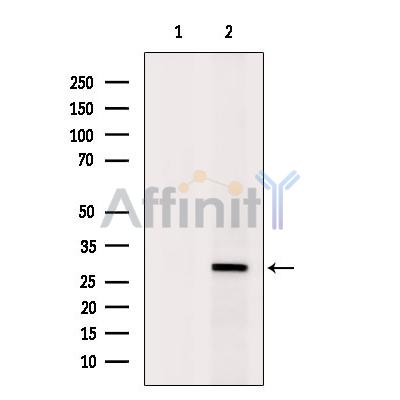
SFRS1 Antibody - #DF6529
| Product: | SFRS1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6529 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to SFRS1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 28kDa; 28kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q07955 |
| RRID: | AB_2838491 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6529, RRID:AB_2838491.
Fold/Unfold
Alternative splicing factor 1; Alternative-splicing factor 1; arginine/serine-rich 1; ASF 1; ASF; ASF-1; ASF1; FLJ53078; MGC5228; P33 subunit; Pre mRNA splicing factor SF2 P33 subunit; pre-mRNA-splicing factor SF2; Serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 1; SF2; SF2P33; SFRS1; Splicing factor 2 alternate splicing factor; Splicing factor 2; Splicing factor; Splicing factor arginine/serine rich 1; SR Splicing factor 1; SRp30a; srsf1; SRSF1_HUMAN;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human SFRS1, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- Q07955 SRSF1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSGGGVIRGPAGNNDCRIYVGNLPPDIRTKDIEDVFYKYGAIRDIDLKNRRGGPPFAFVEFEDPRDAEDAVYGRDGYDYDGYRLRVEFPRSGRGTGRGGGGGGGGGAPRGRYGPPSRRSENRVVVSGLPPSGSWQDLKDHMREAGDVCYADVYRDGTGVVEFVRKEDMTYAVRKLDNTKFRSHEGETAYIRVKVDGPRSPSYGRSRSRSRSRSRSRSRSNSRSRSYSPRRSRGSPRYSPRHSRSRSRT
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Plays a role in preventing exon skipping, ensuring the accuracy of splicing and regulating alternative splicing. Interacts with other spliceosomal components, via the RS domains, to form a bridge between the 5'- and 3'-splice site binding components, U1 snRNP and U2AF. Can stimulate binding of U1 snRNP to a 5'-splice site-containing pre-mRNA. Binds to purine-rich RNA sequences, either the octamer, 5'-RGAAGAAC-3' (r=A or G) or the decamers, AGGACAGAGC/AGGACGAAGC. Binds preferentially to the 5'-CGAGGCG-3' motif in vitro. Three copies of the octamer constitute a powerful splicing enhancer in vitro, the ASF/SF2 splicing enhancer (ASE) which can specifically activate ASE-dependent splicing. Isoform ASF-2 and isoform ASF-3 act as splicing repressors. May function as export adapter involved in mRNA nuclear export through the TAP/NXF1 pathway.
Phosphorylated by CLK1, CLK2, CLK3 and CLK4. Phosphorylated by SRPK1 at multiple serines in its RS domain via a directional (C-terminal to N-terminal) and a dual-track mechanism incorporating both processive phosphorylation (in which the kinase stays attached to the substrate after each round of phosphorylation) and distributive phosphorylation steps (in which the kinase and substrate dissociate after each phosphorylation event). The RS domain of SRSF1 binds to a docking groove in the large lobe of the kinase domain of SRPK1 and this induces certain structural changes in SRPK1 and/or RRM 2 domain of SRSF1, allowing RRM 2 to bind the kinase and initiate phosphorylation. The cycles continue for several phosphorylation steps in a processive manner (steps 1-8) until the last few phosphorylation steps (approximately steps 9-12). During that time, a mechanical stress induces the unfolding of the beta-4 motif in RRM 2, which then docks at the docking groove of SRPK1. This also signals RRM 2 to begin to dissociate, which facilitates SRSF1 dissociation after phosphorylation is completed.
Asymmetrically dimethylated at arginines, probably by PRMT1, methylation promotes localization to nuclear speckles.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus speckle.
Note: In nuclear speckles. Shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm (PubMed:12215544, PubMed:20308322, PubMed:9420331, PubMed:24449914). Nuclear import is mediated via interaction with TNPO3 (PubMed:24449914).
The RRM 2 domain plays an important role in governing both the binding mode and the phosphorylation mechanism of the RS domain by SRPK1. RS domain and RRM 2 are uniquely positioned to initiate a highly directional (C-terminus to N-terminus) phosphorylation reaction in which the RS domain slides through an extended electronegative channel separating the docking groove of SRPK1 and the active site. RRM 2 binds toward the periphery of the active site and guides the directional phosphorylation mechanism. Both the RS domain and an RRM domain are required for nucleocytoplasmic shuttling.
Belongs to the splicing factor SR family.
Research Fields
· Genetic Information Processing > Transcription > Spliceosome.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Herpes simplex infection.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > IL-17 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.