HMGCR Antibody - #DF6518
| Product: | HMGCR Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6518 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to HMGCR |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 95kDa; 97kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P04035 |
| RRID: | AB_2838480 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6518, RRID:AB_2838480.
Fold/Unfold
3 hydroxy 3 methylglutaryl CoA reductase; 3 hydroxy 3 methylglutaryl Coenzyme A reductase; 3 hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA reductase; 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase (NADPH); 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase; 3H3M; HMDH_HUMAN; HMG CoA reductase; HMG CoAR; HMG-CoA reductase; Hmgcr; Hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA reductase; LDLCQ3; MGC103269; Red;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human HMGCR, corresponding to a region within N-terminal amino acids.
- P04035 HMDH_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MLSRLFRMHGLFVASHPWEVIVGTVTLTICMMSMNMFTGNNKICGWNYECPKFEEDVLSSDIIILTITRCIAILYIYFQFQNLRQLGSKYILGIAGLFTIFSSFVFSTVVIHFLDKELTGLNEALPFFLLLIDLSRASTLAKFALSSNSQDEVRENIARGMAILGPTFTLDALVECLVIGVGTMSGVRQLEIMCCFGCMSVLANYFVFMTFFPACVSLVLELSRESREGRPIWQLSHFARVLEEEENKPNPVTQRVKMIMSLGLVLVHAHSRWIADPSPQNSTADTSKVSLGLDENVSKRIEPSVSLWQFYLSKMISMDIEQVITLSLALLLAVKYIFFEQTETESTLSLKNPITSPVVTQKKVPDNCCRREPMLVRNNQKCDSVEEETGINRERKVEVIKPLVAETDTPNRATFVVGNSSLLDTSSVLVTQEPEIELPREPRPNEECLQILGNAEKGAKFLSDAEIIQLVNAKHIPAYKLETLMETHERGVSIRRQLLSKKLSEPSSLQYLPYRDYNYSLVMGACCENVIGYMPIPVGVAGPLCLDEKEFQVPMATTEGCLVASTNRGCRAIGLGGGASSRVLADGMTRGPVVRLPRACDSAEVKAWLETSEGFAVIKEAFDSTSRFARLQKLHTSIAGRNLYIRFQSRSGDAMGMNMISKGTEKALSKLHEYFPEMQILAVSGNYCTDKKPAAINWIEGRGKSVVCEAVIPAKVVREVLKTTTEAMIEVNINKNLVGSAMAGSIGGYNAHAANIVTAIYIACGQDAAQNVGSSNCITLMEASGPTNEDLYISCTMPSIEIGTVGGGTNLLPQQACLQMLGVQGACKDNPGENARQLARIVCGTVMAGELSLMAALAAGHLVKSHMIHNRSKINLQDLQGACTKKTA
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Transmembrane glycoprotein that is the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis as well as in the biosynthesis of nonsterol isoprenoids that are essential for normal cell function including ubiquinone and geranylgeranyl proteins.
N-glycosylated. Deglycosylated by NGLY1 on release from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in a sterol-mediated manner.
Undergoes sterol-mediated ubiquitination and ER-associated degradation (ERAD). Accumulation of sterols in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane, triggers binding of the reductase to the ER membrane protein INSIG1. This INSIG1 binding leads to the recruitment of the ubiquitin ligase, AMFR/gp78 or RNF145, initiating ubiquitination of the reductase. The ubiquitinated reductase is then extracted from the ER membrane and delivered to cytosolic 26S proteosomes by a mechanism probably mediated by the ATPase Valosin-containing protein VCP/p97. Lys-248 is the main site of ubiquitination. Ubiquitination is enhanced by the presence of a geranylgeranylated protein.
Endoplasmic reticulum membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein.
Belongs to the HMG-CoA reductase family.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > AMPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Metabolism > Metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides > Terpenoid backbone biosynthesis.
· Metabolism > Global and overview maps > Metabolic pathways.
References
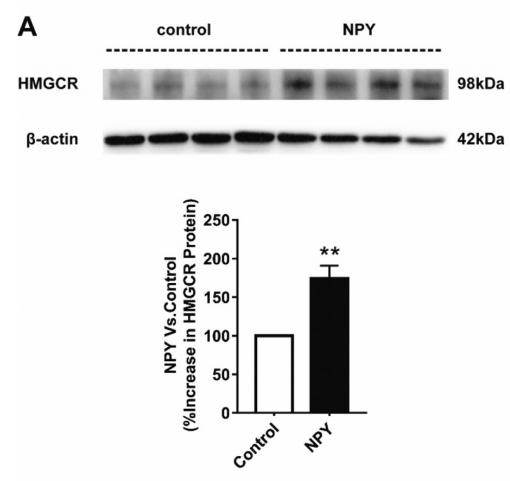
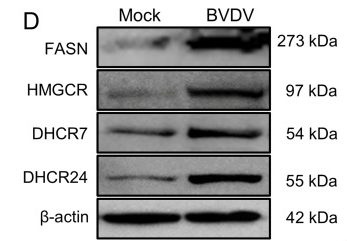
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: L02 cell
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: hippocampus
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: liver
Application: WB Species: bovine Sample: bovine cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.



![Fig. 1 The significant decrease of hippocampal cholesterol level in 5xFAD mice. A Quantification of cholesterol level in hippocampus of WT and 5xFAD mice (3 month) by LC–MS/MS analysis. n = 3–4 sample/group, every sample was included 2–3 mice randomly. B–D The fold change expression of mRNA of DHCR24, HMGCR and SREBP2 in hippocampus of WT and 5xFAD mice (3 month) by RT-PCR. E The immunoblotting bands of DHCR24, HMGCR, SREBP2 in hippocampus of 3-month-old WT mice and 5xFAD mice. F Analysis of western blot with mean gray value which all were quantification on the ratio of target proteins against GAPDH. G The fluorescence images of DHCR24 (red) in hippocampus of 3-month-old WT and 5xFAD mice (scale bar, 20 μm). H Mean fluorescence intensity of DHCR24. n = 3 mice per group in [B-H]. Data expressed as mean ± SEM, statistical analysis was performed using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. *P HMGCR Antibody - Fig.](http://img.affbiotech.cn/uploads/202508/4d1c88b80ba0c92ee789ef6676d2e741.png)