pan Actin Antibody - #AF0115
| Product: | pan Actin Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF0115 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to pan Actin |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 45kDa; 42kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P60709 | Q9BYX7 | P63261 |
| RRID: | AB_2833265 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF0115, RRID:AB_2833265.
Fold/Unfold
A26C1A; A26C1B; ACTB; ACTB_HUMAN; Actin beta; Actin cytoplasmic 1; Actin, cytoplasmic 1, N-terminally processed; Actx; b actin; Beta cytoskeletal actin; Beta-actin; BRWS1; E430023M04Rik; MGC128179; PS1TP5 binding protein 1; PS1TP5BP1; ACT; ACTBL3; FKSG30; POTE ankyrin domain family member K pseudogene; POTE2delta; POTEK; ACT; ACTB; ACTG; ACTG_HUMAN; actg1; Actin; Actin, cytoplasmic 2; Actin, gamma 1; Actin, gamma 1 propeptide; Actin, gamma; BRWS2; cytoplasmic 2; Cytoskeletal gamma actin; Deafness, autosomal dominant 20; Deafness, autosomal dominant 26; DFNA20; DFNA26; epididymis luminal protein 176; Gamma-actin; HEL-176; N-terminally processed;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Actin-pan.
- P60709 ACTB_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MDDDIAALVVDNGSGMCKAGFAGDDAPRAVFPSIVGRPRHQGVMVGMGQKDSYVGDEAQSKRGILTLKYPIEHGIVTNWDDMEKIWHHTFYNELRVAPEEHPVLLTEAPLNPKANREKMTQIMFETFNTPAMYVAIQAVLSLYASGRTTGIVMDSGDGVTHTVPIYEGYALPHAILRLDLAGRDLTDYLMKILTERGYSFTTTAEREIVRDIKEKLCYVALDFEQEMATAASSSSLEKSYELPDGQVITIGNERFRCPEALFQPSFLGMESCGIHETTFNSIMKCDVDIRKDLYANTVLSGGTTMYPGIADRMQKEITALAPSTMKIKIIAPPERKYSVWIGGSILASLSTFQQMWISKQEYDESGPSIVHRKCF
- Q9BYX7 ACTBM_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MDDDTAVLVIDNGSGMCKAGFAGDDAPQAVFPSIVGRPRHQGMMEGMHQKESYVGKEAQSKRGMLTLKYPMEHGIITNWDDMEKIWHHTFYNELRVAPEEHPILLTEAPLNPKANREKMTQIMFETFNTPAMYVAIQAVLSLYTSGRTTGIVMDSGDGFTHTVPIYEGNALPHATLRLDLAGRELTDYLMKILTERGYRFTTTAEQEIVRDIKEKLCYVALDSEQEMAMAASSSSVEKSYELPDGQVITIGNERFRCPEALFQPCFLGMESCGIHKTTFNSIVKSDVDIRKDLYTNTVLSGGTTMYPGIAHRMQKEITALAPSIMKIKIIAPPKRKYSVWVGGSILASLSTFQQMWISKQEYDESGPSIVHRKCF
- P63261 ACTG_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MEEEIAALVIDNGSGMCKAGFAGDDAPRAVFPSIVGRPRHQGVMVGMGQKDSYVGDEAQSKRGILTLKYPIEHGIVTNWDDMEKIWHHTFYNELRVAPEEHPVLLTEAPLNPKANREKMTQIMFETFNTPAMYVAIQAVLSLYASGRTTGIVMDSGDGVTHTVPIYEGYALPHAILRLDLAGRDLTDYLMKILTERGYSFTTTAEREIVRDIKEKLCYVALDFEQEMATAASSSSLEKSYELPDGQVITIGNERFRCPEALFQPSFLGMESCGIHETTFNSIMKCDVDIRKDLYANTVLSGGTTMYPGIADRMQKEITALAPSTMKIKIIAPPERKYSVWIGGSILASLSTFQQMWISKQEYDESGPSIVHRKCF
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Actin is a highly conserved protein that polymerizes to produce filaments that form cross-linked networks in the cytoplasm of cells. Actin exists in both monomeric (G-actin) and polymeric (F-actin) forms, both forms playing key functions, such as cell motility and contraction. In addition to their role in the cytoplasmic cytoskeleton, G- and F-actin also localize in the nucleus, and regulate gene transcription and motility and repair of damaged DNA.
ISGylated.
Oxidation of Met-44 and Met-47 by MICALs (MICAL1, MICAL2 or MICAL3) to form methionine sulfoxide promotes actin filament depolymerization. MICAL1 and MICAL2 produce the (R)-S-oxide form. The (R)-S-oxide form is reverted by MSRB1 and MSRB2, which promote actin repolymerization.
Monomethylation at Lys-84 (K84me1) regulates actin-myosin interaction and actomyosin-dependent processes. Demethylation by ALKBH4 is required for maintaining actomyosin dynamics supporting normal cleavage furrow ingression during cytokinesis and cell migration.
Methylated at His-73 by SETD3. Methylation at His-73 is required for smooth muscle contraction of the laboring uterus during delivery (By similarity).
N-terminal acetylation by NAA80 affects actin filament depolymerization and elongation, including elongation driven by formins. In contrast, filament nucleation by the Arp2/3 complex is not affected.
(Microbial infection) Monomeric actin is cross-linked by V.cholerae toxins RtxA and VgrG1 in case of infection: bacterial toxins mediate the cross-link between Lys-50 of one monomer and Glu-270 of another actin monomer, resulting in formation of highly toxic actin oligomers that cause cell rounding. The toxin can be highly efficient at very low concentrations by acting on formin homology family proteins: toxic actin oligomers bind with high affinity to formins and adversely affect both nucleation and elongation abilities of formins, causing their potent inhibition in both profilin-dependent and independent manners.
Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton. Nucleus.
Note: Localized in cytoplasmic mRNP granules containing untranslated mRNAs.
Belongs to the actin family.
Oxidation of Met-44 and Met-47 by MICALs (MICAL1, MICAL2 or MICAL3) to form methionine sulfoxide promotes actin filament depolymerization. MICAL1 and MICAL2 produce the (R)-S-oxide form. The (R)-S-oxide form is reverted by MSRB1 and MSRB2, which promote actin repolymerization (By similarity).
Monomethylation at Lys-84 (K84me1) regulates actin-myosin interaction and actomyosin-dependent processes. Demethylation by ALKBH4 is required for maintaining actomyosin dynamics supporting normal cleavage furrow ingression during cytokinesis and cell migration.
Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton.
Expressed in some hepatocellular carcinomas.
Belongs to the actin family.
Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells.
Oxidation of Met-44 and Met-47 by MICALs (MICAL1, MICAL2 or MICAL3) to form methionine sulfoxide promotes actin filament depolymerization. MICAL1 and MICAL2 produce the (R)-S-oxide form. The (R)-S-oxide form is reverted by MSRB1 and MSRB2, which promote actin repolymerization.
Monomethylation at Lys-84 (K84me1) regulates actin-myosin interaction and actomyosin-dependent processes. Demethylation by ALKBH4 is required for maintaining actomyosin dynamics supporting normal cleavage furrow ingression during cytokinesis and cell migration.
N-terminal acetylation by NAA80 affects actin filament depolymerization and elongation, including elongation driven by formins. In contrast, filament nucleation by the Arp2/3 complex is not affected.
Methylated at His-73 by SETD3.
(Microbial infection) Monomeric actin is cross-linked by V.cholerae toxins RtxA and VgrG1 in case of infection: bacterial toxins mediate the cross-link between Lys-50 of one monomer and Glu-270 of another actin monomer, resulting in formation of highly toxic actin oligomers that cause cell rounding. The toxin can be highly efficient at very low concentrations by acting on formin homology family proteins: toxic actin oligomers bind with high affinity to formins and adversely affect both nucleation and elongation abilities of formins, causing their potent inhibition in both profilin-dependent and independent manners.
Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton.
Belongs to the actin family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Phagosome. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Focal adhesion. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Adherens junction. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Tight junction. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell motility > Regulation of actin cytoskeleton. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Rap1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Vibrio cholerae infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Shigellosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Salmonella infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM).
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC).
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM).
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Viral myocarditis.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Platelet activation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Leukocyte transendothelial migration. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Thyroid hormone signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Oxytocin signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Gastric acid secretion.
References
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: testes
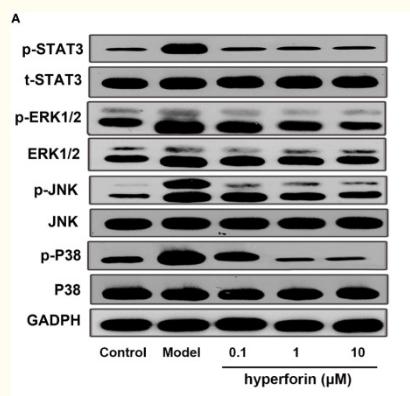
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: γδ T Cells
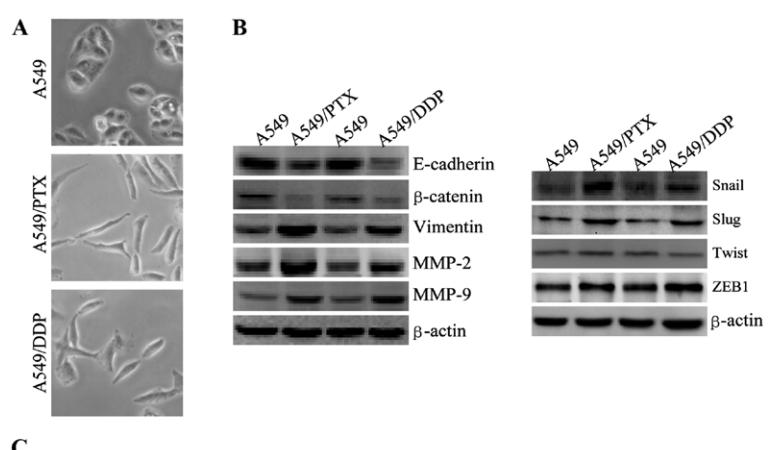
Application: WB Species: human Sample: A549 cells
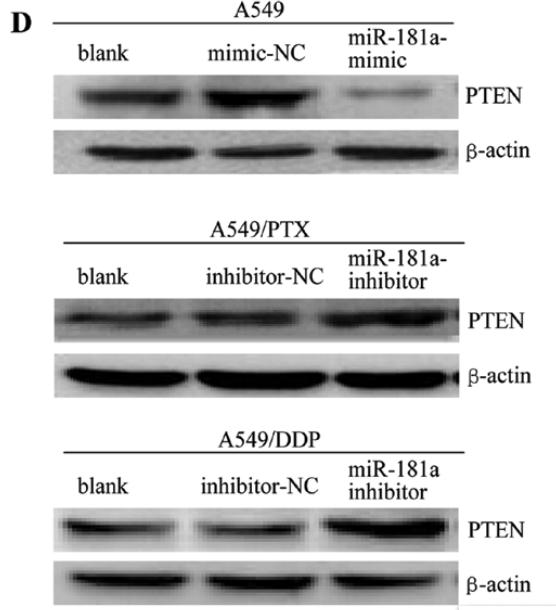
Application: WB Species: human Sample: A549, A549/PTX or A549/DDP cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.