CLU Antibody - #DF6421
| Product: | CLU Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6421 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to CLU |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Mol.Wt.: | 53kDa; 52kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P10909 |
| RRID: | AB_2838384 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6421, RRID:AB_2838384.
Fold/Unfold
40; AAG 4; AAG4; Aging associated protein 4; Aging-associated gene 4 protein; AI893575; APO J; Apo-J; APOJ; ApoJalpha; ApoJbeta; Apolipoprotein J; ApolipoproteinJ; CLI; CLU; CLU1; CLU2; CLUS_HUMAN; Clusterin alpha chain; Clusterin; Clusterin beta chain; Complement associated protein SP 40 40; Complement associated protein SP 40; Complement associated protein SP40; Complement cytolysis inhibitor a chain; Complement cytolysis inhibitor; Complement cytolysis inhibitor b chain; Complement lysis inhibitor; Complement-associated protein SP-40; D14Ucla3; Dimeric acid glycoprotein; Glycoprotein 80; Glycoprotein III; GP80; Ku70-binding protein 1; KUB 1; KUB1; MGC24903; NA1/NA2; RATTRPM2B; SGP 2; SGP2; SP 40; SP40; Sugp-2; Sulfated glycoprotein 2; Testosterone repressed prostate message 2; Testosterone-repressed prostate message 2; TRPM 2; TRPM-2; TRPM2; TRPM2B; Trpmb;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human CLU, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Detected in blood plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, milk, seminal plasma and colon mucosa. Detected in the germinal center of colon lymphoid nodules and in colon parasympathetic ganglia of the Auerbach plexus (at protein level). Ubiquitous. Detected in brain, testis, ovary, liver and pancreas, and at lower levels in kidney, heart, spleen and lung.
- P10909 CLUS_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MMKTLLLFVGLLLTWESGQVLGDQTVSDNELQEMSNQGSKYVNKEIQNAVNGVKQIKTLIEKTNEERKTLLSNLEEAKKKKEDALNETRESETKLKELPGVCNETMMALWEECKPCLKQTCMKFYARVCRSGSGLVGRQLEEFLNQSSPFYFWMNGDRIDSLLENDRQQTHMLDVMQDHFSRASSIIDELFQDRFFTREPQDTYHYLPFSLPHRRPHFFFPKSRIVRSLMPFSPYEPLNFHAMFQPFLEMIHEAQQAMDIHFHSPAFQHPPTEFIREGDDDRTVCREIRHNSTGCLRMKDQCDKCREILSVDCSTNNPSQAKLRRELDESLQVAERLTRKYNELLKSYQWKMLNTSSLLEQLNEQFNWVSRLANLTQGEDQYYLRVTTVASHTSDSDVPSGVTEVVVKLFDSDPITVTVPVEVSRKNPKFMETVAEKALQEYRKKHREE
Research Backgrounds
Functions as extracellular chaperone that prevents aggregation of non native proteins. Prevents stress-induced aggregation of blood plasma proteins. Inhibits formation of amyloid fibrils by APP, APOC2, B2M, CALCA, CSN3, SNCA and aggregation-prone LYZ variants (in vitro). Does not require ATP. Maintains partially unfolded proteins in a state appropriate for subsequent refolding by other chaperones, such as HSPA8/HSC70. Does not refold proteins by itself. Binding to cell surface receptors triggers internalization of the chaperone-client complex and subsequent lysosomal or proteasomal degradation. Protects cells against apoptosis and against cytolysis by complement. Intracellular forms interact with ubiquitin and SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes and promote the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins. Promotes proteasomal degradation of COMMD1 and IKBKB. Modulates NF-kappa-B transcriptional activity. A mitochondrial form suppresses BAX-dependent release of cytochrome c into the cytoplasm and inhibit apoptosis. Plays a role in the regulation of cell proliferation. An intracellular form suppresses stress-induced apoptosis by stabilizing mitochondrial membrane integrity through interaction with HSPA5. Secreted form does not affect caspase or BAX-mediated intrinsic apoptosis and TNF-induced NF-kappa-B-activity. Secreted form act as an important modulator during neuronal differentiation through interaction with STMN3 (By similarity). Plays a role in the clearance of immune complexes that arise during cell injury (By similarity).
