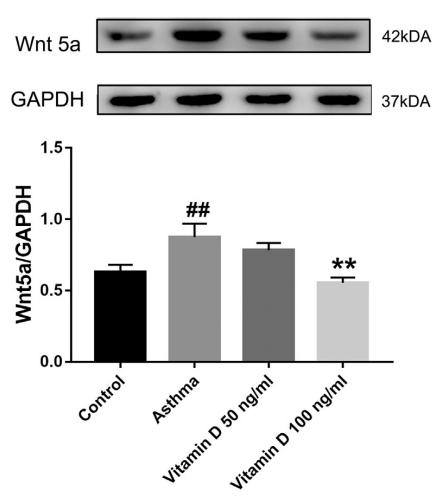
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: lung
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: H9c2 cells
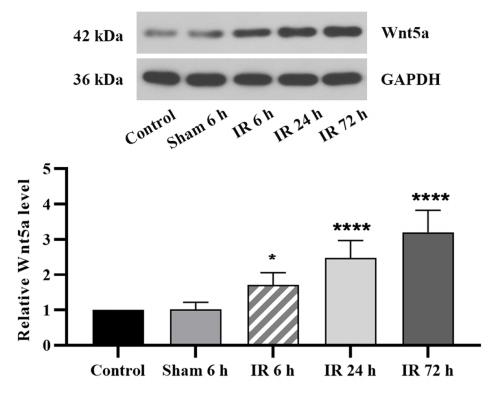
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: brain
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.