GRO alpha Antibody - #AF5403
| Product: | GRO alpha Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF5403 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to GRO alpha |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Mol.Wt.: | 11 kDa; 11kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P09341 |
| RRID: | AB_2837887 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5403, RRID:AB_2837887.
Fold/Unfold
C-X-C motif chemokine 1; Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (melanoma growth stimulating activity, alpha); chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1; CINC-1; CXCL1; Cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant 1; Fibroblast secretory protein; Fsp; Gro 1; Gro A; Gro; GRO protein, alpha; GRO-alpha(1-73); GRO-alpha(6-73); Gro1; GRO1 oncogene (melanoma growth stimulating activity, alpha); GRO1 oncogene (melanoma growth-stimulating activity); Gro1 oncogene; GROa; GROA_HUMAN; Growth-regulated alpha protein; KC; KC chemokine, mouse, homolog of; melanoma growth stimulatory activity alpha; Melanoma growth stimulatory activity; Melanoma growth stimulatory activity, alpha; MGSA alpha; MGSA; MGSA-a; N51; NAP-3; NAP3; Neutrophil-activating protein 3; Platelet-derived growth factor-inducible protein KC; Scyb 1; Scyb1; Secretory protein N51; Small inducible cytokine subfamily B, member 1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human GRO alpha, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- P09341 GROA_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MARAALSAAPSNPRLLRVALLLLLLVAAGRRAAGASVATELRCQCLQTLQGIHPKNIQSVNVKSPGPHCAQTEVIATLKNGRKACLNPASPIVKKIIEKMLNSDKSN
Research Backgrounds
Has chemotactic activity for neutrophils. May play a role in inflammation and exerts its effects on endothelial cells in an autocrine fashion. In vitro, the processed forms GRO-alpha(4-73), GRO-alpha(5-73) and GRO-alpha(6-73) show a 30-fold higher chemotactic activity.
N-terminal processed forms GRO-alpha(4-73), GRO-alpha(5-73) and GRO-alpha(6-73) are produced by proteolytic cleavage after secretion from peripheral blood monocytes.
Secreted.
Belongs to the intercrine alpha (chemokine CxC) family.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TNF signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Salmonella infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Legionellosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Amoebiasis.
· Human Diseases > Immune diseases > Rheumatoid arthritis.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Chemokine signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > NOD-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > IL-17 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
Application: IF/ICC Species: Mouse Sample: Raw264.7 cells
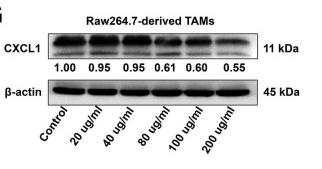
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: M2 phenotype RAW264.7 cells
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: breast tumor tissues
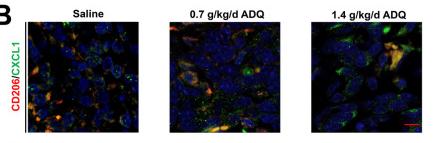
Application: IF/ICC Species: Mice Sample: breast tumor tissues
Application: IF/ICC Species: Mouse Sample: breast cancer cells
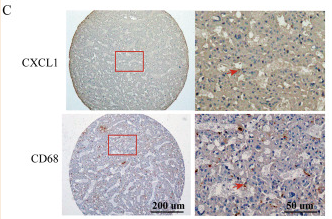
Application: IHC Species: Human Sample:
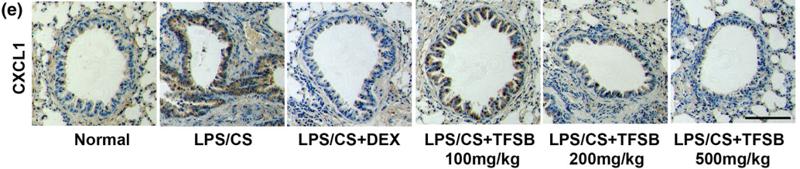
Application: IHC Species: mouse Sample: lung
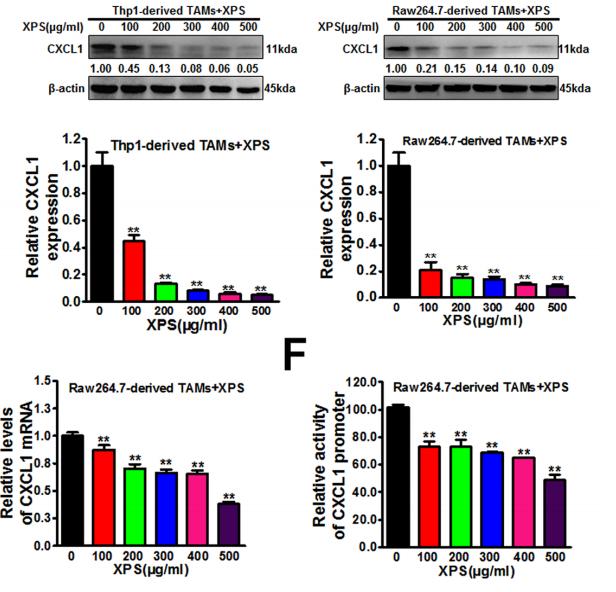
Application: WB Species: human and mouse Sample: TAMs
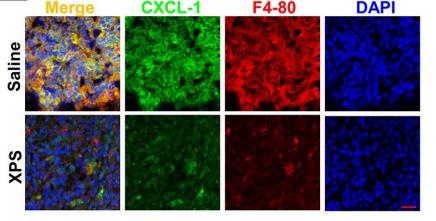
Application: IF/ICC Species: mouse Sample: macrophages
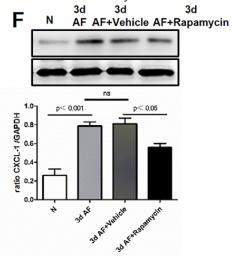
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: corneas
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.