Does not affect caspase or BAX-mediated intrinsic apoptosis and TNF-induced NF-kappa-B-activity.
Does not affect caspase or BAX-mediated intrinsic apoptosis and TNF-induced NF-kappa-B-activity. Promotes cell death through interaction with BCL2L1 that releases and activates BAX.
Proteolytically cleaved on its way through the secretory system, probably within the Golgi lumen. Proteolytic cleavage is not necessary for its chaperone activity. All non-secreted forms are not proteolytically cleaved. Chaperone activity of uncleaved forms is dependent on a non-reducing envoronment.
Polyubiquitinated, leading to proteasomal degradation. Under cellular stress, the intracellular level of cleaved form is reduced due to proteasomal degradation.
Extensively glycosylated with sulfated N-linked carbohydrates. About 30% of the protein mass is comprised of complex N-linked carbohydrate. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress induces changes in glycosylation status and increases level of hypoglycosylated forms. Core carbohydrates are essential for chaperone activity. Non-secreted forms are hypoglycosylated or unglycosylated.
Secreted.
Note: Can retrotranslocate from the secretory compartments to the cytosol upon cellular stress.
Cytoplasm.
Note: Keeps cytoplasmic localization in stressed and unstressed cell.
Cytoplasm.
Note: Keeps cytoplasmic localization in stressed and unstressed cell.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Mitochondrion membrane>Peripheral membrane protein>Cytoplasmic side. Cytoplasm>Cytosol. Microsome. Endoplasmic reticulum. Mitochondrion. Mitochondrion membrane. Cytoplasm>Perinuclear region. Cytoplasmic vesicle>Secretory vesicle>Chromaffin granule.
Note: Secreted isoforms can retrotranslocate from the secretory compartments to the cytosol upon cellular stress (PubMed:17451556). Detected in perinuclear foci that may be aggresomes containing misfolded, ubiquitinated proteins (PubMed:20068069). Detected at the mitochondrion membrane upon induction of apoptosis (PubMed:17689225). Under ER stress, a immaturely glycosylated pre-secreted form retrotranslocates from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-Golgi network to the cytoplasm to localize in the mitochondria through HSPA5 interaction (PubMed:22689054). ER stress reduces secretion (PubMed:22689054). Under the stress, minor amounts of non-secreted forms accumulate in cytoplasm (PubMed:24073260, PubMed:22689054, PubMed:17451556). Non-secreted forms emerge mainly from failed translocation, alternative splicing or non-canonical initiation start codon (PubMed:24073260, PubMed:12551933).
Detected in blood plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, milk, seminal plasma and colon mucosa. Detected in the germinal center of colon lymphoid nodules and in colon parasympathetic ganglia of the Auerbach plexus (at protein level). Ubiquitous. Detected in brain, testis, ovary, liver and pancreas, and at lower levels in kidney, heart, spleen and lung.
Belongs to the clusterin family.
Research Fields
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Complement and coagulation cascades. (View pathway)
References
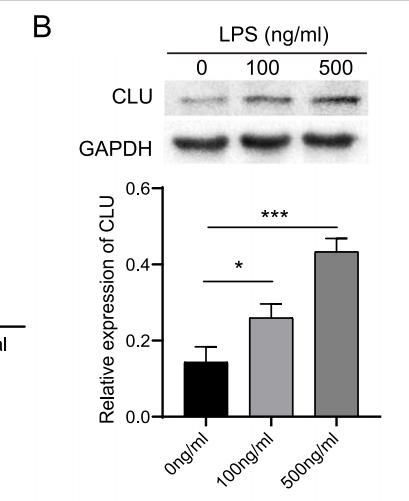
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: TEV-1 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.