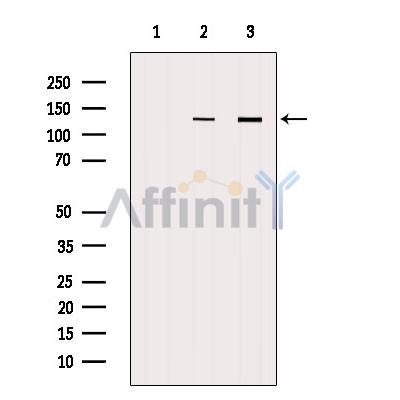
UPF1 Antibody - #DF6440
| Product: | UPF1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6440 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to UPF1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 123kDa; 124kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q92900 |
| RRID: | AB_2838403 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6440, RRID:AB_2838403.
Fold/Unfold
ATP dependent helicase RENT1; ATP-dependent helicase RENT1; Delta helicase; FLJ43809; FLJ46894; HUPF 1; hUpf1; KIAA0221; Nonsense mRNA reducing factor 1; NORF 1; NORF1; pNORF 1; pNORF1; Regulator of nonsense transcripts 1; RENT 1; RENT1; RENT1_HUMAN; Smg 2; Smg 2 homolog nonsense mediated mRNA decay factor; UP Frameshift 1; Up frameshift mutation 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae); Up frameshift mutation 1 homolog; Up frameshift suppressor 1 homolog; Up-frameshift suppressor 1 homolog; UPF 1; UPF 1 regulator of nonsense transcripts homolog; upf1; UPF1 regulator of nonsense transcripts homolog; UPF1 RNA helicase and ATPase; Yeast Upf1p homolog;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human UPF1, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
- Q92900 RENT1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSVEAYGPSSQTLTFLDTEEAELLGADTQGSEFEFTDFTLPSQTQTPPGGPGGPGGGGAGGPGGAGAGAAAGQLDAQVGPEGILQNGAVDDSVAKTSQLLAELNFEEDEEDTYYTKDLPIHACSYCGIHDPACVVYCNTSKKWFCNGRGNTSGSHIVNHLVRAKCKEVTLHKDGPLGETVLECYNCGCRNVFLLGFIPAKADSVVVLLCRQPCASQSSLKDINWDSSQWQPLIQDRCFLSWLVKIPSEQEQLRARQITAQQINKLEELWKENPSATLEDLEKPGVDEEPQHVLLRYEDAYQYQNIFGPLVKLEADYDKKLKESQTQDNITVRWDLGLNKKRIAYFTLPKTDSGNEDLVIIWLRDMRLMQGDEICLRYKGDLAPLWKGIGHVIKVPDNYGDEIAIELRSSVGAPVEVTHNFQVDFVWKSTSFDRMQSALKTFAVDETSVSGYIYHKLLGHEVEDVIIKCQLPKRFTAQGLPDLNHSQVYAVKTVLQRPLSLIQGPPGTGKTVTSATIVYHLARQGNGPVLVCAPSNIAVDQLTEKIHQTGLKVVRLCAKSREAIDSPVSFLALHNQIRNMDSMPELQKLQQLKDETGELSSADEKRYRALKRTAERELLMNADVICCTCVGAGDPRLAKMQFRSILIDESTQATEPECMVPVVLGAKQLILVGDHCQLGPVVMCKKAAKAGLSQSLFERLVVLGIRPIRLQVQYRMHPALSAFPSNIFYEGSLQNGVTAADRVKKGFDFQWPQPDKPMFFYVTQGQEEIASSGTSYLNRTEAANVEKITTKLLKAGAKPDQIGIITPYEGQRSYLVQYMQFSGSLHTKLYQEVEIASVDAFQGREKDFIILSCVRANEHQGIGFLNDPRRLNVALTRARYGVIIVGNPKALSKQPLWNHLLNYYKEQKVLVEGPLNNLRESLMQFSKPRKLVNTINPGARFMTTAMYDAREAIIPGSVYDRSSQGRPSSMYFQTHDQIGMISAGPSHVAAMNIPIPFNLVMPPMPPPGYFGQANGPAAGRGTPKGKTGRGGRQKNRFGLPGPSQTNLPNSQASQDVASQPFSQGALTQGYISMSQPSQMSQPGLSQPELSQDSYLGDEFKSQIDVALSQDSTYQGERAYQHGGVTGLSQY
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
RNA-dependent helicase and ATPase required for nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) of mRNAs containing premature stop codons. Is recruited to mRNAs upon translation termination and undergoes a cycle of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation; its phosphorylation appears to be a key step in NMD. Recruited by release factors to stalled ribosomes together with the SMG1C protein kinase complex to form the transient SURF (SMG1-UPF1-eRF1-eRF3) complex. In EJC-dependent NMD, the SURF complex associates with the exon junction complex (EJC) (located 50-55 or more nucleotides downstream from the termination codon) through UPF2 and allows the formation of an UPF1-UPF2-UPF3 surveillance complex which is believed to activate NMD. Phosphorylated UPF1 is recognized by EST1B/SMG5, SMG6 and SMG7 which are thought to provide a link to the mRNA degradation machinery involving exonucleolytic and endonucleolytic pathways, and to serve as adapters to protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), thereby triggering UPF1 dephosphorylation and allowing the recycling of NMD factors. UPF1 can also activate NMD without UPF2 or UPF3, and in the absence of the NMD-enhancing downstream EJC indicative for alternative NMD pathways. Plays a role in replication-dependent histone mRNA degradation at the end of phase S; the function is independent of UPF2. For the recognition of premature termination codons (PTC) and initiation of NMD a competitive interaction between UPF1 and PABPC1 with the ribosome-bound release factors is proposed. The ATPase activity of UPF1 is required for disassembly of mRNPs undergoing NMD. Essential for embryonic viability. Together with UPF2 and dependent on TDRD6, mediates the degradation of mRNA hardoring long 3'UTR by inducing the NMD machinery (By similarity).
Phosphorylated by SMG1; required for formation of mRNA surveillance complexes.
Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm>P-body. Nucleus.
Note: Hyperphosphorylated form is targeted to the P-body, while unphosphorylated protein is distributed throughout the cytoplasm. Localized in the chromatoid bodies of round spermatids (By similarity).
Ubiquitous.
The [ST]-Q motif constitutes a recognition sequence for kinases from the PI3/PI4-kinase family.
Belongs to the DNA2/NAM7 helicase family.
Research Fields
· Genetic Information Processing > Translation > RNA transport.
· Genetic Information Processing > Translation > mRNA surveillance pathway.
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.