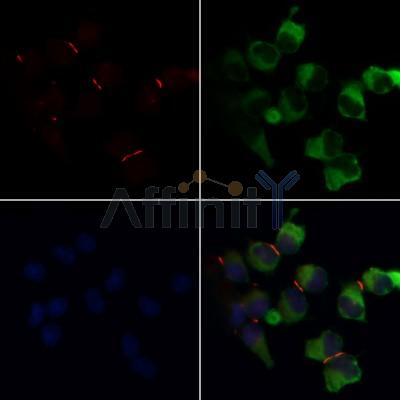
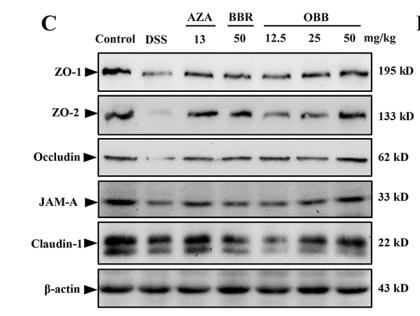
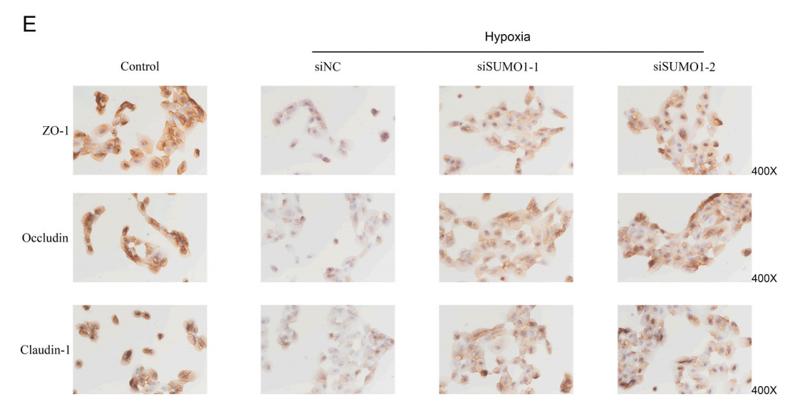
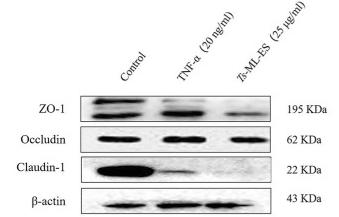
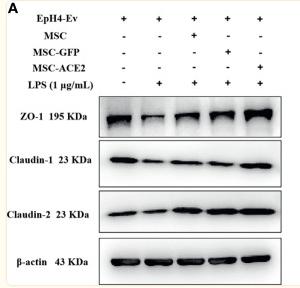
ZO 1 Antibody - #AF5145
| Product: | ZO 1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF5145 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to ZO 1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Pig, Monkey |
| Prediction: | Horse, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 195 kDa; 195kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q07157 |
| RRID: | AB_2837631 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5145, RRID:AB_2837631.
Fold/Unfold
Tight junction protein 1; Tight junction protein ZO-1; Tight junction protein ZO1; TJP1; zo-1; Zo1; ZO1_HUMAN; Zona occludens 1; Zona occludens 1 protein; Zona occludens protein 1; Zonula occludens 1 protein; Zonula occludens protein 1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human ZO 1, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
The alpha-containing isoform is found in most epithelial cell junctions. The short isoform is found both in endothelial cells and the highly specialized epithelial junctions of renal glomeruli and Sertoli cells of the seminiferous tubules.
