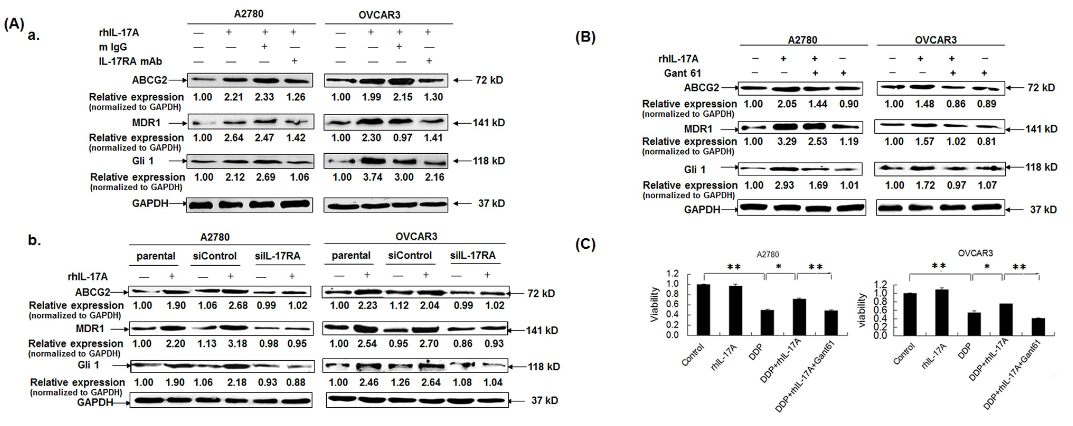
P Glycoprotein 1(MDR1) Antibody - #AF5185
| Product: | P Glycoprotein 1(MDR1) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF5185 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to P Glycoprotein 1(MDR1) |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Horse, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 141 kDa; 141kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P08183 |
| RRID: | AB_2837671 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5185, RRID:AB_2837671.
Fold/Unfold
ABC20; ABCB1; ATP binding cassette, sub family B (MDR/TAP), member 1; ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 1; CD243; CLCS; Colchicin sensitivity; Doxorubicin resistance; GP170; MDR1; MDR1_HUMAN; Multidrug resistance 1; Multidrug resistance protein 1; P glycoprotein 1; P gp; P-glycoprotein 1; PGY1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human P Glycoprotein 1(MDR1), corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- P08183 MDR1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MDLEGDRNGGAKKKNFFKLNNKSEKDKKEKKPTVSVFSMFRYSNWLDKLYMVVGTLAAIIHGAGLPLMMLVFGEMTDIFANAGNLEDLMSNITNRSDINDTGFFMNLEEDMTRYAYYYSGIGAGVLVAAYIQVSFWCLAAGRQIHKIRKQFFHAIMRQEIGWFDVHDVGELNTRLTDDVSKINEGIGDKIGMFFQSMATFFTGFIVGFTRGWKLTLVILAISPVLGLSAAVWAKILSSFTDKELLAYAKAGAVAEEVLAAIRTVIAFGGQKKELERYNKNLEEAKRIGIKKAITANISIGAAFLLIYASYALAFWYGTTLVLSGEYSIGQVLTVFFSVLIGAFSVGQASPSIEAFANARGAAYEIFKIIDNKPSIDSYSKSGHKPDNIKGNLEFRNVHFSYPSRKEVKILKGLNLKVQSGQTVALVGNSGCGKSTTVQLMQRLYDPTEGMVSVDGQDIRTINVRFLREIIGVVSQEPVLFATTIAENIRYGRENVTMDEIEKAVKEANAYDFIMKLPHKFDTLVGERGAQLSGGQKQRIAIARALVRNPKILLLDEATSALDTESEAVVQVALDKARKGRTTIVIAHRLSTVRNADVIAGFDDGVIVEKGNHDELMKEKGIYFKLVTMQTAGNEVELENAADESKSEIDALEMSSNDSRSSLIRKRSTRRSVRGSQAQDRKLSTKEALDESIPPVSFWRIMKLNLTEWPYFVVGVFCAIINGGLQPAFAIIFSKIIGVFTRIDDPETKRQNSNLFSLLFLALGIISFITFFLQGFTFGKAGEILTKRLRYMVFRSMLRQDVSWFDDPKNTTGALTTRLANDAAQVKGAIGSRLAVITQNIANLGTGIIISFIYGWQLTLLLLAIVPIIAIAGVVEMKMLSGQALKDKKELEGSGKIATEAIENFRTVVSLTQEQKFEHMYAQSLQVPYRNSLRKAHIFGITFSFTQAMMYFSYAGCFRFGAYLVAHKLMSFEDVLLVFSAVVFGAMAVGQVSSFAPDYAKAKISAAHIIMIIEKTPLIDSYSTEGLMPNTLEGNVTFGEVVFNYPTRPDIPVLQGLSLEVKKGQTLALVGSSGCGKSTVVQLLERFYDPLAGKVLLDGKEIKRLNVQWLRAHLGIVSQEPILFDCSIAENIAYGDNSRVVSQEEIVRAAKEANIHAFIESLPNKYSTKVGDKGTQLSGGQKQRIAIARALVRQPHILLLDEATSALDTESEKVVQEALDKAREGRTCIVIAHRLSTIQNADLIVVFQNGRVKEHGTHQQLLAQKGIYFSMVSVQAGTKRQ
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Translocates drugs and phospholipids across the membrane. Catalyzes the flop of phospholipids from the cytoplasmic to the exoplasmic leaflet of the apical membrane. Participates mainly to the flop of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, beta-D-glucosylceramides and sphingomyelins. Energy-dependent efflux pump responsible for decreased drug accumulation in multidrug-resistant cells.
Cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Apical cell membrane.
Expressed in liver, kidney, small intestine and brain.
Belongs to the ABC transporter superfamily. ABCB family. Multidrug resistance exporter (TC 3.A.1.201) subfamily.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Membrane transport > ABC transporters.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > MicroRNAs in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
References
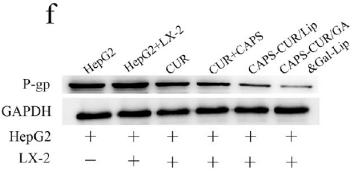
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HepG2 cells
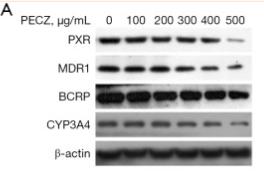
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: BLCA cells
Application: WB Species: human Sample: EOC ascites cells
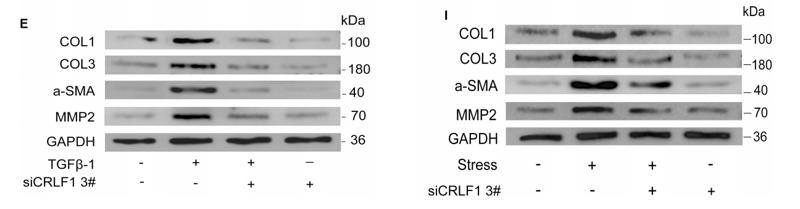
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
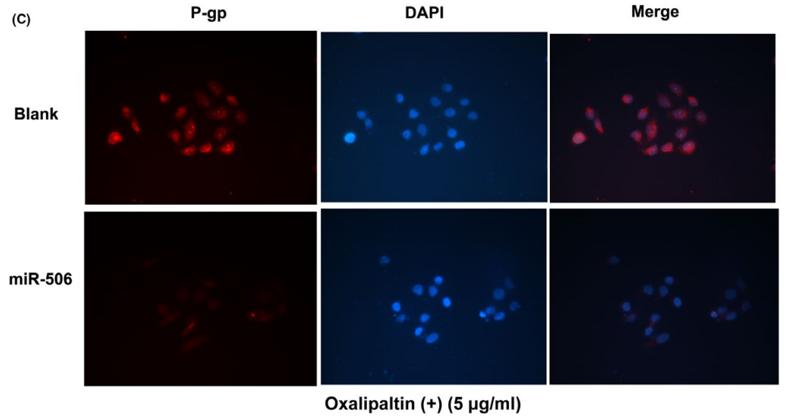
Application: IF/ICC Species: human Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.