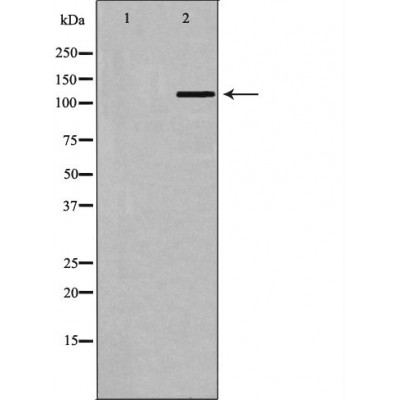
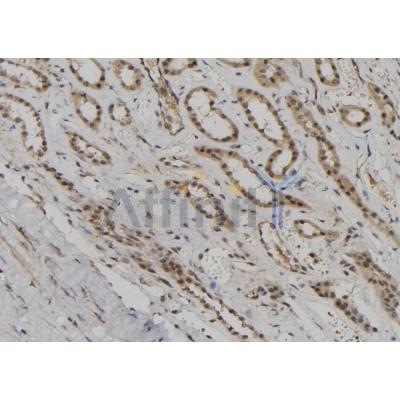
BUB1B Antibody - #DF6609
| Product: | BUB1B Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6609 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to BUB1B |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 120kDa; 120kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | O60566 |
| RRID: | AB_2838571 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6609, RRID:AB_2838571.
Fold/Unfold
Beta homolg of S. cerevisiae BUB 1; Beta homolg of S. cerevisiae budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles; BUB 1B; BUB1 budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1 homolog beta; Bub1A; BUB1B; BUB1B_HUMAN; BUB1beta; BUBR1; Budding Uninhibited by Benzimidazoles 1 beta; Budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1 homolog beta (yeast); hBUBR1; MAD3/BUB1 related protein kinase; MAD3/BUB1-related protein kinase; MAD3L; Mitotic checkpoint gene BUB1B; Mitotic checkpoint kinase MAD3L; Mitotic checkpoint serine/threonine protein kinase BUB1 beta; Mitotic checkpoint serine/threonine-protein kinase BUB1 beta; MVA1; OTTHUMP00000160319; Protein SSK1; SSK 1; SSK1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human BUB1B, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Highly expressed in thymus followed by spleen. Preferentially expressed in tissues with a high mitotic index.
- O60566 BUB1B_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAAVKKEGGALSEAMSLEGDEWELSKENVQPLRQGRIMSTLQGALAQESACNNTLQQQKRAFEYEIRFYTGNDPLDVWDRYISWTEQNYPQGGKESNMSTLLERAVEALQGEKRYYSDPRFLNLWLKLGRLCNEPLDMYSYLHNQGIGVSLAQFYISWAEEYEARENFRKADAIFQEGIQQKAEPLERLQSQHRQFQARVSRQTLLALEKEEEEEVFESSVPQRSTLAELKSKGKKTARAPIIRVGGALKAPSQNRGLQNPFPQQMQNNSRITVFDENADEASTAELSKPTVQPWIAPPMPRAKENELQAGPWNTGRSLEHRPRGNTASLIAVPAVLPSFTPYVEETARQPVMTPCKIEPSINHILSTRKPGKEEGDPLQRVQSHQQASEEKKEKMMYCKEKIYAGVGEFSFEEIRAEVFRKKLKEQREAELLTSAEKRAEMQKQIEEMEKKLKEIQTTQQERTGDQQEETMPTKETTKLQIASESQKIPGMTLSSSVCQVNCCARETSLAENIWQEQPHSKGPSVPFSIFDEFLLSEKKNKSPPADPPRVLAQRRPLAVLKTSESITSNEDVSPDVCDEFTGIEPLSEDAIITGFRNVTICPNPEDTCDFARAARFVSTPFHEIMSLKDLPSDPERLLPEEDLDVKTSEDQQTACGTIYSQTLSIKKLSPIIEDSREATHSSGFSGSSASVASTSSIKCLQIPEKLELTNETSENPTQSPWCSQYRRQLLKSLPELSASAELCIEDRPMPKLEIEKEIELGNEDYCIKREYLICEDYKLFWVAPRNSAELTVIKVSSQPVPWDFYINLKLKERLNEDFDHFCSCYQYQDGCIVWHQYINCFTLQDLLQHSEYITHEITVLIIYNLLTIVEMLHKAEIVHGDLSPRCLILRNRIHDPYDCNKNNQALKIVDFSYSVDLRVQLDVFTLSGFRTVQILEGQKILANCSSPYQVDLFGIADLAHLLLFKEHLQVFWDGSFWKLSQNISELKDGELWNKFFVRILNANDEATVSVLGELAAEMNGVFDTTFQSHLNKALWKVGKLTSPGALLFQ
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Essential component of the mitotic checkpoint. Required for normal mitosis progression. The mitotic checkpoint delays anaphase until all chromosomes are properly attached to the mitotic spindle. One of its checkpoint functions is to inhibit the activity of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) by blocking the binding of CDC20 to APC/C, independently of its kinase activity. The other is to monitor kinetochore activities that depend on the kinetochore motor CENPE. Required for kinetochore localization of CENPE. Negatively regulates PLK1 activity in interphase cells and suppresses centrosome amplification. Also implicated in triggering apoptosis in polyploid cells that exit aberrantly from mitotic arrest. May play a role for tumor suppression.
Proteolytically cleaved by caspase-3 in a cell cycle specific manner. The cleavage might be involved in the durability of the cell cycle delay. Caspase-3 cleavage is associated with abrogation of the mitotic checkpoint. The major site of cleavage is at Asp-610.
Acetylation at Lys-250 regulates its degradation and timing in anaphase entry.
Ubiquitinated. Degraded by the proteasome.
Sumoylated with SUMO2 and SUMO3. The sumoylation mediates the association with CENPE at the kinetochore.
Autophosphorylated in vitro. Intramolecular autophosphorylation is stimulated by CENPE. Phosphorylated during mitosis and hyperphosphorylated in mitotically arrested cells. Phosphorylation at Ser-670 and Ser-1043 occurs at kinetochores upon mitotic entry with dephosphorylation at the onset of anaphase.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Chromosome>Centromere>Kinetochore. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Microtubule organizing center>Centrosome.
Note: Cytoplasmic in interphase cells. Associates with the kinetochores in early prophase. Kinetochore localization requires BUB1, PLK1 and KNL1.
Highly expressed in thymus followed by spleen. Preferentially expressed in tissues with a high mitotic index.
The D-box targets the protein for rapid degradation by ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis during the transition from mitosis to interphase.
The BUB1 N-terminal domain directs kinetochore localization and binding to BUB3.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Ser/Thr protein kinase family. BUB1 subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.