DR5 Antibody - #DF6368
| Product: | DR5 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6368 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to DR5 |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Mol.Wt.: | 48kDa; 48kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | O14763 |
| RRID: | AB_2838332 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6368, RRID:AB_2838332.
Fold/Unfold
Fas like protein; Apoptosis inducing protein TRICK2A/2B; Apoptosis inducing receptor TRAIL R2; CD262; CD262 antigen; Cytotoxic TRAIL receptor 2; Death domain containing receptor for TRAIL/Apo 2L; Death receptor 5; DR5; KILLER; KILLER/DR5; OTTHUMP00000123492; OTTHUMP00000123493; p53 regulated DNA damage inducible cell death receptor(killer); TNF related apoptosis inducing ligand receptor 2; TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 2; TNFRSF10B; TR10B_HUMAN; TRAIL R2; TRAIL receptor 2; TRAIL-R2; TRAILR2; TRICK2; TRICK2A; TRICK2B; TRICKB; Tumor necrosis factor receptor like protein ZTNFR9; Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 10B; Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 10b; ZTNFR9;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human DR5, corresponding to a region within N-terminal amino acids.
Widely expressed in adult and fetal tissues; very highly expressed in tumor cell lines such as HeLaS3, K-562, HL-60, SW480, A-549 and G-361; highly expressed in heart, peripheral blood lymphocytes, liver, pancreas, spleen, thymus, prostate, ovary, uterus, placenta, testis, esophagus, stomach and throughout the intestinal tract; not detectable in brain.
- O14763 TR10B_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MEQRGQNAPAASGARKRHGPGPREARGARPGPRVPKTLVLVVAAVLLLVSAESALITQQDLAPQQRAAPQQKRSSPSEGLCPPGHHISEDGRDCISCKYGQDYSTHWNDLLFCLRCTRCDSGEVELSPCTTTRNTVCQCEEGTFREEDSPEMCRKCRTGCPRGMVKVGDCTPWSDIECVHKESGTKHSGEVPAVEETVTSSPGTPASPCSLSGIIIGVTVAAVVLIVAVFVCKSLLWKKVLPYLKGICSGGGGDPERVDRSSQRPGAEDNVLNEIVSILQPTQVPEQEMEVQEPAEPTGVNMLSPGESEHLLEPAEAERSQRRRLLVPANEGDPTETLRQCFDDFADLVPFDSWEPLMRKLGLMDNEIKVAKAEAAGHRDTLYTMLIKWVNKTGRDASVHTLLDALETLGERLAKQKIEDHLLSSGKFMYLEGNADSAMS
Research Backgrounds
Receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TNFSF10/TRAIL. The adapter molecule FADD recruits caspase-8 to the activated receptor. The resulting death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) performs caspase-8 proteolytic activation which initiates the subsequent cascade of caspases (aspartate-specific cysteine proteases) mediating apoptosis. Promotes the activation of NF-kappa-B. Essential for ER stress-induced apoptosis.
Membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein.
Widely expressed in adult and fetal tissues; very highly expressed in tumor cell lines such as HeLaS3, K-562, HL-60, SW480, A-549 and G-361; highly expressed in heart, peripheral blood lymphocytes, liver, pancreas, spleen, thymus, prostate, ovary, uterus, placenta, testis, esophagus, stomach and throughout the intestinal tract; not detectable in brain.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > p53 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Necroptosis. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Measles.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity. (View pathway)
References
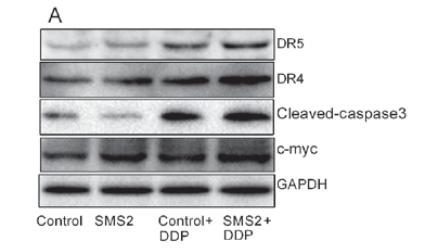
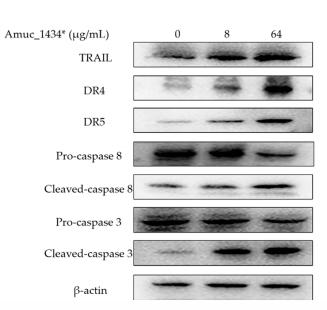
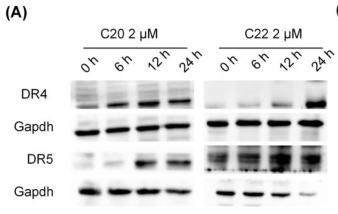
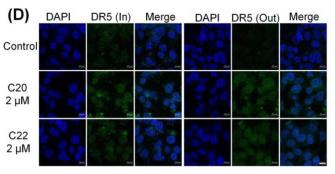
Application: WB Species: human Sample: LS174T cells
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HepG2 cells
Application: IF/ICC Species: Human Sample: HepG2 cells
Application: WB Species: human Sample: HepG2 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.