Glut 4 Antibody - #AF5386
| Product: | Glut 4 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF5386 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Glut 4 |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit |
| Mol.Wt.: | 54 kDa; 55kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P14672 |
| RRID: | AB_2837871 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5386, RRID:AB_2837871.
Fold/Unfold
insulin-responsive; Glucose transporter GLUT 4; Glucose transporter type 4; Glucose transporter type 4 insulin responsive; GLUT 4; GLUT-4; GLUT4; GTR4_HUMAN; Insulin responsive glucose transporter type 4; kug; SLC 2A4; SLC2A4; solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter) member 4; Solute carrier family 2 member 4; Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 4;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Glut 4, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- P14672 GLUT4_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MPSGFQQIGSEDGEPPQQRVTGTLVLAVFSAVLGSLQFGYNIGVINAPQKVIEQSYNETWLGRQGPEGPSSIPPGTLTTLWALSVAIFSVGGMISSFLIGIISQWLGRKRAMLVNNVLAVLGGSLMGLANAAASYEMLILGRFLIGAYSGLTSGLVPMYVGEIAPTHLRGALGTLNQLAIVIGILIAQVLGLESLLGTASLWPLLLGLTVLPALLQLVLLPFCPESPRYLYIIQNLEGPARKSLKRLTGWADVSGVLAELKDEKRKLERERPLSLLQLLGSRTHRQPLIIAVVLQLSQQLSGINAVFYYSTSIFETAGVGQPAYATIGAGVVNTVFTLVSVLLVERAGRRTLHLLGLAGMCGCAILMTVALLLLERVPAMSYVSIVAIFGFVAFFEIGPGPIPWFIVAELFSQGPRPAAMAVAGFSNWTSNFIIGMGFQYVAEAMGPYVFLLFAVLLLGFFIFTFLRVPETRGRTFDQISAAFHRTPSLLEQEVKPSTELEYLGPDEND
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Insulin-regulated facilitative glucose transporter, which plays a key role in removal of glucose from circulation. Response to insulin is regulated by its intracellular localization: in the absence of insulin, it is efficiently retained intracellularly within storage compartments in muscle and fat cells. Upon insulin stimulation, translocates from these compartments to the cell surface where it transports glucose from the extracellular milieu into the cell.
Sumoylated.
Cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Endomembrane system>Multi-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasm>Perinuclear region.
Note: Localizes primarily to the perinuclear region, undergoing continued recycling to the plasma membrane where it is rapidly reinternalized (PubMed:8300557). The dileucine internalization motif is critical for intracellular sequestration (PubMed:8300557). Insulin stimulation induces translocation to the cell membrane (By similarity).
Skeletal and cardiac muscles; brown and white fat.
The dileucine internalization motif is critical for intracellular sequestration.
Belongs to the major facilitator superfamily. Sugar transporter (TC 2.A.1.1) family. Glucose transporter subfamily.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > FoxO signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > AMPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Type II diabetes mellitus.
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Insulin resistance.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Insulin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Adipocytokine signaling pathway.
References
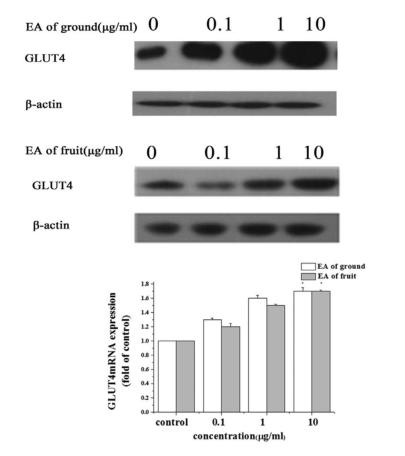
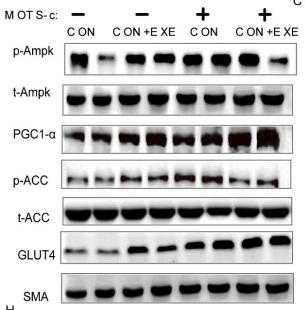
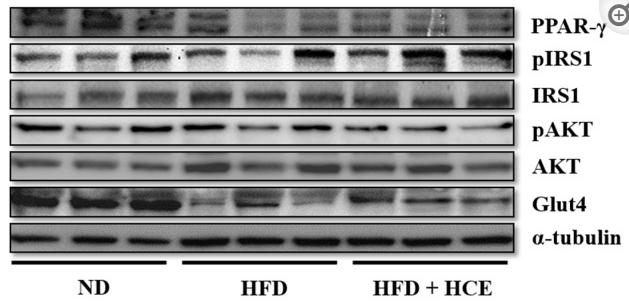
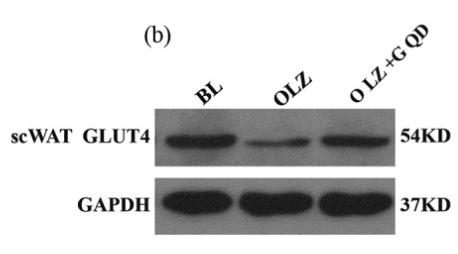
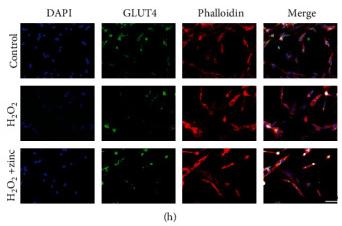
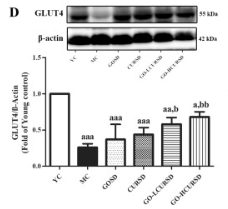
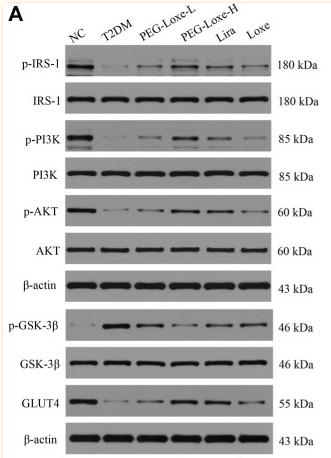
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: hippocampal homogenates
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: epididymal white adipose tissue
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: TCMK-1 cells
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: skeletal muscle cells
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample:
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.