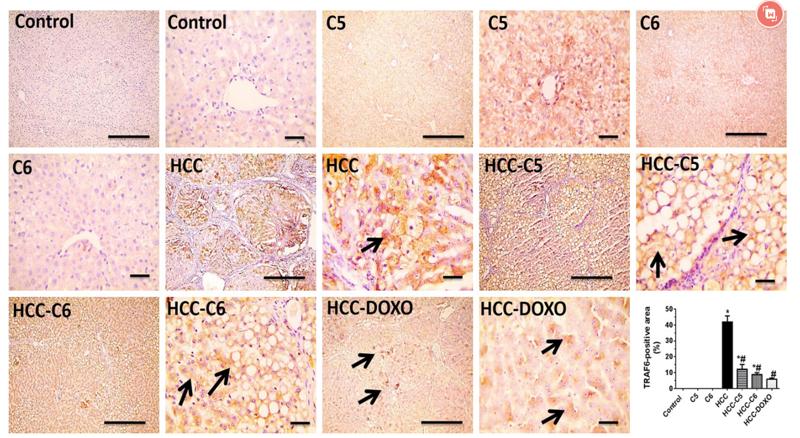
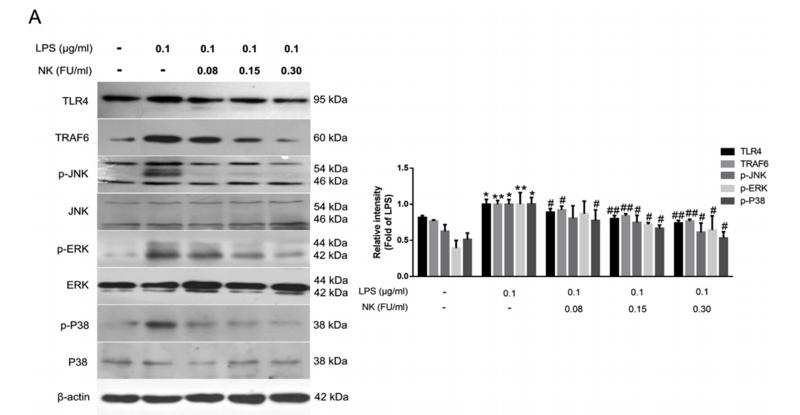
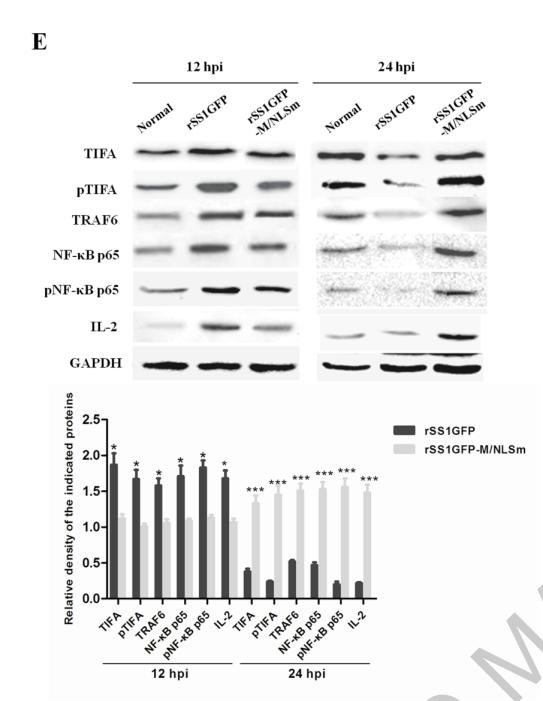
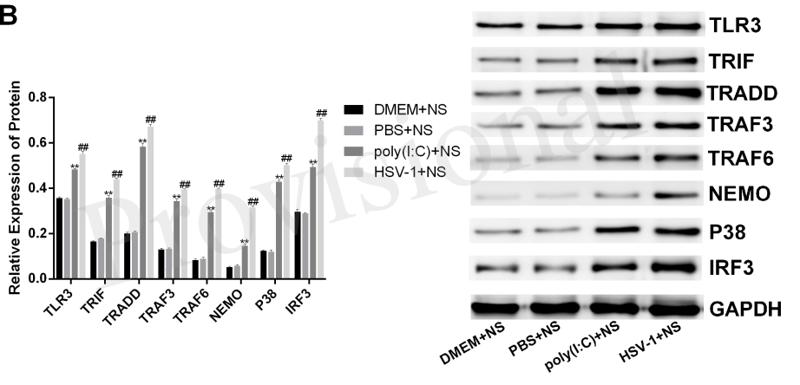
TRAF6 Antibody - #AF5376
| Product: | TRAF6 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF5376 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to TRAF6 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 58 kDa; 60kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q9Y4K3 |
| RRID: | AB_2810280 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5376, RRID:AB_2810280.
