EPHB2 Antibody - #AF5246
| Product: | EPHB2 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF5246 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to EPHB2 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Mol.Wt.: | 117 kDa; 117kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P29323 |
| RRID: | AB_2837732 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5246, RRID:AB_2837732.
Fold/Unfold
cek5; Developmentally regulated EPH related tyrosine kinase; DRT; EK5; ELK related protein tyrosine kinase; Eph receptor B2; EPH tyrosine kinase 3; EPH-like kinase 5; EPHB2; EPHB2_HUMAN; Ephrin type B receptor 2; Ephrin type-B receptor 2; EPHT 3; ERK; ETECK; hEK5; Nuk; Prkm 5; Receptor protein tyrosine kinase HEK 5; Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-47; Sek 3; Tyro 5; Tyrosine protein kinase receptor CEK 5; Tyrosine protein kinase receptor EPH 3; Tyrosine protein kinase receptor QEK 5; Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor EPH-3; Tyrosine-protein kinase TYRO5;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human EPHB2, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Brain, heart, lung, kidney, placenta, pancreas, liver and skeletal muscle. Preferentially expressed in fetal brain.
- P29323 EPHB2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MALRRLGAALLLLPLLAAVEETLMDSTTATAELGWMVHPPSGWEEVSGYDENMNTIRTYQVCNVFESSQNNWLRTKFIRRRGAHRIHVEMKFSVRDCSSIPSVPGSCKETFNLYYYEADFDSATKTFPNWMENPWVKVDTIAADESFSQVDLGGRVMKINTEVRSFGPVSRSGFYLAFQDYGGCMSLIAVRVFYRKCPRIIQNGAIFQETLSGAESTSLVAARGSCIANAEEVDVPIKLYCNGDGEWLVPIGRCMCKAGFEAVENGTVCRGCPSGTFKANQGDEACTHCPINSRTTSEGATNCVCRNGYYRADLDPLDMPCTTIPSAPQAVISSVNETSLMLEWTPPRDSGGREDLVYNIICKSCGSGRGACTRCGDNVQYAPRQLGLTEPRIYISDLLAHTQYTFEIQAVNGVTDQSPFSPQFASVNITTNQAAPSAVSIMHQVSRTVDSITLSWSQPDQPNGVILDYELQYYEKELSEYNATAIKSPTNTVTVQGLKAGAIYVFQVRARTVAGYGRYSGKMYFQTMTEAEYQTSIQEKLPLIIGSSAAGLVFLIAVVVIAIVCNRRGFERADSEYTDKLQHYTSGHMTPGMKIYIDPFTYEDPNEAVREFAKEIDISCVKIEQVIGAGEFGEVCSGHLKLPGKREIFVAIKTLKSGYTEKQRRDFLSEASIMGQFDHPNVIHLEGVVTKSTPVMIITEFMENGSLDSFLRQNDGQFTVIQLVGMLRGIAAGMKYLADMNYVHRDLAARNILVNSNLVCKVSDFGLSRFLEDDTSDPTYTSALGGKIPIRWTAPEAIQYRKFTSASDVWSYGIVMWEVMSYGERPYWDMTNQDVINAIEQDYRLPPPMDCPSALHQLMLDCWQKDRNHRPKFGQIVNTLDKMIRNPNSLKAMAPLSSGINLPLLDRTIPDYTSFNTVDEWLEAIKMGQYKESFANAGFTSFDVVSQMMMEDILRVGVTLAGHQKKILNSIQVMRAQMNQIQSVEGQPLARRPRATGRTKRCQPRDVTKKTCNSNDGKKKGMGKKKTDPGRGREIQGIFFKEDSHKESNDCSCGG
Research Backgrounds
Receptor tyrosine kinase which binds promiscuously transmembrane ephrin-B family ligands residing on adjacent cells, leading to contact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells. The signaling pathway downstream of the receptor is referred to as forward signaling while the signaling pathway downstream of the ephrin ligand is referred to as reverse signaling. Functions in axon guidance during development. Involved in the guidance of commissural axons, that form a major interhemispheric connection between the 2 temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex. Also involved in guidance of contralateral inner ear efferent growth cones at the midline and of retinal ganglion cell axons to the optic disk. In addition to axon guidance, also regulates dendritic spines development and maturation and stimulates the formation of excitatory synapses. Upon activation by EFNB1, abolishes the ARHGEF15-mediated negative regulation on excitatory synapse formation. Controls other aspects of development including angiogenesis, palate development and in inner ear development through regulation of endolymph production. Forward and reverse signaling through the EFNB2/EPHB2 complex regulate movement and adhesion of cells that tubularize the urethra and septate the cloaca. May function as a tumor suppressor. May be involved in the regulation of platelet activation and blood coagulation.
