Elastin Antibody - #AF5226
| Product: | Elastin Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF5226 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Elastin |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Mol.Wt.: | 68 kDa; 68kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P15502 |
| RRID: | AB_2837712 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5226, RRID:AB_2837712.
Fold/Unfold
Elastin; ELN; ELN_HUMAN; SVAS; Tropoelastin; WBS; WS;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Elastin, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Expressed within the outer myometrial smooth muscle and throughout the arteriolar tree of uterus (at protein level). Also expressed in the large arteries, lung and skin.
- P15502 ELN_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAGLTAAAPRPGVLLLLLSILHPSRPGGVPGAIPGGVPGGVFYPGAGLGALGGGALGPGGKPLKPVPGGLAGAGLGAGLGAFPAVTFPGALVPGGVADAAAAYKAAKAGAGLGGVPGVGGLGVSAGAVVPQPGAGVKPGKVPGVGLPGVYPGGVLPGARFPGVGVLPGVPTGAGVKPKAPGVGGAFAGIPGVGPFGGPQPGVPLGYPIKAPKLPGGYGLPYTTGKLPYGYGPGGVAGAAGKAGYPTGTGVGPQAAAAAAAKAAAKFGAGAAGVLPGVGGAGVPGVPGAIPGIGGIAGVGTPAAAAAAAAAAKAAKYGAAAGLVPGGPGFGPGVVGVPGAGVPGVGVPGAGIPVVPGAGIPGAAVPGVVSPEAAAKAAAKAAKYGARPGVGVGGIPTYGVGAGGFPGFGVGVGGIPGVAGVPGVGGVPGVGGVPGVGISPEAQAAAAAKAAKYGAAGAGVLGGLVPGAPGAVPGVPGTGGVPGVGTPAAAAAKAAAKAAQFGLVPGVGVAPGVGVAPGVGVAPGVGLAPGVGVAPGVGVAPGVGVAPGIGPGGVAAAAKSAAKVAAKAQLRAAAGLGAGIPGLGVGVGVPGLGVGAGVPGLGVGAGVPGFGAGADEGVRRSLSPELREGDPSSSQHLPSTPSSPRVPGALAAAKAAKYGAAVPGVLGGLGALGGVGIPGGVVGAGPAAAAAAAKAAAKAAQFGLVGAAGLGGLGVGGLGVPGVGGLGGIPPAAAAKAAKYGAAGLGGVLGGAGQFPLGGVAARPGFGLSPIFPGGACLGKACGRKRK
Research Backgrounds
Major structural protein of tissues such as aorta and nuchal ligament, which must expand rapidly and recover completely. Molecular determinant of the late arterial morphogenesis, stabilizing arterial structure by regulating proliferation and organization of vascular smooth muscle (By similarity).
Elastin is formed through the cross-linking of its soluble precursor tropoelastin. Cross-linking is initiated through the action of lysyl oxidase on exposed lysines to form allysine. Subsequent spontaneous condensation reactions with other allysine or unmodified lysine residues result in various bi-, tri-, and tetrafunctional cross-links. The most abundant cross-links in mature elastin fibers are lysinonorleucine, allysine aldol, desmosine, and isodesmosine.
Hydroxylation on proline residues within the sequence motif, GXPG, is most likely 4-hydroxy as this fits the requirement for 4-hydroxylation in vertebrates.
Secreted>Extracellular space>Extracellular matrix.
Note: Extracellular matrix of elastic fibers.
Expressed within the outer myometrial smooth muscle and throughout the arteriolar tree of uterus (at protein level). Also expressed in the large arteries, lung and skin.
Belongs to the elastin family.
Research Fields
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Protein digestion and absorption.
References
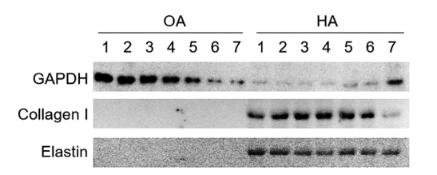
Application: WB Species: human Sample: cruciate ligaments
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.