Fold/Unfold
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRAF6; Interleukin 1 signal transducer; Interleukin-1 signal transducer; MGC 3310; MGC:3310; MGC3310; OTTHUMP00000232772; OTTHUMP00000232773; RING finger protein 85; RNF 85; RNF85; TNF receptor associated factor 6; TNF receptor-associated factor 6; TNF receptor-associated factor 6, E3 ubiquitin protein ligase; TRAF 6; Traf6; TRAF6_HUMAN;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human TRAF6, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Expressed in heart, brain, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney and pancreas.
- Q9Y4K3 TRAF6_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSLLNCENSCGSSQSESDCCVAMASSCSAVTKDDSVGGTASTGNLSSSFMEEIQGYDVEFDPPLESKYECPICLMALREAVQTPCGHRFCKACIIKSIRDAGHKCPVDNEILLENQLFPDNFAKREILSLMVKCPNEGCLHKMELRHLEDHQAHCEFALMDCPQCQRPFQKFHINIHILKDCPRRQVSCDNCAASMAFEDKEIHDQNCPLANVICEYCNTILIREQMPNHYDLDCPTAPIPCTFSTFGCHEKMQRNHLARHLQENTQSHMRMLAQAVHSLSVIPDSGYISEVRNFQETIHQLEGRLVRQDHQIRELTAKMETQSMYVSELKRTIRTLEDKVAEIEAQQCNGIYIWKIGNFGMHLKCQEEEKPVVIHSPGFYTGKPGYKLCMRLHLQLPTAQRCANYISLFVHTMQGEYDSHLPWPFQGTIRLTILDQSEAPVRQNHEEIMDAKPELLAFQRPTIPRNPKGFGYVTFMHLEALRQRTFIKDDTLLVRCEVSTRFDMGSLRREGFQPRSTDAGV
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
E3 ubiquitin ligase that, together with UBE2N and UBE2V1, mediates the synthesis of 'Lys-63'-linked-polyubiquitin chains conjugated to proteins, such as IKBKG, IRAK1, AKT1 and AKT2. Also mediates ubiquitination of free/unanchored polyubiquitin chain that leads to MAP3K7 activation. Leads to the activation of NF-kappa-B and JUN. May be essential for the formation of functional osteoclasts. Seems to also play a role in dendritic cells (DCs) maturation and/or activation. Represses c-Myb-mediated transactivation, in B-lymphocytes. Adapter protein that seems to play a role in signal transduction initiated via TNF receptor, IL-1 receptor and IL-17 receptor. Regulates osteoclast differentiation by mediating the activation of adapter protein complex 1 (AP-1) and NF-kappa-B, in response to RANK-L stimulation. Together with MAP3K8, mediates CD40 signals that activate ERK in B-cells and macrophages, and thus may play a role in the regulation of immunoglobulin production.
Sumoylated on Lys-124, Lys-142 and Lys-453 with SUMO1.
Polyubiquitinated on Lys-124; after cell stimulation with IL-1-beta or TGF-beta. This ligand-induced cell stimulation leads to dimerization/oligomerization of TRAF6 molecules, followed by auto-ubiquitination which involves UBE2N and UBE2V1 and leads to TRAF6 activation. This 'Lys-63' site-specific poly-ubiquitination appears to be associated with the activation of signaling molecules. Endogenous autoubiquitination occurs only for the cytoplasmic form. Deubiquitinated by USP10 in a TANK-dependent manner, leading to the negative regulation of NF-kappaB signaling upon DNA damage.
Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm>Cell cortex. Nucleus. Lipid droplet.