Autophosphorylated; ligand binding stimulates autophosphorylation on tyrosine residues.
Polyubiquitinated; ligand binding stimulates ubiquitination.
Ligand binding induces cleavage by matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) such as MMP7/MMP9, producing an EphB2/N-terminal fragment (NTF) and a C-terminal long fragment (EphB2-LF). EphB2-LF is further cleaved by MMPs, producing EphB2/CTF1 which is further cleaved by the PS1/gamma-secretase producing EphB2/CTF2.
Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection>Axon. Cell projection>Dendrite.
Brain, heart, lung, kidney, placenta, pancreas, liver and skeletal muscle. Preferentially expressed in fetal brain.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. Ephrin receptor subfamily.
Research Fields
· Organismal Systems > Development > Axon guidance. (View pathway)
References
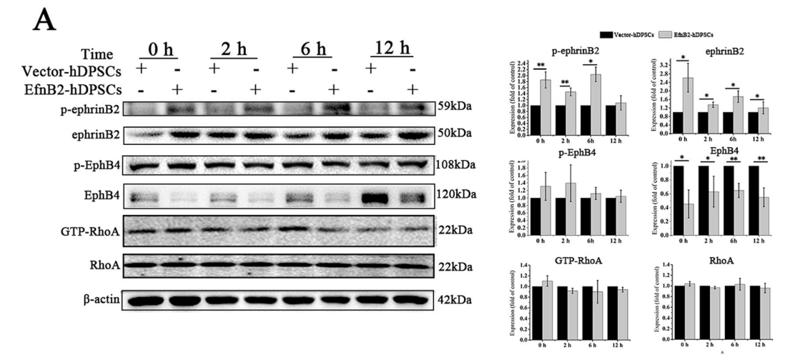
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: hDPSCs
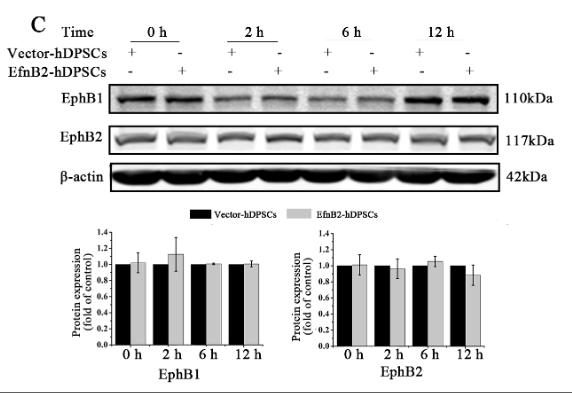
Application: WB Species: human Sample: hDPSCs
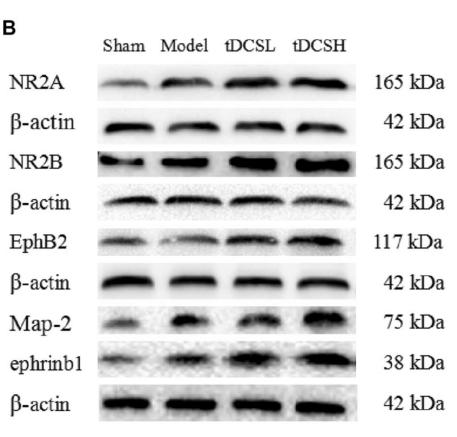
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: hippocampal
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.