GSTA1 Antibody - #DF6514
| Product: | GSTA1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6514 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to GSTA1 |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 26kDa; 26kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P08263 |
| RRID: | AB_2838476 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6514, RRID:AB_2838476.
Fold/Unfold
Glutathione S alkyltransferase A1; Glutathione S aryltransferase A1; Glutathione S transferase 2; Glutathione S transferase A1; Glutathione S transferase alpha 1; Glutathione S transferase Ha subunit 1; Glutathione S-transferase A1; GST class-alpha member 1; GST epsilon; GST HA subunit 1; GST, class alpha, 1; GST-epsilon; GST2; GSTA1 1; GSTA1; GSTA1-1; GSTA1_HUMAN; GTH1; HA subunit 1; MGC131939; OTTHUMP00000016611; S (hydroxyalkyl)glutathione lyase A1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human GSTA1, corresponding to a region within N-terminal amino acids.
- P08263 GSTA1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAEKPKLHYFNARGRMESTRWLLAAAGVEFEEKFIKSAEDLDKLRNDGYLMFQQVPMVEIDGMKLVQTRAILNYIASKYNLYGKDIKERALIDMYIEGIADLGEMILLLPVCPPEEKDAKLALIKEKIKNRYFPAFEKVLKSHGQDYLVGNKLSRADIHLVELLYYVEELDSSLISSFPLLKALKTRISNLPTVKKFLQPGSPRKPPMDEKSLEEARKIFRF
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Glutathione S-transferase that catalyzes the nucleophilic attack of the sulfur atom of glutathione on the electrophilic groups of a wide range of exogenous and endogenous compounds (Probable). Involved in the formation of glutathione conjugates of both prostaglandin A2 (PGA2) and prostaglandin J2 (PGJ2). It also catalyzes the isomerization of D5-androstene-3,17-dione (AD) into D4-androstene-3,17-dione and may therefore play an important role in hormone biosynthesis. Through its glutathione-dependent peroxidase activity toward the fatty acid hydroperoxide (13S)-hydroperoxy-(9Z,11E)-octadecadienoate/13-HPODE it is also involved in the metabolism of oxidized linoleic acid.
Cytoplasm.
Liver.
The C-terminal domain may form a component of the hydrophobic substrate-binding site, but in contrast appears not to be directly involved in GSH binding and is not absolutely essential for catalytic activity.
Belongs to the GST superfamily. Alpha family.
Research Fields
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Platinum drug resistance.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Chemical carcinogenesis.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Metabolism > Metabolism of other amino acids > Glutathione metabolism.
· Metabolism > Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism > Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450.
· Metabolism > Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism > Drug metabolism - cytochrome P450.
· Metabolism > Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism > Drug metabolism - other enzymes.
References
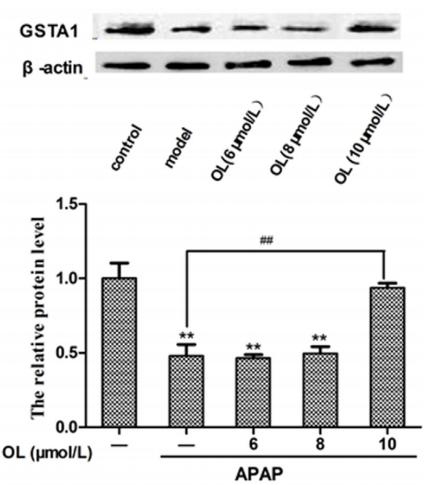
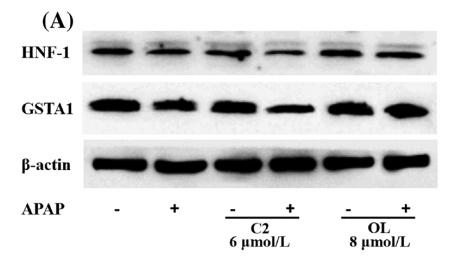
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: liver
Application: WB Species: Sample: hepatocytes
Application: WB Species: human Sample: HepG2 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.