Note: Found in the nuclei of some aggressive B-cell lymphoma cell lines as well as in the nuclei of both resting and activated T- and B-lymphocytes. Found in punctate nuclear body protein complexes. Ubiquitination may occur in the cytoplasm and sumoylation in the nucleus. RSAD2/viperin recruits it to the lipid droplet (By similarity).
Expressed in heart, brain, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney and pancreas.
The coiled coil domain mediates homo- and hetero-oligomerization.
The MATH/TRAF domain binds to receptor cytoplasmic domains.
Belongs to the TNF receptor-associated factor family. A subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Autophagy - animal. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Endocytosis. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > NF-kappa B signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pertussis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Leishmaniasis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Toxoplasmosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Tuberculosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis C.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Measles.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Herpes simplex infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Development > Osteoclast differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > NOD-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > IL-17 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Neurotrophin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
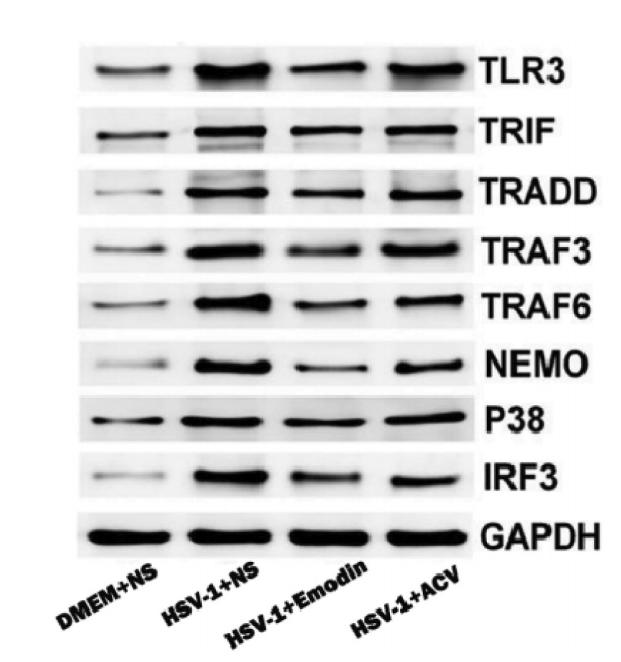
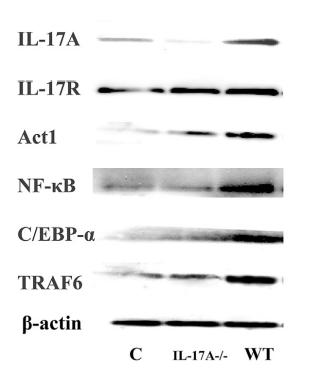
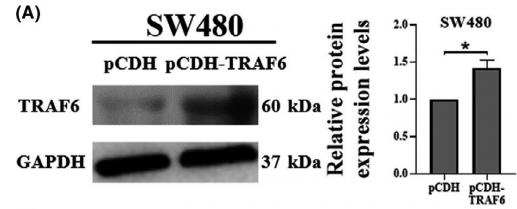
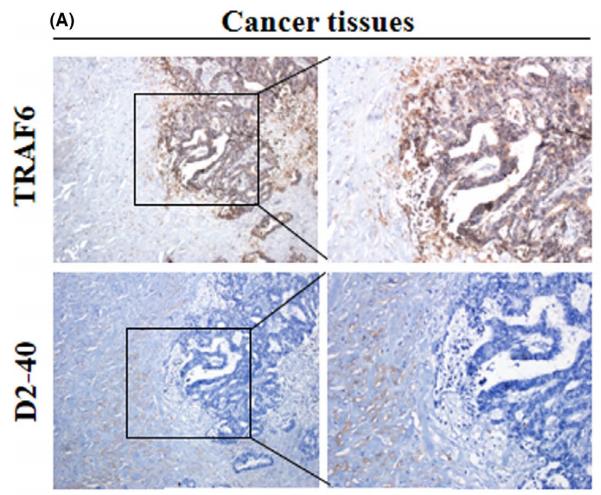
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: RAW264.7 cells
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: testes
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: BSR-T7/5 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.