- Q07157 ZO1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSARAAAAKSTAMEETAIWEQHTVTLHRAPGFGFGIAISGGRDNPHFQSGETSIVISDVLKGGPAEGQLQENDRVAMVNGVSMDNVEHAFAVQQLRKSGKNAKITIRRKKKVQIPVSRPDPEPVSDNEEDSYDEEIHDPRSGRSGVVNRRSEKIWPRDRSASRERSLSPRSDRRSVASSQPAKPTKVTLVKSRKNEEYGLRLASHIFVKEISQDSLAARDGNIQEGDVVLKINGTVTENMSLTDAKTLIERSKGKLKMVVQRDERATLLNVPDLSDSIHSANASERDDISEIQSLASDHSGRSHDRPPRRSRSRSPDQRSEPSDHSRHSPQQPSNGSLRSRDEERISKPGAVSTPVKHADDHTPKTVEEVTVERNEKQTPSLPEPKPVYAQVGQPDVDLPVSPSDGVLPNSTHEDGILRPSMKLVKFRKGDSVGLRLAGGNDVGIFVAGVLEDSPAAKEGLEEGDQILRVNNVDFTNIIREEAVLFLLDLPKGEEVTILAQKKKDVYRRIVESDVGDSFYIRTHFEYEKESPYGLSFNKGEVFRVVDTLYNGKLGSWLAIRIGKNHKEVERGIIPNKNRAEQLASVQYTLPKTAGGDRADFWRFRGLRSSKRNLRKSREDLSAQPVQTKFPAYERVVLREAGFLRPVTIFGPIADVAREKLAREEPDIYQIAKSEPRDAGTDQRSSGIIRLHTIKQIIDQDKHALLDVTPNAVDRLNYAQWYPIVVFLNPDSKQGVKTMRMRLCPESRKSARKLYERSHKLRKNNHHLFTTTINLNSMNDGWYGALKEAIQQQQNQLVWVSEGKADGATSDDLDLHDDRLSYLSAPGSEYSMYSTDSRHTSDYEDTDTEGGAYTDQELDETLNDEVGTPPESAITRSSEPVREDSSGMHHENQTYPPYSPQAQPQPIHRIDSPGFKPASQQKAEASSPVPYLSPETNPASSTSAVNHNVNLTNVRLEEPTPAPSTSYSPQADSLRTPSTEAAHIMLRDQEPSLSSHVDPTKVYRKDPYPEEMMRQNHVLKQPAVSHPGHRPDKEPNLTYEPQLPYVEKQASRDLEQPTYRYESSSYTDQFSRNYEHRLRYEDRVPMYEEQWSYYDDKQPYPSRPPFDNQHSQDLDSRQHPEESSERGYFPRFEEPAPLSYDSRPRYEQAPRASALRHEEQPAPGYDTHGRLRPEAQPHPSAGPKPAESKQYFEQYSRSYEQVPPQGFTSRAGHFEPLHGAAAVPPLIPSSQHKPEALPSNTKPLPPPPTQTEEEEDPAMKPQSVLTRVKMFENKRSASLETKKDVNDTGSFKPPEVASKPSGAPIIGPKPTSQNQFSEHDKTLYRIPEPQKPQLKPPEDIVRSNHYDPEEDEEYYRKQLSYFDRRSFENKPPAHIAASHLSEPAKPAHSQNQSNFSSYSSKGKPPEADGVDRSFGEKRYEPIQATPPPPPLPSQYAQPSQPVTSASLHIHSKGAHGEGNSVSLDFQNSLVSKPDPPPSQNKPATFRPPNREDTAQAAFYPQKSFPDKAPVNGTEQTQKTVTPAYNRFTPKPYTSSARPFERKFESPKFNHNLLPSETAHKPDLSSKTPTSPKTLVKSHSLAQPPEFDSGVETFSIHAEKPKYQINNISTVPKAIPVSPSAVEEDEDEDGHTVVATARGIFNSNGGVLSSIETGVSIIIPQGAIPEGVEQEIYFKVCRDNSILPPLDKEKGETLLSPLVMCGPHGLKFLKPVELRLPHCDPKTWQNKCLPGDPNYLVGANCVSVLIDHF
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
TJP1, TJP2, and TJP3 are closely related scaffolding proteins that link tight junction (TJ) transmembrane proteins such as claudins, junctional adhesion molecules, and occludin to the actin cytoskeleton. The tight junction acts to limit movement of substances through the paracellular space and as a boundary between the compositionally distinct apical and basolateral plasma membrane domains of epithelial and endothelial cells. Necessary for lumenogenesis, and particularly efficient epithelial polarization and barrier formation (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of cell migration by targeting CDC42BPB to the leading edge of migrating cells. Plays an important role in podosome formation and associated function, thus regulating cell adhesion and matrix remodeling. With TJP2 and TJP3, participates to the junctional retention and stability of the transcription factor DBPA, but is not involved in its shuttling to the nucleus (By similarity).
