DDIT3/CHOP Antibody - #AF5280
| Product: | DDIT3/CHOP Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF5280 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to DDIT3/CHOP |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 19~30kD; 19kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P35638 |
| RRID: | AB_2837766 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5280, RRID:AB_2837766.
Fold/Unfold
C/EBP homologous protein; C/EBP Homology Protein; C/EBP zeta; C/EBP-homologous protein 10; C/EBP-homologous protein; CCAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein; CEBPZ; CHOP 10; CHOP; CHOP-10; CHOP10; DDIT 3; DDIT-3; Ddit3; DDIT3_HUMAN; DNA Damage Inducible Transcript 3; DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein; GADD 153; GADD153; Growth Arrest and DNA Damage Inducible Protein 153; Growth arrest and DNA damage inducible protein GADD153; Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD153; MGC4154;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human DDIT3, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- P35638 DDIT3_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAAESLPFSFGTLSSWELEAWYEDLQEVLSSDENGGTYVSPPGNEEEESKIFTTLDPASLAWLTEEEPEPAEVTSTSQSPHSPDSSQSSLAQEEEEEDQGRTRKRKQSGHSPARAGKQRMKEKEQENERKVAQLAEENERLKQEIERLTREVEATRRALIDRMVNLHQA
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Multifunctional transcription factor in ER stress response. Plays an essential role in the response to a wide variety of cell stresses and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in response to ER stress. Plays a dual role both as an inhibitor of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) function and as an activator of other genes. Acts as a dominant-negative regulator of C/EBP-induced transcription: dimerizes with members of the C/EBP family, impairs their association with C/EBP binding sites in the promoter regions, and inhibits the expression of C/EBP regulated genes. Positively regulates the transcription of TRIB3, IL6, IL8, IL23, TNFRSF10B/DR5, PPP1R15A/GADD34, BBC3/PUMA, BCL2L11/BIM and ERO1L. Negatively regulates; expression of BCL2 and MYOD1, ATF4-dependent transcriptional activation of asparagine synthetase (ASNS), CEBPA-dependent transcriptional activation of hepcidin (HAMP) and CEBPB-mediated expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG). Inhibits the canonical Wnt signaling pathway by binding to TCF7L2/TCF4, impairing its DNA-binding properties and repressing its transcriptional activity. Plays a regulatory role in the inflammatory response through the induction of caspase-11 (CASP4/CASP11) which induces the activation of caspase-1 (CASP1) and both these caspases increase the activation of pro-IL1B to mature IL1B which is involved in the inflammatory response.
Ubiquitinated, leading to its degradation by the proteasome.
Phosphorylation at serine residues by MAPK14 enhances its transcriptional activation activity while phosphorylation at serine residues by CK2 inhibits its transcriptional activation activity.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: Present in the cytoplasm under non-stressed conditions and ER stress leads to its nuclear accumulation.
The N-terminal region is necessary for its proteasomal degradation, transcriptional activity and interaction with EP300/P300.
Belongs to the bZIP family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Transcriptional misregulation in cancer.
References
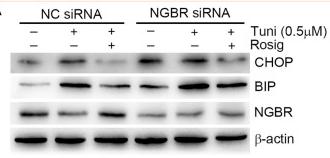
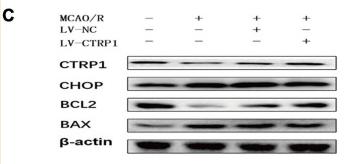
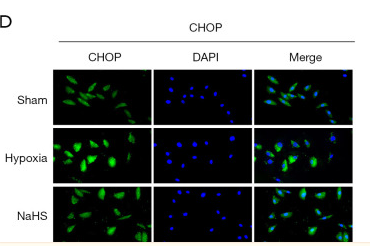
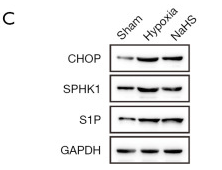
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HUVEC cells
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: cortex
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: MC3T3-E1 osteoblast cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.