BUB1 Antibody - #DF6698
| Product: | BUB1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6698 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to BUB1 |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 122kDa; 122kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | O43683 |
| RRID: | AB_2838660 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6698, RRID:AB_2838660.
Fold/Unfold
Bub1; BUB1 budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1 homolog; BUB1 budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1 homolog (yeast); BUB1 mitotic checkpoint serine/threonine kinase; BUB1, S. cerevisiae, homolog of; BUB1_HUMAN; BUB1A; BUB1L; Budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1 (yeast homolog); Budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1 homolog; Budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1, S. cerevisiae, homolog of; hBUB1; Homolog of mitotic checkpoint gene BUB1; Mitotic checkpoint gene BUB1; Mitotic checkpoint serine/threonine protein kinase BUB1; Mitotic checkpoint serine/threonine-protein kinase BUB1; Mitotic spindle checkpoint kinase; Putative serine/threonine protein kinase;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human BUB1, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
High expression in testis and thymus, less in colon, spleen, lung and small intestine. Expressed in fetal thymus, bone marrow, heart, liver, spleen and thymus. Expression is associated with cells/tissues with a high mitotic index.
- O43683 BUB1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MDTPENVLQMLEAHMQSYKGNDPLGEWERYIQWVEENFPENKEYLITLLEHLMKEFLDKKKYHNDPRFISYCLKFAEYNSDLHQFFEFLYNHGIGTLSSPLYIAWAGHLEAQGELQHASAVLQRGIQNQAEPREFLQQQYRLFQTRLTETHLPAQARTSEPLHNVQVLNQMITSKSNPGNNMACISKNQGSELSGVISSACDKESNMERRVITISKSEYSVHSSLASKVDVEQVVMYCKEKLIRGESEFSFEELRAQKYNQRRKHEQWVNEDRHYMKRKEANAFEEQLLKQKMDELHKKLHQVVETSHEDLPASQERSEVNPARMGPSVGSQQELRAPCLPVTYQQTPVNMEKNPREAPPVVPPLANAISAALVSPATSQSIAPPVPLKAQTVTDSMFAVASKDAGCVNKSTHEFKPQSGAEIKEGCETHKVANTSSFHTTPNTSLGMVQATPSKVQPSPTVHTKEALGFIMNMFQAPTLPDISDDKDEWQSLDQNEDAFEAQFQKNVRSSGAWGVNKIISSLSSAFHVFEDGNKENYGLPQPKNKPTGARTFGERSVSRLPSKPKEEVPHAEEFLDDSTVWGIRCNKTLAPSPKSPGDFTSAAQLASTPFHKLPVESVHILEDKENVVAKQCTQATLDSCEENMVVPSRDGKFSPIQEKSPKQALSSHMYSASLLRLSQPAAGGVLTCEAELGVEACRLTDTDAAIAEDPPDAIAGLQAEWMQMSSLGTVDAPNFIVGNPWDDKLIFKLLSGLSKPVSSYPNTFEWQCKLPAIKPKTEFQLGSKLVYVHHLLGEGAFAQVYEATQGDLNDAKNKQKFVLKVQKPANPWEFYIGTQLMERLKPSMQHMFMKFYSAHLFQNGSVLVGELYSYGTLLNAINLYKNTPEKVMPQGLVISFAMRMLYMIEQVHDCEIIHGDIKPDNFILGNGFLEQDDEDDLSAGLALIDLGQSIDMKLFPKGTIFTAKCETSGFQCVEMLSNKPWNYQIDYFGVAATVYCMLFGTYMKVKNEGGECKPEGLFRRLPHLDMWNEFFHVMLNIPDCHHLPSLDLLRQKLKKVFQQHYTNKIRALRNRLIVLLLECKRSRK
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Serine/threonine-protein kinase that performs 2 crucial functions during mitosis: it is essential for spindle-assembly checkpoint signaling and for correct chromosome alignment. Has a key role in the assembly of checkpoint proteins at the kinetochore, being required for the subsequent localization of CENPF, BUB1B, CENPE and MAD2L1. Required for the kinetochore localization of PLK1. Required for centromeric enrichment of AUKRB in prometaphase. Plays an important role in defining SGO1 localization and thereby affects sister chromatid cohesion. Acts as a substrate for anaphase-promoting complex or cyclosome (APC/C) in complex with its activator CDH1 (APC/C-Cdh1). Necessary for ensuring proper chromosome segregation and binding to BUB3 is essential for this function. Can regulate chromosome segregation in a kinetochore-independent manner. Can phosphorylate BUB3. The BUB1-BUB3 complex plays a role in the inhibition of APC/C when spindle-assembly checkpoint is activated and inhibits the ubiquitin ligase activity of APC/C by phosphorylating its activator CDC20. This complex can also phosphorylate MAD1L1. Kinase activity is essential for inhibition of APC/CCDC20 and for chromosome alignment but does not play a major role in the spindle-assembly checkpoint activity. Mediates cell death in response to chromosome missegregation and acts to suppress spontaneous tumorigenesis.
