CEP55 Antibody - #DF3918
| Product: | CEP55 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF3918 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to CEP55 |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Mol.Wt.: | 54 KD; 54kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q53EZ4 |
| RRID: | AB_2836271 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF3918, RRID:AB_2836271.
Fold/Unfold
C10orf3; cancer/testis antigen 111; Centrosomal protein 55kDa; Centrosomal protein of 55 kDa; CEP 55; Cep55; CEP55_HUMAN; CT111; FLJ10540; Up regulated in colon cancer 6; Up-regulated in colon cancer 6; URCC 6; URCC6;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human CEP55, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Expressed in embryonic brain (PubMed:28264986). Expressed in fetal brain ganglionic eminence, kidney tubules and multinucleate neurons in the temporal cortex (PubMed:28264986). Expressed in adult brain, cerebellum, kidney tubules, intestine and muscles (at protein level) (PubMed:28295209, PubMed:28264986). Widely expressed, mostly in proliferative tissues. Highly expressed in testis. Intermediate levels in adult and fetal thymus, as well as in various cancer cell lines. Low levels in different parts of the digestive tract, bone marrow, lymph nodes, placenta, fetal heart and fetal spleen. Hardly detected in brain.
- Q53EZ4 CEP55_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSSRSTKDLIKSKWGSKPSNSKSETTLEKLKGEIAHLKTSVDEITSGKGKLTDKERHRLLEKIRVLEAEKEKNAYQLTEKDKEIQRLRDQLKARYSTTTLLEQLEETTREGERREQVLKALSEEKDVLKQQLSAATSRIAELESKTNTLRLSQTVAPNCFNSSINNIHEMEIQLKDALEKNQQWLVYDQQREVYVKGLLAKIFELEKKTETAAHSLPQQTKKPESEGYLQEEKQKCYNDLLASAKKDLEVERQTITQLSFELSEFRRKYEETQKEVHNLNQLLYSQRRADVQHLEDDRHKTEKIQKLREENDIARGKLEEEKKRSEELLSQVQFLYTSLLKQQEEQTRVALLEQQMQACTLDFENEKLDRQHVQHQLHVILKELRKARNQITQLESLKQLHEFAITEPLVTFQGETENREKVAASPKSPTAALNESLVECPKCNIQYPATEHRDLLVHVEYCSK
Research Backgrounds
Plays a role in mitotic exit and cytokinesis. Recruits PDCD6IP and TSG101 to midbody during cytokinesis. Required for successful completion of cytokinesis. Not required for microtubule nucleation. Plays a role in the development of the brain and kidney.
There is a hierachy of phosphorylation, where both Ser-425 and Ser-428 are phosphorylated at the onset of mitosis, prior to Ser-436. Phosphorylation at Ser-425 and Ser-428 is required for dissociation from the centrosome at the G2/M boundary. Phosphorylation at the 3 sites, Ser-425, Ser-428 and Ser-436, is required for protein function at the final stages of cell division to complete cytokinesis successfully.
Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Microtubule organizing center>Centrosome>Centriole. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Microtubule organizing center>Centrosome. Cleavage furrow. Midbody>Midbody ring.
Note: Present at the centrosomes at interphase. A small portion is associated preferentially with the mother centriole, whereas the majority localizes to the pericentriolar material. During mitosis, loses affinity for the centrosome at the onset of prophase and diffuses throughout the cell. This dissociation from the centrosome is phosphorylation-dependent. May remain localized at the centrosome during mitosis in certain cell types. Appears at the cleavage furrow in late anaphase and in the midbody in cytokinesis.
Expressed in embryonic brain. Expressed in fetal brain ganglionic eminence, kidney tubules and multinucleate neurons in the temporal cortex. Expressed in adult brain, cerebellum, kidney tubules, intestine and muscles (at protein level). Widely expressed, mostly in proliferative tissues. Highly expressed in testis. Intermediate levels in adult and fetal thymus, as well as in various cancer cell lines. Low levels in different parts of the digestive tract, bone marrow, lymph nodes, placenta, fetal heart and fetal spleen. Hardly detected in brain.
References
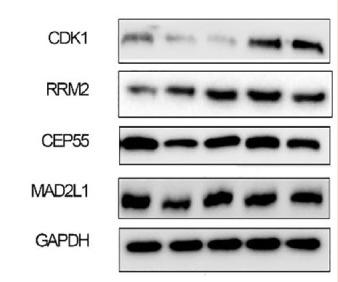
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: breast cancer tissue
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.