PDGFA Antibody - #AF5179
| Product: | PDGFA Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF5179 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to PDGFA |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Rabbit, Dog, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 24 kDa; 24kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P04085 |
| RRID: | AB_2837665 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5179, RRID:AB_2837665.
Fold/Unfold
PDGF A; PDGF A chain; PDGF subunit A; PDGF-1; PDGF1; PDGFA; PDGFA_HUMAN; Platelet derived growth factor alpha chain; Platelet derived growth factor alpha isoform 2 preproprotein; Platelet derived growth factor alpha polypeptide; Platelet-derived growth factor A chain; Platelet-derived growth factor alpha polypeptide; Platelet-derived growth factor subunit A;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human PDGFA, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- P04085 PDGFA_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MRTLACLLLLGCGYLAHVLAEEAEIPREVIERLARSQIHSIRDLQRLLEIDSVGSEDSLDTSLRAHGVHATKHVPEKRPLPIRRKRSIEEAVPAVCKTRTVIYEIPRSQVDPTSANFLIWPPCVEVKRCTGCCNTSSVKCQPSRVHHRSVKVAKVEYVRKKPKLKEVQVRLEEHLECACATTSLNPDYREEDTGRPRESGKKRKRKRLKPT
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Growth factor that plays an essential role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell migration, survival and chemotaxis. Potent mitogen for cells of mesenchymal origin. Required for normal lung alveolar septum formation during embryogenesis, normal development of the gastrointestinal tract, normal development of Leydig cells and spermatogenesis. Required for normal oligodendrocyte development and normal myelination in the spinal cord and cerebellum. Plays an important role in wound healing. Signaling is modulated by the formation of heterodimers with PDGFB (By similarity).
Secreted.
Note: Released by platelets upon wounding.
The long form contains a basic insert which acts as a cell retention signal.
Belongs to the PDGF/VEGF growth factor family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Focal adhesion. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Gap junction. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell motility > Regulation of actin cytoskeleton. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Ras signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Rap1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Phospholipase D signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Jak-STAT signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Transcriptional misregulation in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > MicroRNAs in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Glioma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Melanoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Choline metabolism in cancer. (View pathway)
References
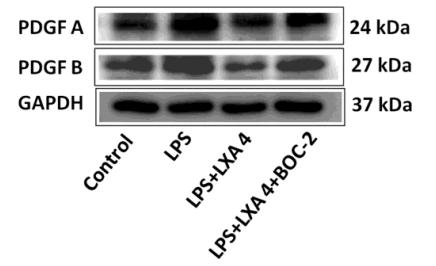
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: HSC-T6 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.