Upon spindle-assembly checkpoint activation it is hyperphosphorylated and its kinase activity toward CDC20 is stimulated. Phosphorylation at Thr-609 is required for interaction with PLK1, phosphorylation at this site probably creates a binding site for the POLO-box domain of PLK1, thus enhancing the PLK1-BUB1 interaction.
Ubiquitinated and degraded during mitotic exit by APC/C-Cdh1.
Nucleus. Chromosome>Centromere>Kinetochore.
Note: Nuclear in interphase cells. Accumulates gradually during G1 and S phase of the cell cycle, peaks at G2/M, and drops dramatically after mitosis. Localizes to the outer kinetochore. Kinetochore localization is required for normal mitotic timing and checkpoint response to spindle damage and occurs very early in prophase. AURKB, KNL1 and INCENP are required for kinetochore localization (By similarity).
High expression in testis and thymus, less in colon, spleen, lung and small intestine. Expressed in fetal thymus, bone marrow, heart, liver, spleen and thymus. Expression is associated with cells/tissues with a high mitotic index.
The KEN box is required for its ubiquitination and degradation.
BUB1 N-terminal domain directs kinetochore localization and binding to BUB3.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Ser/Thr protein kinase family. BUB1 subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Oocyte meiosis. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation.
References
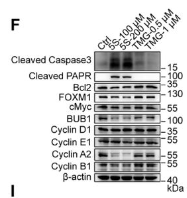
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: OS cells
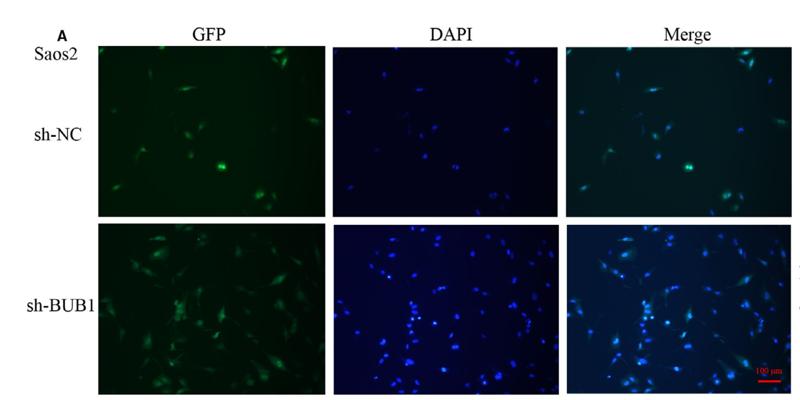
Application: IF/ICC Species: Mice Sample: OS cells
Application: IHC Species: Rat Sample: gastric tissue
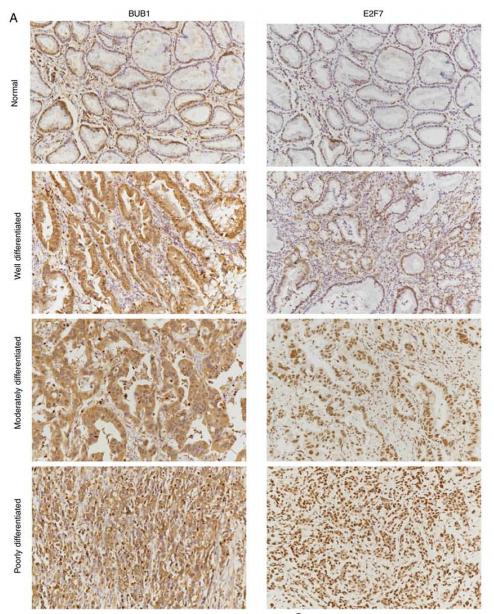
Application: IHC Species: human Sample: gastric cancer
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HuCCT1 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.