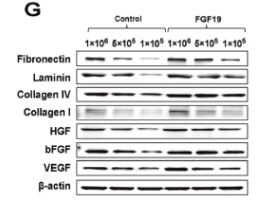
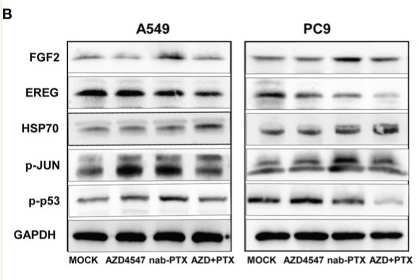
FGF2 Antibody - #DF6038
| Product: | FGF2 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6038 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to FGF2 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Mol.Wt.: | 21kDa; 31kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P09038 |
| RRID: | AB_2838011 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6038, RRID:AB_2838011.
Fold/Unfold
Basic fibroblast growth factor; Basic fibroblast growth factor bFGF; BFGF; FGF 2; FGF B; FGF-2; Fgf2; FGF2 basic; FGF2_HUMAN; FGFB; Fibroblast growth factor 2 (basic); Fibroblast growth factor 2; Fibroblast growth factor, basic; HBGF 2; HBGF-2; HBGF2; HBGH 2; HBGH2; Heparin binding growth factor 2 precursor; Heparin-binding growth factor 2; Prostatropin;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human FGF2, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Expressed in granulosa and cumulus cells. Expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma cells, but not in non-cancerous liver tissue.
- P09038 FGF2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MVGVGGGDVEDVTPRPGGCQISGRGARGCNGIPGAAAWEAALPRRRPRRHPSVNPRSRAAGSPRTRGRRTEERPSGSRLGDRGRGRALPGGRLGGRGRGRAPERVGGRGRGRGTAAPRAAPAARGSRPGPAGTMAAGSITTLPALPEDGGSGAFPPGHFKDPKRLYCKNGGFFLRIHPDGRVDGVREKSDPHIKLQLQAEERGVVSIKGVCANRYLAMKEDGRLLASKCVTDECFFFERLESNNYNTYRSRKYTSWYVALKRTGQYKLGSKTGPGQKAILFLPMSAKS
Research Backgrounds
Acts as a ligand for FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4. Also acts as an integrin ligand which is required for FGF2 signaling. Binds to integrin ITGAV:ITGB3. Plays an important role in the regulation of cell survival, cell division, cell differentiation and cell migration. Functions as a potent mitogen in vitro. Can induce angiogenesis.
Phosphorylation at Tyr-215 regulates FGF2 unconventional secretion.
Several N-termini starting at positions 94, 125, 126, 132, 143 and 162 have been identified by direct sequencing.
Secreted. Nucleus.
Note: Exported from cells by an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)/Golgi-independent mechanism. Unconventional secretion of FGF2 occurs by direct translocation across the plasma membrane. Binding of exogenous FGF2 to FGFR facilitates endocytosis followed by translocation of FGF2 across endosomal membrane into the cytosol. Nuclear import from the cytosol requires the classical nuclear import machinery, involving proteins KPNA1 and KPNB1, as well as CEP57.
Expressed in granulosa and cumulus cells. Expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma cells, but not in non-cancerous liver tissue.
Belongs to the heparin-binding growth factors family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell motility > Regulation of actin cytoskeleton. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Ras signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Rap1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Melanoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
References
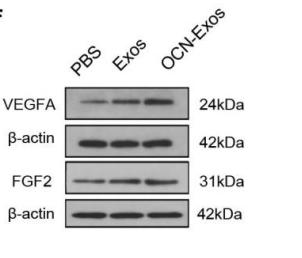
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: ADSCs
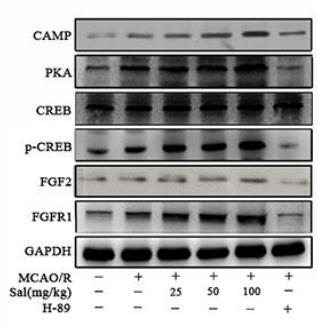
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample:
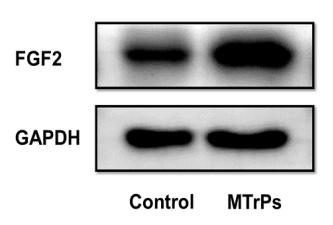
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: CDSCs
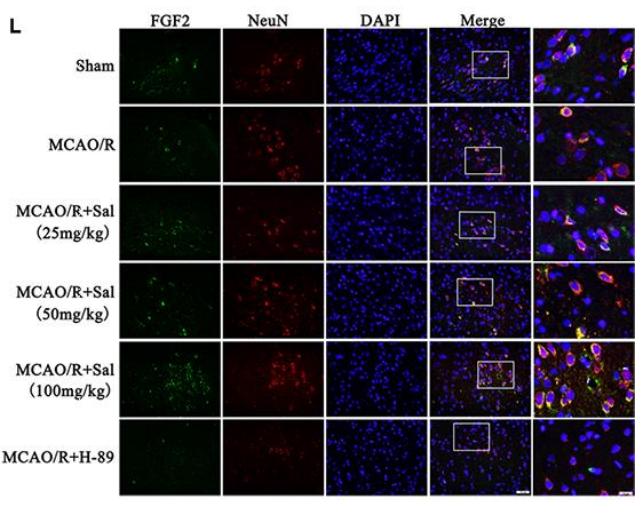
Application: IHC Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: RAOECs
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.