ARG1 Antibody - #DF6657
| Product: | ARG1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6657 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to ARG1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 35kDa; 35kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P05089 |
| RRID: | AB_2838619 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6657, RRID:AB_2838619.
Fold/Unfold
A I; Al; ARG 1; arg1; ARGI1_HUMAN; Arginase 1; Arginase liver; Arginase type I; Arginase, liver; Arginase-1; Arginase1; Liver type arginase; Liver-type arginase; Type I arginase;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human ARG1, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Within the immune system initially reported to be selectively expressed in granulocytes (polymorphonuclear leukocytes [PMNs]) (PubMed:15546957). Also detected in macrophages mycobacterial granulomas (PubMed:23749634). Expressed in group2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) during lung disease (PubMed:27043409).
- P05089 ARGI1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSAKSRTIGIIGAPFSKGQPRGGVEEGPTVLRKAGLLEKLKEQECDVKDYGDLPFADIPNDSPFQIVKNPRSVGKASEQLAGKVAEVKKNGRISLVLGGDHSLAIGSISGHARVHPDLGVIWVDAHTDINTPLTTTSGNLHGQPVSFLLKELKGKIPDVPGFSWVTPCISAKDIVYIGLRDVDPGEHYILKTLGIKYFSMTEVDRLGIGKVMEETLSYLLGRKKRPIHLSFDVDGLDPSFTPATGTPVVGGLTYREGLYITEEIYKTGLLSGLDIMEVNPSLGKTPEEVTRTVNTAVAITLACFGLAREGNHKPIDYLNPPK
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Key element of the urea cycle converting L-arginine to urea and L-ornithine, which is further metabolized into metabolites proline and polyamides that drive collagen synthesis and bioenergetic pathways critical for cell proliferation, respectively; the urea cycle takes place primarily in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the kidneys.
Functions in L-arginine homeostasis in nonhepatic tissues characterized by the competition between nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and arginase for the available intracellular substrate arginine. Arginine metabolism is a critical regulator of innate and adaptive immune responses. Involved in an antimicrobial effector pathway in polymorphonuclear granulocytes (PMN). Upon PMN cell death is liberated from the phagolysosome and depletes arginine in the microenvironment leading to suppressed T cell and natural killer (NK) cell proliferation and cytokine secretion. In group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) promotes acute type 2 inflammation in the lung and is involved in optimal ILC2 proliferation but not survival (By similarity). In humans, the immunological role in the monocytic/macrophage/dendritic cell (DC) lineage is unsure.
Cytoplasm. Cytoplasmic granule.
Note: Localized in azurophil granules of neutrophils (PubMed:15546957).
Within the immune system initially reported to be selectively expressed in granulocytes (polymorphonuclear leukocytes [PMNs]). Also detected in macrophages mycobacterial granulomas. Expressed in group2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) during lung disease.
Belongs to the arginase family.
Research Fields
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Amoebiasis.
· Metabolism > Amino acid metabolism > Arginine biosynthesis.
· Metabolism > Amino acid metabolism > Arginine and proline metabolism.
· Metabolism > Global and overview maps > Metabolic pathways.
· Metabolism > Global and overview maps > Biosynthesis of amino acids.
References
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.


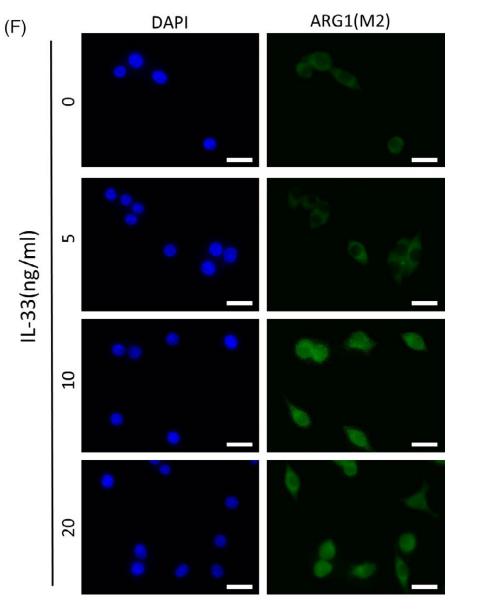
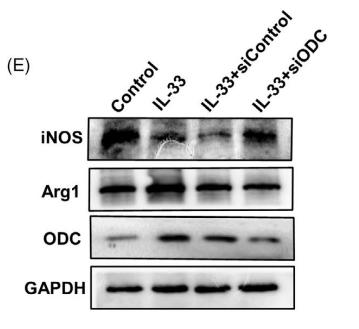
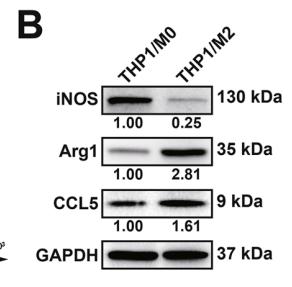



