VDAC1 Antibody - #DF6140
| Product: | VDAC1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6140 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to VDAC1 |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 31kDa; 31kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P21796 |
| RRID: | AB_2838107 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6140, RRID:AB_2838107.
Fold/Unfold
N2441; OMP2; POR1; hVDAC1; MGC111064; Mitochondrial Porin; Outer mitochondrial membrane protein porin 1; Plasmalemmal porin; Porin 31HL; Porin 31HM; VDAC; VDAC-1; Vdac1; VDAC1_HUMAN; Voltage dependent anion channel 1; Voltage dependent anion selective channel protein 1; Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 1; YNL055C; YNL2441C;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human VDAC1, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
- P21796 VDAC1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAVPPTYADLGKSARDVFTKGYGFGLIKLDLKTKSENGLEFTSSGSANTETTKVTGSLETKYRWTEYGLTFTEKWNTDNTLGTEITVEDQLARGLKLTFDSSFSPNTGKKNAKIKTGYKREHINLGCDMDFDIAGPSIRGALVLGYEGWLAGYQMNFETAKSRVTQSNFAVGYKTDEFQLHTNVNDGTEFGGSIYQKVNKKLETAVNLAWTAGNSNTRFGIAAKYQIDPDACFSAKVNNSSLIGLGYTQTLKPGIKLTLSALLDGKNVNAGGHKLGLGLEFQA
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Forms a channel through the mitochondrial outer membrane and also the plasma membrane. The channel at the outer mitochondrial membrane allows diffusion of small hydrophilic molecules; in the plasma membrane it is involved in cell volume regulation and apoptosis. It adopts an open conformation at low or zero membrane potential and a closed conformation at potentials above 30-40 mV. The open state has a weak anion selectivity whereas the closed state is cation-selective. May participate in the formation of the permeability transition pore complex (PTPC) responsible for the release of mitochondrial products that triggers apoptosis.
Phosphorylation at Ser-193 by NEK1 promotes the open conformational state preventing excessive mitochondrial membrane permeability and subsequent apoptotic cell death after injury. Phosphorylation by the AKT-GSK3B axis stabilizes the protein probably by preventing ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation.
Ubiquitinated by PRKN during mitophagy, leading to its degradation and enhancement of mitophagy. Deubiquitinated by USP30.
Mitochondrion outer membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Membrane raft>Multi-pass membrane protein.
Heart, liver and skeletal muscle.
Consists mainly of a membrane-spanning beta-barrel formed by 19 beta-strands. The helical N-terminus folds back into the pore opening and plays a role in voltage-gated channel activity.
Belongs to the eukaryotic mitochondrial porin family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Necroptosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cellular senescence. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Calcium signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Parkinson's disease.
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Huntington's disease.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > NOD-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Cholesterol metabolism.
References
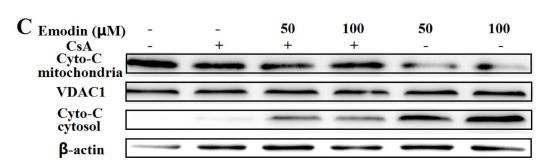
Application: WB Species: Human Sample:
Application: WB Species: human Sample:
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: cholangiocarcinoma cell
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: L02 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.