Phosphorylated at tyrosine redidues in response to epidermal growth factor (EGF). This response is dependent on an intact actin microfilament system. Dephosphorylated by PTPRJ.
Cell membrane>Peripheral membrane protein>Cytoplasmic side. Cell junction>Tight junction. Cell junction. Cell junction>Gap junction. Cell projection>Podosome.
Note: Moves from the cytoplasm to the cell membrane concurrently with cell-cell contact (PubMed:7798316). At podosomal sites, is predominantly localized in the ring structure surrounding the actin core (PubMed:20930113).
The alpha-containing isoform is found in most epithelial cell junctions. The short isoform is found both in endothelial cells and the highly specialized epithelial junctions of renal glomeruli and Sertoli cells of the seminiferous tubules.
The 244-aa domain between residues 633 and 876 is the primary occludin (OCLN)-binding site and is required for stable association with the tight junction (PubMed:9792688).
The C-terminal region (residues 1151-1372) is an actin-binding region (ABR) that interacts directly with F-actin and plays an important role in the localization of TJP1 at junctions (PubMed:9792688, PubMed:12354695, PubMed:20930113). The ABR is also required for the localization to puncta at the free edge of cells before initiation of cell-cell contact (PubMed:12354695). The ABR is also necessary for TJP1 recruitment to podosomes (PubMed:20930113).
The second PDZ domain (PDZ2) mediates homodimerization and heterodimerization with TJP2 and TJP3 (PubMed:9792688, PubMed:17928286).
Belongs to the MAGUK family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Adherens junction. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Tight junction. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Gap junction. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Vibrio cholerae infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Salmonella infection.
References
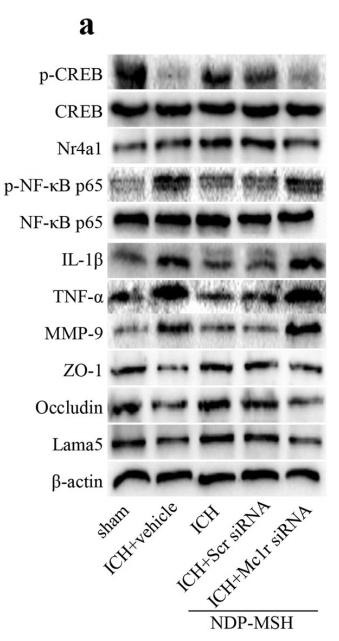
Application: WB Species: human Sample: Caco2 cells
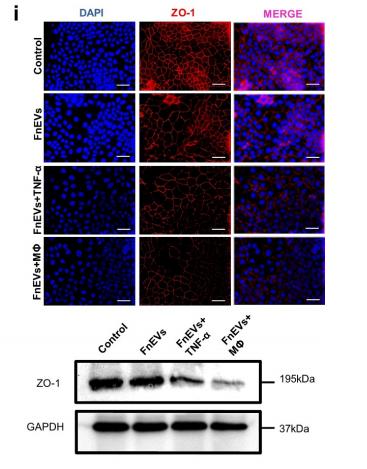
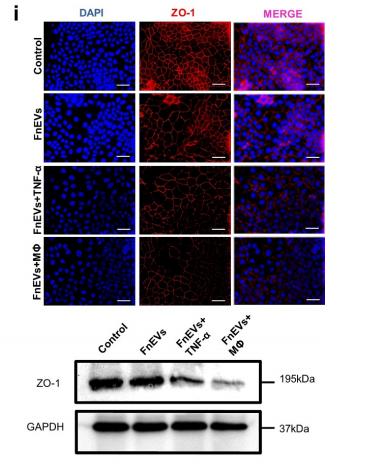
Application: IF/ICC Species: human Sample: Caco2 cells
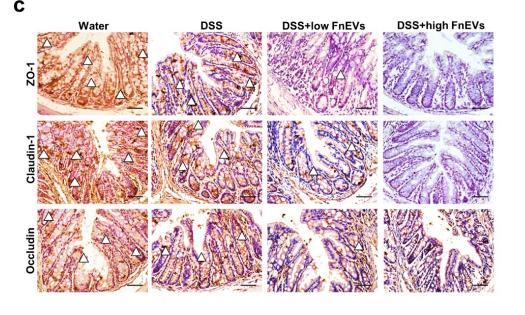
Application: IHC Species: mouse Sample: colon
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.