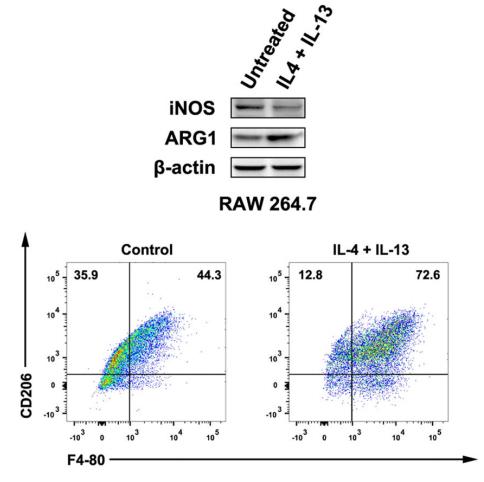







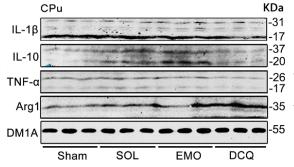





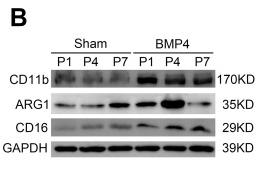
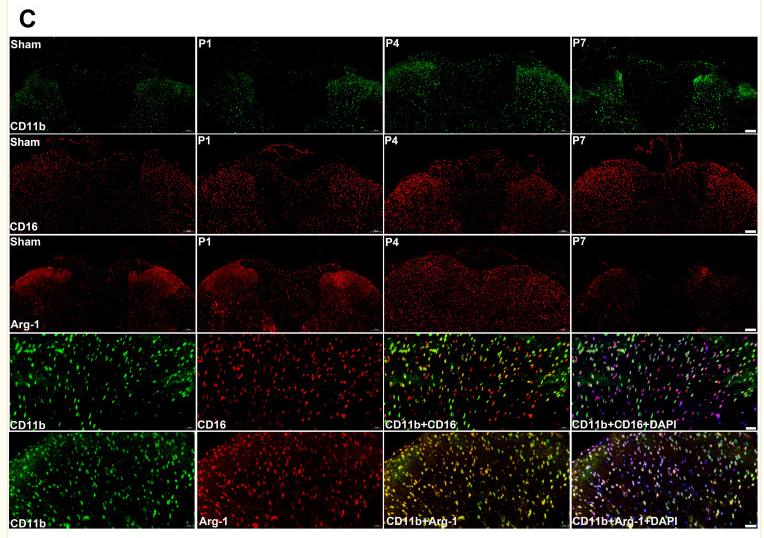
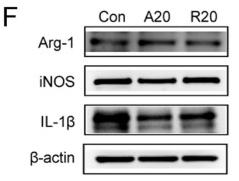
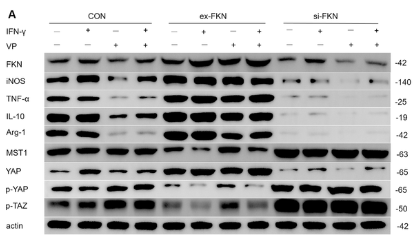





![Figure 3. MiR-22-3p induces macrophages into the M2 phenotype in ApoE–/– mice fed a high fat diet: (a) immunofluorescence staining (original magnification, × 40, bar = 50 μm) and quantitative analysis of macrophage accumulation and macrophage polarization by detection of (a) the macrophage marker cluster of differentiation (CD)68 and M1 marker inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and (b) the M2 markers CD206 and arginase (Arg)-1, in aortic sections from MiR-22-3p agomir or normal control (NC) mice; and (c) western blot and quantitative analysis of relative protein levels of the M1 markers (iNOS, interleukin [IL]-6, and tumour necrosis factor [TNF]-α) and M2 markers (Arg1 and CD206) in aortic sections from MiR-22-3p agomir or NC mice. ARG1 Antibody - Figure 3.](http://img.affbiotech.cn/uploads/202403/846c086f865acda93b58450407f3e751.png)
![Figure 3. MiR-22-3p induces macrophages into the M2 phenotype in ApoE–/– mice fed a high fat diet: (a) immunofluorescence staining (original magnification, × 40, bar = 50 μm) and quantitative analysis of macrophage accumulation and macrophage polarization by detection of (a) the macrophage marker cluster of differentiation (CD)68 and M1 marker inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and (b) the M2 markers CD206 and arginase (Arg)-1, in aortic sections from MiR-22-3p agomir or normal control (NC) mice; and (c) western blot and quantitative analysis of relative protein levels of the M1 markers (iNOS, interleukin [IL]-6, and tumour necrosis factor [TNF]-α) and M2 markers (Arg1 and CD206) in aortic sections from MiR-22-3p agomir or NC mice. ARG1 Antibody - Figure 3.](http://img.affbiotech.cn/uploads/202403/e19e9c4edc76f1b95745d6d2f41154f2.png)



