ATP2A2 Antibody - #DF6240
| Product: | ATP2A2 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6240 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to ATP2A2 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 115kDa; 115kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P16615 |
| RRID: | AB_2838206 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6240, RRID:AB_2838206.
Fold/Unfold
AT2A2_HUMAN; Atp2a2; ATP2B; ATPase Ca++ transporting cardiac muscle slow twitch 2; Calcium pump 2; Calcium-transporting ATPase sarcoplasmic reticulum type; Calcium-transporting ATPase sarcoplasmic reticulum type slow twitch skeletal muscle isoform; Cardiac Ca2+ ATPase; DAR; DD; Endoplasmic reticulum class 1/2 Ca(2+) ATPase; MGC45367; Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2; SERCA 2; SERCA2; serca2a; slow twitch skeletal muscle isoform; SR Ca(2+)-ATPase 2;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human ATP2A2, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Isoform 1 is widely expressed in smooth muscle and nonmuscle tissues such as in adult skin epidermis, with highest expression in liver, pancreas and lung, and intermediate expression in brain, kidney and placenta. Also expressed at lower levels in heart and skeletal muscle. Isoforms 2 and 3 are highly expressed in the heart and slow twitch skeletal muscle. Expression of isoform 3 is predominantly restricted to cardiomyocytes and in close proximity to the sarcolemma. Both isoforms are mildly expressed in lung, kidney, liver, pancreas and placenta. Expression of isoform 3 is amplified during monocytic differentiation and also observed in the fetal heart.
- P16615 AT2A2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MENAHTKTVEEVLGHFGVNESTGLSLEQVKKLKERWGSNELPAEEGKTLLELVIEQFEDLLVRILLLAACISFVLAWFEEGEETITAFVEPFVILLILVANAIVGVWQERNAENAIEALKEYEPEMGKVYRQDRKSVQRIKAKDIVPGDIVEIAVGDKVPADIRLTSIKSTTLRVDQSILTGESVSVIKHTDPVPDPRAVNQDKKNMLFSGTNIAAGKAMGVVVATGVNTEIGKIRDEMVATEQERTPLQQKLDEFGEQLSKVISLICIAVWIINIGHFNDPVHGGSWIRGAIYYFKIAVALAVAAIPEGLPAVITTCLALGTRRMAKKNAIVRSLPSVETLGCTSVICSDKTGTLTTNQMSVCRMFILDRVEGDTCSLNEFTITGSTYAPIGEVHKDDKPVNCHQYDGLVELATICALCNDSALDYNEAKGVYEKVGEATETALTCLVEKMNVFDTELKGLSKIERANACNSVIKQLMKKEFTLEFSRDRKSMSVYCTPNKPSRTSMSKMFVKGAPEGVIDRCTHIRVGSTKVPMTSGVKQKIMSVIREWGSGSDTLRCLALATHDNPLRREEMHLEDSANFIKYETNLTFVGCVGMLDPPRIEVASSVKLCRQAGIRVIMITGDNKGTAVAICRRIGIFGQDEDVTSKAFTGREFDELNPSAQRDACLNARCFARVEPSHKSKIVEFLQSFDEITAMTGDGVNDAPALKKAEIGIAMGSGTAVAKTASEMVLADDNFSTIVAAVEEGRAIYNNMKQFIRYLISSNVGEVVCIFLTAALGFPEALIPVQLLWVNLVTDGLPATALGFNPPDLDIMNKPPRNPKEPLISGWLFFRYLAIGCYVGAATVGAAAWWFIAADGGPRVSFYQLSHFLQCKEDNPDFEGVDCAIFESPYPMTMALSVLVTIEMCNALNSLSENQSLLRMPPWENIWLVGSICLSMSLHFLILYVEPLPLIFQITPLNVTQWLMVLKISLPVILMDETLKFVARNYLEPGKECVQPATKSCSFSACTDGISWPFVLLIMPLVIWVYSTDTNFSDMFWS
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the translocation of calcium from the cytosol to the sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen. Isoform 2 is involved in the regulation of the contraction/relaxation cycle. Acts as a regulator of TNFSF11-mediated Ca(2+) signaling pathways via its interaction with TMEM64 which is critical for the TNFSF11-induced CREB1 activation and mitochondrial ROS generation necessary for proper osteoclast generation. Association between TMEM64 and SERCA2 in the ER leads to cytosolic Ca (2+) spiking for activation of NFATC1 and production of mitochondrial ROS, thereby triggering Ca (2+) signaling cascades that promote osteoclast differentiation and activation (By similarity).
Nitrated under oxidative stress. Nitration on the two tyrosine residues inhibits catalytic activity.
Endoplasmic reticulum membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein.
Isoform 1 is widely expressed in smooth muscle and nonmuscle tissues such as in adult skin epidermis, with highest expression in liver, pancreas and lung, and intermediate expression in brain, kidney and placenta. Also expressed at lower levels in heart and skeletal muscle. Isoforms 2 and 3 are highly expressed in the heart and slow twitch skeletal muscle. Expression of isoform 3 is predominantly restricted to cardiomyocytes and in close proximity to the sarcolemma. Both isoforms are mildly expressed in lung, kidney, liver, pancreas and placenta. Expression of isoform 3 is amplified during monocytic differentiation and also observed in the fetal heart.
Ca(2+) and ATP binding cause major rearrangements of the cytoplasmic and transmembrane domains. According to the E1-E2 model, Ca(2+) binding to the cytosolic domain of the pump in the high-affinity E1 conformation is followed by the ATP-dependent phosphorylation of the active site Asp, giving rise to E1P. A conformational change of the phosphoenzyme gives rise to the low-affinity E2P state that exposes the Ca(2+) ions to the lumenal side and promotes Ca(2+) release. Dephosphorylation of the active site Asp mediates the subsequent return to the E1 conformation.
PLN and SLN both have a single transmembrane helix; both occupy a similar binding site that is situated between the ATP2A2 transmembrane helices.
Belongs to the cation transport ATPase (P-type) (TC 3.A.3) family. Type IIA subfamily.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Calcium signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Alzheimer's disease.
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM).
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC).
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM).
· Organismal Systems > Circulatory system > Cardiac muscle contraction. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Circulatory system > Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Thyroid hormone signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Pancreatic secretion.
References
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample:
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample:
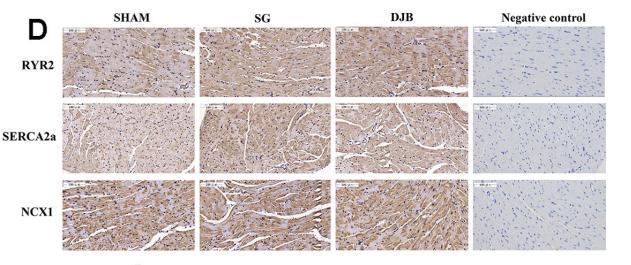
Application: IHC Species: rat Sample: myocardial Ca2
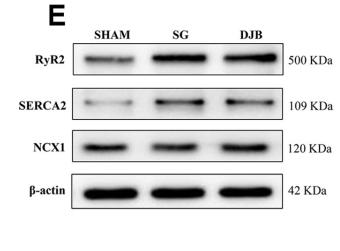
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: myocardial Ca2
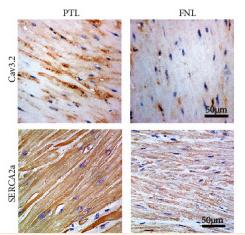
Application: IHC Species: Human Sample: clinical myometrium tissues
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.